Sebastian Munster (1489 - 1552)
Profile :
After Waldseemuller three names dominated cartography in the 16th century; Mercator, Ortelius & Munster, and of these three Munster probably had the widest influence in spreading geographical knowledge throughout Europe in the middle years of the century. His Cosmographica, issued in 1544, contained not only the latest views of many well known cities, but included an encyclopedic amount of detail about the known – and unknown – world and undoubtedly must have been one of the most widely read books of its time, going through nearly forty editions in six languages.
An eminent German mathematician and linguist, Munster became professor of Hebrew at Heidelberg and later at Basle, where he settled in 1529. In 1528, following his first mapping of Germany, he appealed to German scholars to send him descriptions, so that all Germany with its villages, towns, trades etc. may be seen in a `mirror`, even going so far as to give instructions on how they should map their own localities. The response was far greater than expected and much information was sent by foreigners as well as Germans so that, eventually, he was able to include many up-to-date, if not very accurate, maps in his atlases. He was the first to provide a separate map of each of the four known continents and the first separately printed map of England. His maps, printed from woodblocks, are now greatly valued by collectors. His two major works, the Geographia and Cosmographia were published in Basle by his sep-son, Henri Petri, who continued to issue many editions after Munsters death of the plague in 1552.
Munster’s dominance of the cartographic market was relatively short lived once Ortelius produced his “Theatrum Orbis Terrarum” in 1570. Munster's somewhat naive engravings of the world, continents and countries were revised and re-published by Sebastian Petri with more sophisticated maps in 1588, using the Ortelius Atlas as a guide. In Munsters defense though, he had little in the way of examples or reference to help produce what was the first comprehensive atlas of the known world.
Sebastian Munster'sGeographia (first published in 1540) and his later Cosmographia (first published in 1544) were cartographic landmarks. TheGeographia included not only Ptolemaic maps, but also a number of landmark modern maps, including the first separate maps of the 4 continents, the first map of England and the earliest obtainable map of Scandinavia. The Cosmographia was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographia appeared between 1544 and 1628.
Munster dominated cartographic publication during the mid-16th Century and is generally regarded as one of the important map makers of the 16th Century. Originally a scholar studying Hebrew, Greek and mathematics, Munster (1489-1552) eventually specialised in mathematical geography and cartography. He is best known for his edition of the Geographia, a translation of Ptolemy's landmark geographical text. Munster's version is illustrated with maps based on Ptolemy's calculations, but also, in recognition of the increased geographical awareness of the period, contains a section of modern maps including the first set of maps of each continent. In the first edition of the Geographia, Munster included twenty-seven ancient Ptolemaic maps and twenty-one modern maps, printed from woodblocks. Subsequent editions of the Cosmographia much expanded his Geographia and contained a vast number of maps and plans.
Sebastian Munster (10)
1574 Munster Large Antique Print - View of The German City of Landau, Bavaria
- Title : Die Statt Landaw
- Ref #: 22668
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the Bavarian City of Landau NE of Munich was engraved in 1547 - the date is engraved at the foot of the image - and was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1574 edition of Cosmographia.
Landau or Landau in der Pfalz (pop. 41,821) is an autonomous (kreisfrei) city surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, Europe's largest contiguous forest, direct on the German Wine Route.
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle hisCosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographiaappeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications ofCosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: -None
Verso: - None
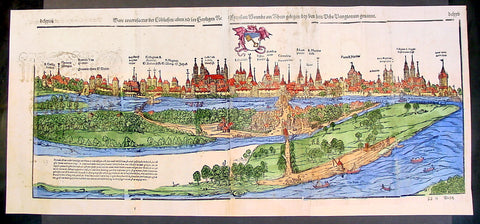
1574 Munster Large Antique Print View of The City of Wormbs, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wormbs
- Ref #: 22670
- Size: 27in x 13in (685mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large folding original antique print a View of the important German city ofWormbs, south of Hamburg was published in the 1574 release of Sebastian MunstersCosmographia published by Sebastian Petri, Basle.
(This is a reasonably scarce map as the large fold out maps in Cosmographia were easily damaged and lost)
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 13in (685mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 10in (635 x 255m)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: -Folds re-joined small loss, light soiling, light creasing
Verso: - Light soiling, colour show through, half the map backed in archival material
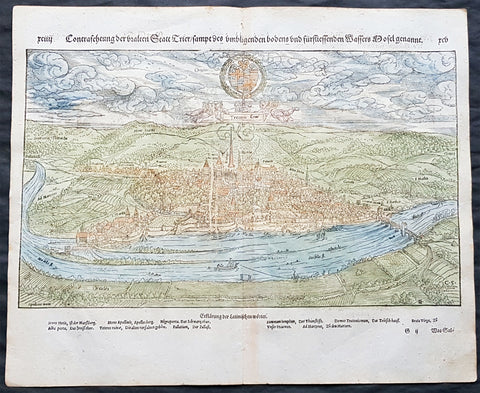
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map - City View of Trier, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Treir
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 33540
- Size : 16in x 13in (405mm x 330mm)
Description:
This finely engraved hand coloured original antique double page view of the German city of Trier in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate was published in the early 1574 edition of Sebastian Munsters Cosmographia by Sebastian Petri, Basle.
Sebastian Petri re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps in the copperplate style. The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (405mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Trier is a city in Germany on the banks of the Moselle. Trier lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Moselle wine region. The German philosopher and one of the founders of Marxism, Karl Marx was born in the city in 1818.
Founded by the Celts in the late-4th century BC as Treuorum, it was later conquered by the Romans in the late-1st century BC and renamed Trevorum or Augusta Treverorum (Latin for The City of Augustus among the Treveri). Trier may be the oldest city in Germany. It is also the oldest seat of a bishop north of the Alps. In the Middle Ages, the Archbishop-Elector of Trier was an important prince of the church, as the archbishop-electorate controlled land from the French border to the Rhine. The Archbishop-Elector also had great significance as one of the seven electors of the Holy Roman Empire.
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the City of Lubeck, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Lubeck
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 22708
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Lubeck, in the northern German state Schleswig-Holstein was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1574 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Lübeck is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany, on the river Trave.
In the 14th century Lübeck became the Queen of the Hanseatic League, being by far the largest and most powerful member of that medieval trade organization. In 1375 Emperor Charles IV named Lübeck one of the five Glories of the Empire, a title shared with Venice, Rome, Pisa and Florence. Several conflicts about trading privileges resulted in fighting between Lübeck (with the Hanseatic League) and Denmark and Norway – with varying outcome. While Lübeck and the Hanseatic League prevailed in conflicts in 1435 and 1512, Lübeck lost when it became involved in the Count\'s Feud, a civil war that raged in Denmark from 1534 to 1536. Lübeck also joined the pro-Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of the mid-16th century.
After its defeat in the Count\'s Feud, Lübeck\'s power slowly declined. The city remained neutral in the Thirty Years\' War of 1618–1648, but the combination of the devastation from the decades-long war and the new transatlantic orientation of European trade caused the Hanseatic League – and thus Lübeck with it – to decline in importance. However, even after the de facto disbanding of the Hanseatic League in 1669, Lübeck still remained an important trading town on the Baltic Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Weissenburg Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wyssenburg
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 22665
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Weißenburg (Weissenburg) in Bavaria in Middle Franconia - identified by the cities Coate of Arms with double headed eagle atop of a castle - was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1574 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Weißenburg in Bayern (formerly also Weißenburg im Nordgau) is a town in Middle Franconia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen. Weissenburg is located in central Bavaria, in the south of the administrative region Mittelfranken.
The history of Weißenburg is generally traced back to the Roman fort that was built in the area towards the end of the first century. The settlement, which included Thermae, lay on the border of the Roman Empire and on the Tabula Peutingeriana from the 4th century it had the name Biriciana. Germanic tribes destroyed the fort and settled in what is still the city centre. The first mention of the name Weißenburg is in a deed dating from 867. The city became the seat of a royal residence during the reign of the Franks and according to legend, Charlemagne stayed there to supervise the construction of Fossa Carolina.
The city became a Free Imperial City in 1296 and continued to grow until the Reformation. Following the example of Nuremberg the city joined the Protestant side but it suffered heavily in the ensuing wars. However, the rights of the city as a Free Imperial City and an Imperial Estate were restored in the final peace treaty and some growth resumed. Despite its insignificant size and economic importance, the city, like the other 50-odd free imperial cities, was virtually independent.
Weissenburg lost its independence in 1802 and became part of the Bavarian kingdom in 1806. It was however saved from insignificance with the construction of a railway between Nuremberg and Augsburg which goes through the city and which supported industrialisation. Following World War II over 6,000 refugees and people expelled from the territories which Germany lost settled in the city and have since played an important role in its industry and culture.
The many stages in the history of Weissenburg can still be seen today. There are many ruins from the Roman times. One of the finest is the remains of a Roman bath which was excavated in 1977 and has been turned into a museum. The city wall from the Middle Ages has survived almost intact with its towers and in the Gothic Town Hall the city\'s elected members have held their meetings from 1476.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1574 Sebastian Munster Large Antique Birds Eye City View of Heidelberg, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Heidelberg
- Size: 29in x 13in (740mm x 330mm)
- Ref #: 22692
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This large hand coloured, original antique wood-block engraved birds-eye view of the German City of Heidelberg was published in the 1574 edition of Sebastian Munsters Cosmographia.
There were 2 large folding views in Cosmographia, both German cities, Wormbs and Heidelberg. As these were large folding views they were easily torn and damaged and so quiet rare, especially from the earlier editions.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Orange, yellow, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 13in (740mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 13in (740mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to plate-mark, light age toning repair to right & bottom margins
Plate area: - Left plate small loss along centrer-fold, light spotting & creasing
Verso: - Left plate backed onto contemporary paper
Background:
Heidelberg is a college town in Baden-Wurttemberg situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany.
Located about 78 km south of Frankfurt, Heidelberg is the fifth-largest city in the German state.
Founded in 1386, Heidelberg University is Germany\'s oldest and one of Europe\'s most reputable universities.
Heidelberg University played a leading part in the era of humanism and the Reformation, and the conflict between Lutheranism and Calvinism, in the 15th and 16th centuries. Heidelberg\'s library, founded in 1421, is the oldest existing public library in Germany. In April 1518, a few months after proclaiming his 95 Theses, Martin Luther was received in Heidelberg, to defend them. In 1537, the castle located higher up the mountain was destroyed by a gunpowder explosion. The duke\'s palace was built at the site of the lower castle.
The siege of Heidelberg 1622
Elector Frederick III, sovereign of the Electoral Palatinate from 1559 to 1576, commissioned the composition of a new Catechism for his territory. While the catechism\'s introduction credits the entire theological faculty here (at the University of Heidelberg) and all the superintendents and prominent servants of the church for the composition of the catechism, Zacharius Ursinus is commonly regarded as the catechism\'s principal author. Caspar Olevianus (1536–1587) was formerly asserted as a co-author of the document, though this theory has been largely discarded by modern scholarship. Johann Sylvan, Adam Neuser, Johannes Willing, Thomas Erastus, Michael Diller, Johannes Brunner, Tilemann Mumius, Petrus Macheropoeus, Johannes Eisenmenger, Immanuel Tremellius and Pierre Boquin are all likely to have contributed to the Catechism in some way. Frederick himself wrote the preface to the Catechism and closely oversaw its composition and publication. Frederick, who was officially Lutheran but had strong Reformed leanings, wanted to even out the religious situation of his highly Lutheran territory within the primarily Catholic Holy Roman Empire. The Council of Trent had just concluded with its conclusions and decrees against the Protestant faiths, and the Peace of Augsburg had only granted toleration for Lutheranism within the empire where the ruler was Lutheran. One of the aims of the catechism was to counteract the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church as well as Anabaptists and \"strict\" Gnesio-Lutherans like Tilemann Heshusius and Matthias Flacius, who were resisting Frederick\'s Reformed influences, particularly on the matter of Eucharist (the Lord\'s Supper). The Catechism-based each of its statements on biblical proof-texts, and Frederick himself would defend it as biblical, not reformed, at the 1566 Diet of Augsburg when he was called to answer to charges of violating the Peace of Augsburg. This was the Heidelberg Catechism, officially called the Catechism, or Christian Instruction, according to the Usages of the Churches and Schools of the Electoral Palatinate.
In November 1619, the royal crown of Bohemia was offered to the Elector, Frederick V. (He was married to Elizabeth, eldest daughter of James VI and I of Scotland and England, respectively.) Frederick became known as the Winter King, as he reigned for only one winter before the Imperial House of Habsburg regained the crown by force. His overthrow in 1621 marked the beginning of the Thirty Years War. In 1622, after a siege of two months, the armies of the Catholic League, commanded by Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly, captured the town. Tilly gave the famous Bibliotheca Palatina from the Church of the Holy Spirit to the Pope as a present. The Catholic Bavarian branch of the House of Wittelsbach gained control over the Palatinate and the title of Prince-Elector. In 1648, at the end of the war, Frederick Vs son Charles I Louis, Elector Palatine, was able to recover his titles and lands.
In late 1634 Imperialist forces attempted to take back the city, as the Swedish army had conquered it. They quickly took the city, but were unable to take the castle. As they prepared to blow up its fortifications with gunpowder the French army arrived, 30,000 men strong, led by Urbain de Maillé-Brézé, who had fought in many battles and participated in the Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628), and Jacques-Nompar de Caumont, duc de La Force. They ended the siege and drove off the Catholic forces.
To strengthen his dynasty, Charles I Louis arranged the marriage of his daughter Liselotte to Philip I, Duke of Orléans, brother of Louis XIV, king of France. In 1685, after the death of Charles Louis\' son, Elector Charles II, Louis XIV laid claim to his sister-in-laws inheritance. The Germans rejected the claim, in part because of religious differences between local Protestants and the French Catholics, as the Protestant Reformation had divided the peoples of Europe. The War of the Grand Alliance ensued. In 1689, French troops took the town and castle, bringing nearly total destruction to the area in 1693. As a result of the destruction due to repeated French invasions related to the War of the Palatinate Succession coupled with severe winters, thousands of Protestant German Palatines emigrated from the lower Palatinate in the early 18th century. They fled to other European cities and especially to London (where the refugees were called the poor Palatines). In sympathy for the Protestants, in 1709–1710, Queen Anne\'s government arranged transport for nearly 6,000 Palatines to New York. Others were transported to Pennsylvania, and to South Carolina. They worked their passage and later settled in the English colonies there.
In 1720, after assigning a major church for exclusively Catholic use, religious conflicts with the mostly Protestant inhabitants of Heidelberg caused the Roman Catholic Prince-Elector Charles III Philip to transfer his residence to nearby Mannheim. The court remained there until the Elector Charles Theodore became Elector of Bavaria in 1777 and established his court in Munich. In 1742, Elector Charles Theodore began rebuilding the Palace. In 1764, a lightning bolt destroyed other palace buildings during reconstruction, causing the work to be discontinued.
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Luneburg Hamburg, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Leunenburg
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30328
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Lüneburg (Lunenburg) incorporated into the city of Hamburg in Lower Saxony was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Lüneburg also called Lunenburg in English, is a town in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is located about 50 km southeast of Hamburg, and belongs to that citys wider metropolitan region.
With the demise of the Hanseatic League – and the absence of herrings around 1560 around Falsterbo in Scania – the biggest customers of Lüneburg\'s salt broke away and the town rapidly became impoverished. Hardly any new houses were built in central Lüneburg after this time, which is why the historical appearance of the town centre has remained almost unchanged until the present day.
The town became part of the Electorate of Hanover in 1708, the Kingdom of Westphalia in 1807, the First French Empire in 1810, the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814, and the Prussian Province of Hanover in 1866.
In the centuries after the collapse of the League, it was as if Lüneburg had fallen into a Sleeping Beauty slumber. Heinrich Heine, whose parents lived in Lüneburg from 1822 to 1826, called it his residence of boredom (Residenz der Langeweile). Near the end of the 19th century Lüneburg evolved into a garrison town, and it remained so until the 1990s.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold, light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Weissenburg Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wyssenburg
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 30351
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Weißenburg (Weissenburg) in Bavaria in Middle Franconia - identified by the cities Coate of Arms with double headed eagle atop of a castle - was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Weißenburg in Bayern (formerly also Weißenburg im Nordgau) is a town in Middle Franconia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen. Weissenburg is located in central Bavaria, in the south of the administrative region Mittelfranken.
The history of Weißenburg is generally traced back to the Roman fort that was built in the area towards the end of the first century. The settlement, which included Thermae, lay on the border of the Roman Empire and on the Tabula Peutingeriana from the 4th century it had the name Biriciana. Germanic tribes destroyed the fort and settled in what is still the city centre. The first mention of the name Weißenburg is in a deed dating from 867. The city became the seat of a royal residence during the reign of the Franks and according to legend, Charlemagne stayed there to supervise the construction of Fossa Carolina.
The city became a Free Imperial City in 1296 and continued to grow until the Reformation. Following the example of Nuremberg the city joined the Protestant side but it suffered heavily in the ensuing wars. However, the rights of the city as a Free Imperial City and an Imperial Estate were restored in the final peace treaty and some growth resumed. Despite its insignificant size and economic importance, the city, like the other 50-odd free imperial cities, was virtually independent.
Weissenburg lost its independence in 1802 and became part of the Bavarian kingdom in 1806. It was however saved from insignificance with the construction of a railway between Nuremberg and Augsburg which goes through the city and which supported industrialisation. Following World War II over 6,000 refugees and people expelled from the territories which Germany lost settled in the city and have since played an important role in its industry and culture.
The many stages in the history of Weissenburg can still be seen today. There are many ruins from the Roman times. One of the finest is the remains of a Roman bath which was excavated in 1977 and has been turned into a museum. The city wall from the Middle Ages has survived almost intact with its towers and in the Gothic Town Hall the city\'s elected members have held their meetings from 1476.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom margin, no loss
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
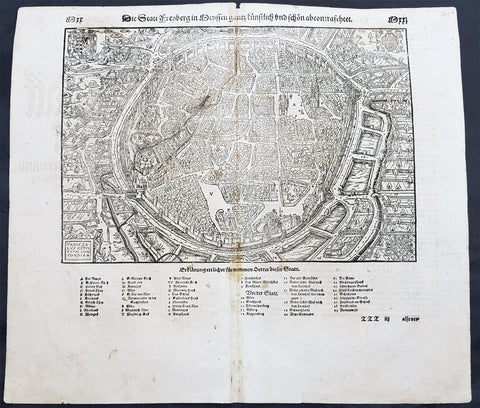
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map View of Freiberg, Saxony Southern Germany
- Title : Die Statt Freyberg
- Date : 1598
- Size: 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
- Ref #: 30329
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the German City of Freiberg, Saxony was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1598 edition of Cosmographia.
Freiberg (German for "free for mining activities") is a university and mining town in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called Große Kreisstadt (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsendistrict.
Background:
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning along centerfold
1628 Sebastian Munster & RMD Antique Map View Nordlingen Swabia, Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Nordlingen
- Ref #: 33587
- Size: 17in x 15in (435mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1628
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German town of Nördlingen in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria,, was engraved by Hans Rudolf Manuel Deutsch (RMD) in 1549 - dated - and published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1628 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Hans Rudolf Manuel Deutsch (1525–1571) was a Swiss artist. He made several of the woodcuts for De re metallica (the metals and mining treatise by Georgius Agricola, the father of mineralogy) and for Sebastian Münsters Cosmographia.
Deutschs father, Niklaus Manuel Deutsch (the Elder), and Deutsch\'s brother, Niklaus Manuel Deutsch the Younger, were also artists. The elder Niklaus had taken the last name Manuel, but all three also commonly used Deutsch as part of their names and signed their paintings with initials ending in D.
Nördlingen is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. The town was the location of two battles during the Thirty Years\' War, which took place between 1618–1648. Today it is one of only three towns in Germany that still has a completely established city wall, the other two being Rothenburg ob der Tauber and Dinkelsbühl.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 15in (435mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 15in (435mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light offsetting
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - Light offsetting
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.