Johannes Jansson (1588 - 1664)
Profile :
Johannes Janssonius, more commonly known to us as Jan Jansson, was born in Arnhem where his father was a bookseller and publisher (Jan Janszoon the Elder).
In 1612 he married the daughter of the cartographer and publisher Jodocus Hondius, and then set up in business in Amsterdam as a book publisher. In 1616 he published his first maps of France and Italy and from then onwards he produced a very large number of maps, perhaps not quite rivaling those of the Blaeu family but running a very close second in quantity and quality.
From about 1630 to 1638 he was in partnership with his brother-in-law, Henricus Hondius, issuing further editions of the Mercator/Hondius atlases to which his name was added. On the death of Henricus he took over the business, expanding the atlas still further, until eventually he published an 11-volume Atlas Major on a scale similar to Blaeu's Atlas Major.
The first full edition of Jansson's English County Maps was published in 1646 but some years earlier he issued a number of British maps in the Mercator/Hondius/Jansson series of atlases (1636-44); the maps were printed from newly engraved plates and are different from the later 1646 issue and are now rarely seen (see Appendix B for further details). In general appearance Jansson's maps are very similar to those of Blaeu and, in fact, were often copied from them, but they tend to be more flamboyant and decorative.
After Jansson's death his heirs published a number of maps in an Atlas Contractus in 1666, later still many of the plates of his British maps were acquired by Pieter Schenk and Gerard Valck who published them again in 1683 as separate maps
Jan Jansson (3)
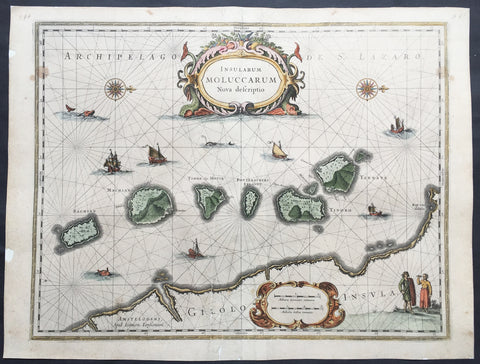
1633 Jan Jansson Old, Antique Map of The Maluku or Spice Islands, Indonesia
- Title : Insularum Moluccarum Nova descriptio
- Ref #: 42018
- Size: 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1633
- Condition: (B+) Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Maluku or Spice Islands of Indonesia was published by Jan Jansson in the 1633 edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: The Maluku Islands (also known as the Moluccas, Moluccan Islands, the Spice Islands) are an archipelago in Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi (Celebes), west of New Guinea, and north of Timor. The islands were also historically known as the Spice Islands by the Chinese and Europeans, but this term has also been applied to other islands. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top and bottom margin, slight separation into border
Plate area: - Repairs adjacent to bottom centrefold, slight separation
Verso: - Map professionally backed onto archival paper
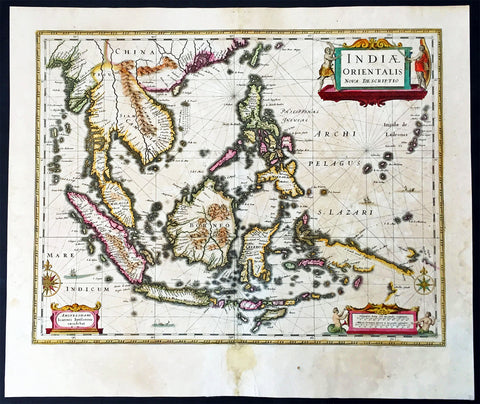
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of East Indies, Australia - Voyage of Dufken, Spice Islands
- Title : Indiae Orientalis Nova Descriptio
- Ref #: 43144
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautiful, very significant original antique map of SE Asia, the East Indies PNG and significantly a small portion of the west coast of Australia's Cape York Peninsular was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning, bottom centerfold restored
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, centerfold re-joined
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background: This landmark map is the first published record of the discoveries made by the Dutch ship Dufken on route to Cape York in Australia. New Guinea ("Landt vande Papuos") is marked the (Is)land next to it is called ÔNieu ZeelandtÕ and the island Duyfkens is named after the ship Duyfken.
With the first publication of this map 27 years had passed since the voyage of the Dufken and its discoveries of PNG and NW Australia had been completed. The Dutch East India Company had suppressed the discoveries until it was sure how profitable or not Australia would be.
Jansson & Hondius were the first to published this map in 1630 and it is believed the information was leaked from the Blaeu firm - the official cartographers to the Dutch East India Company. Surprisingly Blaeu did not publish a similar map for another two years. It must have been incredibly galling for Blaeu to have known of the discoveries for nearly thirty years and then to have been beaten to publication by his fiercest rival Jansson & Hondius.
Given this information this is an incredibly significant map of this imporatant region being the first map published with concrete first hand knowledge of the area which prior had been mapped based mainly on speculation or second hand knowledge.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
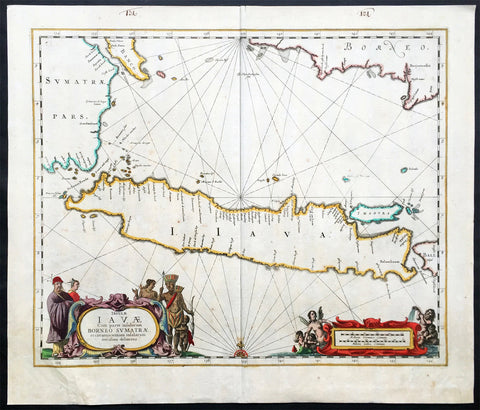
1650 Jan Jansson Antique Map Island of Java, Indonesia - Dutch East India Co
- Title: Insulae Java Cum Parte insularum Borneo Sumatrae
- Date: 1650
- Ref: 60603
- Size: 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large elegant & very impressive hand coloured original antique map, a sea chart of the Indonesian Island of Java including Sumatra, Borneo and Bali was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 3/4in (520mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair & ink notations
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Java & the port of Batavia was at the time of publication of the utmost importance to the Dutch East India Company and its domination of the Spice Trade.
This elegant chart focuses on the islands coast with the lack of detail on the interior correctly reflecting the lack of knowledge (or possible lack of importance) to the Dutch, who's primary concern was the sea and sea charts used in the trade of the ever lucrative Spice Trade.
The Dutch capital in the East Indies is Batavia (Jakarta) located on the NW coast. The beautiful chart is richly embellished with two fine cartouche featuring local Javanese warrior and Chinese merchants flanking the title and Neptune and mermaids surrounding the scale of miles... The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia. It was the second multinational corporation in the world (the British East India Company was founded two years earlier) and the first company to issue stock. It was also arguably the first mega-corporation, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, coin money, and establish colonies.
Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asian trade on 4,785 ships, and netted for their efforts more than 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. By contrast, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882,412 people from 1500 to 1795, and the fleet of the English (later British) East India Company, the VOC’s nearest competitor, was a distant second to its total traffic with 2,690 ships and a mere one-fifth the tonnage of goods carried by the VOC. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century.
Having been set up in 1602, to profit from the Malukan spice trade, in 1619 the VOC established a capital in the port city of Batavia (now Jakarta) on the Indonesian Island of Java. Over the next two centuries the Company acquired additional ports as trading bases and safeguarded their interests by taking over surrounding territory. It remained an important trading concern and paid an 18% annual dividend for almost 200 years.
Weighed down by corruption in the late 18th century, the Company went bankrupt and was formally dissolved in 1800, its possessions and the debt being taken over by the government of the Dutch Batavian Republic. The VOC's territories became the Dutch East Indies and were expanded over the course of the 19th century to include the whole of the Indonesian archipelago, and in the 20th century would form Indonesia. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)