James Cook (1728-1779)
Profile:
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) was a British explorer, navigator, and cartographer who is known for his extensive voyages to the Pacific Ocean. Born in Marton, Yorkshire, England, Cook began his maritime career as an apprentice at the age of 17. He served as a naval officer during the Seven Years' War, mapping the coastlines of Newfoundland and St. Lawrence River.
In 1768, Cook was selected to lead an expedition to the Pacific Ocean to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, and to search for the fabled southern continent. During this voyage, he charted the east coast of Australia, claiming it for Britain and naming it New South Wales. Cook's second voyage, from 1772 to 1775, was dedicated to exploring the southern oceans, circumnavigating Antarctica and proving that it was a continent.
Cook's third voyage, from 1776 to 1779, was his most famous. He was tasked with finding a northwest passage to connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. While he did not find the passage, he did explore the coast of Alaska and made detailed maps of the region. Cook was also the first European to visit Hawaii, where he was initially welcomed, but was later killed in a skirmish with locals.
Cook was known for his excellent navigational skills and his ability to prevent scurvy among his crew by introducing fresh food and lemon juice into their diets. He also made significant contributions to the field of cartography, creating accurate maps of the Pacific and the coastlines he explored.
Cook's voyages had a significant impact on the scientific and cultural understanding of the world. His accurate maps and charts greatly improved navigational methods and were used by sailors for many years to come. Cook's legacy also includes his interactions with the people he encountered during his voyages, which played a significant role in shaping the understanding of different cultures in Europe.
Cook's First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cook's command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth's distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research. Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere.
Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
Cook's Second Voyage (1772-1775)
Based on the success of his first voyage, Cook was appointed by the Admiralty to lead a second expedition. Two ships were employed with Cook commanding the Resolution and Captain Tobias Furneaux in charge of the Adventure. The purpose was to circumnavigate the globe as far south as possible to confirm the location of a southern continent. Cook proved that there was no "Terra Australis," which supposedly was located between New Zealand and South America. Cook was convinced, however, that there was land beyond the southern ice fields.
In his pursuit of this idea, this expedition was the first European voyage to cross the Antarctic Circle. In addition, in two great sweeps through the Southern latitudes, Cook made an incredible number of landfalls including New Zealand, Easter Island, the Marquesas, Tahiti and the Society Islands, the Tonga Islands, the New Hebrides, New Caledonia, and a number of smaller islands. In addition to these navigational accomplishments and the accompanying expansion of geographical knowledge, the expedition also recorded a vast amount of information regarding the Pacific islands and peoples, proved the value of the chronometer as an instrument for calculating longitude, and improved techniques for preventing scurvy.
Cook's Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook's third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century.
England's growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route. Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook's death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook's death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years.
Captain James Cook (2)
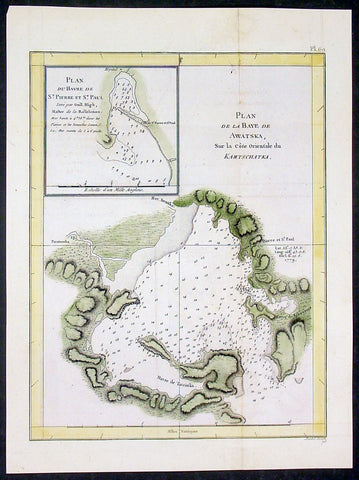
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Map Avacha Bay, Petropavlovsk, Kamchatka, Russia in 1779
- Title : Plan du Havre de St Pierre et St Paul; Plan des Havres qu on trouve au Cote N D Eimeo
- Size: 12in x 9in (300mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 32174
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Avacha Bay and what is today the city of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, on the Kamchatka Peninsula in Eastern Russia, visited by HMS Resolution & Discovery in December 1779, after the death of Cook, with Resolution under the command of Captain Clerk, the 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\\\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Clerks journal.......On 25th Clerke saw land \"making with appearance of an Inlet which by our Account we suppose to be the Mouth of ye Bay Awatscha\". Avacha Bay lies on the south-east side of the Kamchatka Peninsula, where the Pacific Ocean becomes the Bering Sea. The next day he \"wore and stood off for the Night during which we had a very heavy snow & severe Frost, with fresh Gales & squally Wear. The poor fellows after broiling as they have lately done several Months on the Torrid Zone are now miserably pinch\'d with the Cold. The Doctors list increases every day, several of them are frost bit; they are at an abundant allowance of Provision & appear however in good spirits…
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 8 1/2in (245mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 8 1/2in (245mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a 1,250 kilometer long peninsula in the Russian Far East.
Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. The circular bay to the north of this on the Pacific side is Avacha Bay with the capital, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish “The Large English Atlas”. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27” x 20”) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print of a Man of Kamchatka Peninsula East Russia, 1779
- Title : Homme Du Kamtchatka
- Ref : 31798
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a man of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Eastern Russia, drawn during a visit by Captain Clerke in 1779 (after Cooks death) during Captain Cooks 3rd and last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Cooks on-board artist, John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a 1,250-kilometre-long peninsula in the Russian Far East.
After the death of James Cook in early 1779, Captain Charles Clerke took control of Cooks 3rd Voyage of Discovery. Clerke, who was dying of tuberculosis, sailed north of Hawaii, landing on the Kamchatka peninsula where the Russians helped him with supplies and to make repairs to the ships. He made a final attempt to pass beyond the Bering Strait and died on his return at Petropavlovsk on 22 August 1779. From here the ships\' reports were sent overland, reaching London five months later. Following the death of Clerke, Resolution and Discovery turned for home commanded by John Gore, a veteran of Cook\'s first voyage (and now in command of the expedition), and James King. After passing down the coast of Japan they reached Macao, in China in the first week of December and from there followed the East India trade route via Sunda Strait to Cape Town
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.