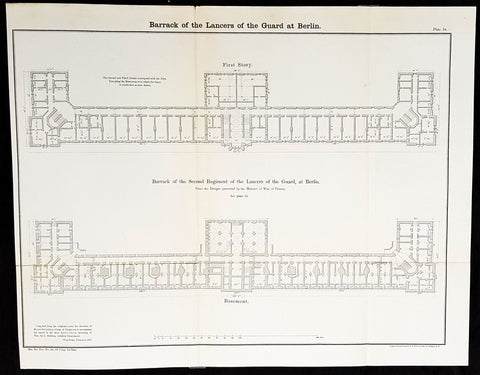
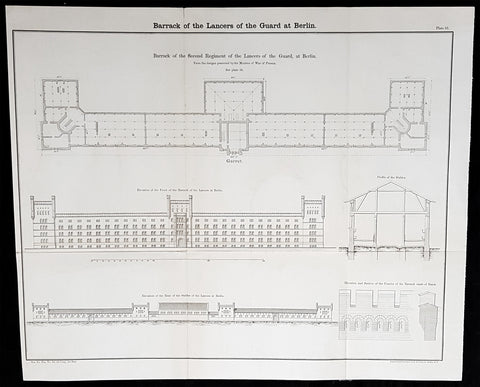
Architectural (28)
1845-63 John Gould Large Antique Print The Mammals of Australia - Tree Kangaroo
- Title : Dendrolagus Ursinus, Mull....H C Richter del et lith....C Hullmandel Imp.
- Ref #: 93441
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1845–63
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare original hand coloured lithograph antique print of The Ursine Tree Kangaroo, by the artist HC Richter was printed by Charles Joseph Hullmandel 1789 – 1850 in the famous Naturalists John Goulds The Mammals of Australiapublished between 1845–63.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Mammals of Australia is a three-volume work written and published by John Gould between 1845–63. It contains 182 illustrations by the author and its artist H. C. Richter. It was intended to be a complete survey of the novel species of mammals, such as the marsupials, discovered in the colonies of Australia.
The author, John Gould, best known for The Birds of Australia and other major works of ornithology, visited Australia in 1838. In his introduction, Gould says:.....It was not until I arrived in the country, and found myself surrounded by objects as strange as if I had been transported to another planet, that I conceived the idea of devoting a portion of my attention to the mammalian class of its extraordinary fauna......During his short stay he made observations on the natural history and employed his skills as a taxidermist to obtain specimens.
The publication of this major work by Gould followed his A Monograph of the Macropodidae or Family of Kangaroos in 1841. This work was the first comprehensive survey of Australian mammals, and gave an account of their classification and description. Gould also included the indigenous names for the species from the lists he made while in Australia. He used these names to make requests of the local peoples for his specimens, and recorded the regions where the names were used. This conserved a number of common names, such as dibbler (Parantechinus apicalis), which were later recommended by authorities.
The large lithographs reproduced the artwork of Richter, after the drawings and watercolours made in Australia by Gould and his wife, Elizabeth. (The contribution by Elizabeth Gould was uncredited). These were hand-coloured by a group of artists, led by Gabriel Bayfield, that required the completion of 26,572 plates. The illustrations produced during their visit to Australia were supplemented by the preserved specimens returned to England and detailed the characteristics of the species. These illustrations have become iconic images of the mammals of Australia. Among the best known of the illustrations from the work are the two of Thylacinus cynocephalus (Tasmanian tiger), copied since its publication and the most frequently reproduced, made more recognizable by Cascade Brewerys appropriation for its label in 1987. The government of Tasmania published a monochromatic reproduction of the same image in 1934, the author Louisa Anne Meredith also copied it for Tasmanian Friends and Foes (1881).
The Mammals of Australia was published by subscription in the format Imperial Folio; 13 parts in three volumes were issued from 1845 until 1863. To these the author added An Introduction to The Mammals of Australia (1863) in a separate work. This provided corrections and updates, a new preface, introduction, and a list of the mammals of the three volumes. The first two volumes were complete surveys of orders Marsupiata (marsupials), and, with Rodentia in the third, it formed the sum of known mammalian species of Australia. With the addition of those contained in the later Introduction the total of species described reached 166. The same work notes the exclusion of marine mammals such as whales from the volumes, but reprints a manuscript by Charles Coxen on the dugong.
Beyond the scientific value of this comprehensive survey, the document is cited in reference to its subjects conservation. Some of the species included in the work, such as Onychogalea lunata (crescent nailtail wallaby), have since succumbed to changes in land use since European colonisation.
The work was received with acclaim, but the high cost of production, especially of the coloured plates, reduced its accessibility. The original listed price was £41 for the complete set of volumes. The public curiosity for the unique fauna of Australia was met by this handsomely illustrated and comprehensive survey, and it spawned imitations in Australia. The curator of the Australian Museum, Gerard Krefft, produced the more affordable The Mammals of Australia (1871); intended for educational purposes and influenced by Goulds illustrations. Gracius Broinowskis abandoned work, Birds and Mammals of Australia (1884), so closely imitated the plates that an injunction was threatened by its publisher.
Gould, John FRS 1804 – 1881
Gould was an English ornithologist and bird artist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates that he produced with the assistance of his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart. He has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed Darwins finches played a role in the inception of Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work is referenced in Charles Darwins book, On the Origin of Species.
Gould was born in Lyme Regis the first son of a gardener. He and the boy probably had a scanty education. Shortly afterwards his father obtained a position on an estate near Guildford, Surrey, and then in 1818 Gould became foreman in the Royal Gardens of Windsor. He was for some time under the care of J. T. Aiton, of the Royal Gardens of Windsor. The young Gould started training as a gardener, being employed under his father at Windsor from 1818 to 1824, and he was subsequently a gardener at Ripley Castle in Yorkshire. He became an expert in the art of taxidermy. In 1824 he set himself up in business in London as a taxidermist, and his skill helped him to become the first Curator and Preserver at the museum of the Zoological Society of London in 1827.
Goulds position brought him into contact with the countrys leading naturalists. This meant that he was often the first to see new collections of birds given to the Zoological Society of London. In 1830 a collection of birds arrived from the Himalayas, many not previously described. Gould published these birds in A Century of Birds from the Himalaya Mountains (1830–1832). The text was by Nicholas Aylward Vigors and the illustrations were drawn and lithographed by Goulds wife Elizabeth Coxen Gould. Most of Goulds work were rough sketches on paper from which other artists created the lithographic plates.
This work was followed by four more in the next seven years, including Birds of Europe in five volumes. It was completed in 1837; Gould wrote the text, and his clerk, Edwin Prince, did the editing. The plates were drawn and lithographed by Elizabeth Coxen Gould. A few of the illustrations were made by Edward Lear as part of his Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae in 1832. Lear, however, was in financial difficulty, and he sold the entire set of lithographs to Gould. The books were published in a very large size, imperial folio, with magnificent coloured plates. Eventually 41 of these volumes were published, with about 3000 plates. They appeared in parts at £3 3s. a number, subscribed for in advance, and in spite of the heavy expense of preparing the plates, Gould succeeded in making his ventures pay, realising a fortune. This was a busy period for Gould who also published Icones Avium in two parts containing 18 leaves of bird studies on 54 cm plates as a supplement to his previous works. No further monographs were published as in 1838 he and his wife moved to Australia to work on the Birds of Australia. Shortly after their return to England, his wife died in 1841. Elizabeth Gould completed 84 plates for Birds of Australia before her death.
When Charles Darwin presented his mammal and bird specimens collected during the second voyage of HMS Beagle to the Zoological Society of London on 4 January 1837, the bird specimens were given to Gould for identification. He set aside his paying work and at the next meeting on 10 January reported that birds from the Galápagos Islands which Darwin had thought were blackbirds, gross-bills and finches were in fact a series of ground Finches which are so peculiar as to form an entirely new group, containing 12 species. This story made the newspapers. In March, Darwin met Gould again, learning that his Galápagos wren was another species of finch and the mockingbirds he had labelled by island were separate species rather than just varieties, with relatives on the South American mainland. Subsequently, Gould advised that the smaller southern Rhea specimen that had been rescued from a Christmas dinner was a separate species which he named Rhea darwinii, whose territory overlapped with the northern rheas. Darwin had not bothered to label his finches by island, but others on the expedition had taken more care. He now sought specimens collected by captain Robert FitzRoy and crewmen. From them he was able to establish that the species were unique to islands, an important step on the inception of his theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work on the birds was published between 1838 and 1842 in five numbers as Part 3 of Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle, edited by Charles Darwin. Elizabeth Gould illustrated all the plates for Part 3.
In 1838 the Goulds sailed to Australia, intending to study the birds of that country and be the first to produce a major work on the subject. They took with them the collector John Gilbert. They arrived in Tasmania in September, making the acquaintance of the governor Sir John Franklin and his wife. Gould and Gilbert collected on the island. In February 1839 Gould sailed to Sydney, leaving his pregnant wife with the Franklins. He travelled to his brother-in-laws station at Yarrundi, spending his time searching for bowerbirds in the Liverpool Range. In April he returned to Tasmania for the birth of his son. In May he sailed to Adelaide to meet Charles Sturt, who was preparing to lead an expedition to the Murray River. Gould collected in the Mount Lofty range, the Murray Scrubs and Kangaroo Island, returning again to Hobart in July. He then travelled with his wife to Yarrundi. They returned home to England in May 1840.
The result of the trip was The Birds of Australia (1840–48). It included a total of 600 plates in seven volumes; 328 of the species described were new to science and named by Gould. He also published A Monograph of the Macropodidae, or Family of Kangaroos (1841–1842) and the three volume work The Mammals of Australia (1849–1861).
Elizabeth died in 1841 after the birth of their eighth child, Sarah, and Goulds books subsequently used illustrations by a number of artists, including Henry Constantine Richter, William Matthew Hart and Joseph Wolf.
Throughout his professional life Gould had a strong interest in hummingbirds. He accumulated a collection of 320 species, which he exhibited at the Great Exhibition of 1851. Despite his interest, Gould had never seen a live hummingbird. In May 1857 he travelled to the United States with his second son, Charles. He arrived in New York too early in the season to see hummingbirds in that city, but on 21 May 1857, in Bartrams Gardens in Philadelphia, he finally saw his first live one, a ruby-throated hummingbird. He then continued to Washington D.C. where he saw large numbers in the gardens of the Capitol. Gould attempted to return to England with live specimens, but, as he was not aware of the conditions necessary to keep them, they only lived for two months at most.
Gould published: A Monograph of the Trochilidae or Humming Birds with 360 plates (1849–61); The Mammals of Australia (1845–63), Handbook to the Birds of Australia (1865), The Birds of Asia (1850–83), The Birds of Great Britain (1862–73) and The Birds of New Guinea and the adjacent Papuan Islands (1875–88).
The University of Glasgow, which owns a copy of Birds of Great Britain, describes John Gould as the greatest figure in bird illustration after Audubon, and auctioneers Sotherans describe the work as Goulds pride and joy.
Gould had already published some of the illustrations in Birds of Europe, but Birds of Great Britain represents a development of his aesthetic style in which he adds illustrations of nests and young on a large scale.
Sotherans Co. reports that Gould published the book himself, producing 750 copies, which remain sought after both as complete volumes, and as individual plates, currently varying in price from £450 – £850. The University of Glasgow records that the volumes were issued in London in 25 parts, to make the complete set, between 1863 and 1873, and each set contained 367 coloured lithographs.
Gould undertook an ornithological tour of Scandinavia in 1856, in preparation for the work, taking with him the artist Henry Wolf who drew 57 of the plates from Goulds preparatory sketches. According to The University of Glasgow Goulds skill was in rapidly producing rough sketches from nature (a majority of the sketches were drawn from newly killed specimens) capturing the distinctiveness of each species. Gould then oversaw the process whereby his artists worked his sketches up into the finished drawings, which were made into coloured lithographs by engraver William Hart.
There were problems: the stone engraving of the snowy owl in volume I was dropped and broken at an early stage in the printing. Later issues of this plate show evidence of this damage and consequently the early issue – printed before the accident – are considered more desirable.
The lithographs were hand coloured. In the introduction for the work, Gould states every sky with its varied tints and every feather of each bird were coloured by hand; and when it is considered that nearly two hundred and eighty thousand illustrations in the present work have been so treated, it will most likely cause some astonishment to those who give the subject a thought.
The work has gathered critical acclaim: according to Mullens and Swann, Birds of Great Britain is the most sumptuous and costly of British bird books, whilst Wood describes it as a magnificent work. Isabella Tree writes that it was seen – perhaps partly because its subject was British, as the culmination of [his] ... genius
1845-63 John Gould Large Antique Print of Tree Kangaroo The Mammals of Australia
- Title : Dendrolagus Inustus, Mull....H C Richter del et lith....C Hullmandel Imp.
- Ref #: 93442
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1845–63
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare original hand coloured lithograph antique print of The Grizzled Tree Kangaroo, by the artist HC Richter was printed by Charles Joseph Hullmandel 1789 – 1850 in the famous Naturalists John Goulds The Mammals of Australiapublished between 1845–63.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Mammals of Australia is a three-volume work written and published by John Gould between 1845–63. It contains 182 illustrations by the author and its artist H. C. Richter. It was intended to be a complete survey of the novel species of mammals, such as the marsupials, discovered in the colonies of Australia.
The author, John Gould, best known for The Birds of Australia and other major works of ornithology, visited Australia in 1838. In his introduction, Gould says:.....It was not until I arrived in the country, and found myself surrounded by objects as strange as if I had been transported to another planet, that I conceived the idea of devoting a portion of my attention to the mammalian class of its extraordinary fauna......During his short stay he made observations on the natural history and employed his skills as a taxidermist to obtain specimens.
The publication of this major work by Gould followed his A Monograph of the Macropodidae or Family of Kangaroos in 1841. This work was the first comprehensive survey of Australian mammals, and gave an account of their classification and description. Gould also included the indigenous names for the species from the lists he made while in Australia. He used these names to make requests of the local peoples for his specimens, and recorded the regions where the names were used. This conserved a number of common names, such as dibbler (Parantechinus apicalis), which were later recommended by authorities.
The large lithographs reproduced the artwork of Richter, after the drawings and watercolours made in Australia by Gould and his wife, Elizabeth. (The contribution by Elizabeth Gould was uncredited). These were hand-coloured by a group of artists, led by Gabriel Bayfield, that required the completion of 26,572 plates. The illustrations produced during their visit to Australia were supplemented by the preserved specimens returned to England and detailed the characteristics of the species. These illustrations have become iconic images of the mammals of Australia. Among the best known of the illustrations from the work are the two of Thylacinus cynocephalus (Tasmanian tiger), copied since its publication and the most frequently reproduced, made more recognizable by Cascade Brewerys appropriation for its label in 1987. The government of Tasmania published a monochromatic reproduction of the same image in 1934, the author Louisa Anne Meredith also copied it for Tasmanian Friends and Foes (1881).
The Mammals of Australia was published by subscription in the format Imperial Folio; 13 parts in three volumes were issued from 1845 until 1863. To these the author added An Introduction to The Mammals of Australia (1863) in a separate work. This provided corrections and updates, a new preface, introduction, and a list of the mammals of the three volumes. The first two volumes were complete surveys of orders Marsupiata (marsupials), and, with Rodentia in the third, it formed the sum of known mammalian species of Australia. With the addition of those contained in the later Introduction the total of species described reached 166. The same work notes the exclusion of marine mammals such as whales from the volumes, but reprints a manuscript by Charles Coxen on the dugong.
Beyond the scientific value of this comprehensive survey, the document is cited in reference to its subjects conservation. Some of the species included in the work, such as Onychogalea lunata (crescent nailtail wallaby), have since succumbed to changes in land use since European colonisation.
The work was received with acclaim, but the high cost of production, especially of the coloured plates, reduced its accessibility. The original listed price was £41 for the complete set of volumes. The public curiosity for the unique fauna of Australia was met by this handsomely illustrated and comprehensive survey, and it spawned imitations in Australia. The curator of the Australian Museum, Gerard Krefft, produced the more affordable The Mammals of Australia (1871); intended for educational purposes and influenced by Goulds illustrations. Gracius Broinowskis abandoned work, Birds and Mammals of Australia (1884), so closely imitated the plates that an injunction was threatened by its publisher.
Gould, John FRS 1804 – 1881
Gould was an English ornithologist and bird artist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates that he produced with the assistance of his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart. He has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed Darwins finches played a role in the inception of Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work is referenced in Charles Darwins book, On the Origin of Species.
Gould was born in Lyme Regis the first son of a gardener. He and the boy probably had a scanty education. Shortly afterwards his father obtained a position on an estate near Guildford, Surrey, and then in 1818 Gould became foreman in the Royal Gardens of Windsor. He was for some time under the care of J. T. Aiton, of the Royal Gardens of Windsor. The young Gould started training as a gardener, being employed under his father at Windsor from 1818 to 1824, and he was subsequently a gardener at Ripley Castle in Yorkshire. He became an expert in the art of taxidermy. In 1824 he set himself up in business in London as a taxidermist, and his skill helped him to become the first Curator and Preserver at the museum of the Zoological Society of London in 1827.
Goulds position brought him into contact with the countrys leading naturalists. This meant that he was often the first to see new collections of birds given to the Zoological Society of London. In 1830 a collection of birds arrived from the Himalayas, many not previously described. Gould published these birds in A Century of Birds from the Himalaya Mountains (1830–1832). The text was by Nicholas Aylward Vigors and the illustrations were drawn and lithographed by Goulds wife Elizabeth Coxen Gould. Most of Goulds work were rough sketches on paper from which other artists created the lithographic plates.
This work was followed by four more in the next seven years, including Birds of Europe in five volumes. It was completed in 1837; Gould wrote the text, and his clerk, Edwin Prince, did the editing. The plates were drawn and lithographed by Elizabeth Coxen Gould. A few of the illustrations were made by Edward Lear as part of his Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae in 1832. Lear, however, was in financial difficulty, and he sold the entire set of lithographs to Gould. The books were published in a very large size, imperial folio, with magnificent coloured plates. Eventually 41 of these volumes were published, with about 3000 plates. They appeared in parts at £3 3s. a number, subscribed for in advance, and in spite of the heavy expense of preparing the plates, Gould succeeded in making his ventures pay, realising a fortune. This was a busy period for Gould who also published Icones Avium in two parts containing 18 leaves of bird studies on 54 cm plates as a supplement to his previous works. No further monographs were published as in 1838 he and his wife moved to Australia to work on the Birds of Australia. Shortly after their return to England, his wife died in 1841. Elizabeth Gould completed 84 plates for Birds of Australia before her death.
When Charles Darwin presented his mammal and bird specimens collected during the second voyage of HMS Beagle to the Zoological Society of London on 4 January 1837, the bird specimens were given to Gould for identification. He set aside his paying work and at the next meeting on 10 January reported that birds from the Galápagos Islands which Darwin had thought were blackbirds, gross-bills and finches were in fact a series of ground Finches which are so peculiar as to form an entirely new group, containing 12 species. This story made the newspapers. In March, Darwin met Gould again, learning that his Galápagos wren was another species of finch and the mockingbirds he had labelled by island were separate species rather than just varieties, with relatives on the South American mainland. Subsequently, Gould advised that the smaller southern Rhea specimen that had been rescued from a Christmas dinner was a separate species which he named Rhea darwinii, whose territory overlapped with the northern rheas. Darwin had not bothered to label his finches by island, but others on the expedition had taken more care. He now sought specimens collected by captain Robert FitzRoy and crewmen. From them he was able to establish that the species were unique to islands, an important step on the inception of his theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work on the birds was published between 1838 and 1842 in five numbers as Part 3 of Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle, edited by Charles Darwin. Elizabeth Gould illustrated all the plates for Part 3.
In 1838 the Goulds sailed to Australia, intending to study the birds of that country and be the first to produce a major work on the subject. They took with them the collector John Gilbert. They arrived in Tasmania in September, making the acquaintance of the governor Sir John Franklin and his wife. Gould and Gilbert collected on the island. In February 1839 Gould sailed to Sydney, leaving his pregnant wife with the Franklins. He travelled to his brother-in-laws station at Yarrundi, spending his time searching for bowerbirds in the Liverpool Range. In April he returned to Tasmania for the birth of his son. In May he sailed to Adelaide to meet Charles Sturt, who was preparing to lead an expedition to the Murray River. Gould collected in the Mount Lofty range, the Murray Scrubs and Kangaroo Island, returning again to Hobart in July. He then travelled with his wife to Yarrundi. They returned home to England in May 1840.
The result of the trip was The Birds of Australia (1840–48). It included a total of 600 plates in seven volumes; 328 of the species described were new to science and named by Gould. He also published A Monograph of the Macropodidae, or Family of Kangaroos (1841–1842) and the three volume work The Mammals of Australia (1849–1861).
Elizabeth died in 1841 after the birth of their eighth child, Sarah, and Goulds books subsequently used illustrations by a number of artists, including Henry Constantine Richter, William Matthew Hart and Joseph Wolf.
Throughout his professional life Gould had a strong interest in hummingbirds. He accumulated a collection of 320 species, which he exhibited at the Great Exhibition of 1851. Despite his interest, Gould had never seen a live hummingbird. In May 1857 he travelled to the United States with his second son, Charles. He arrived in New York too early in the season to see hummingbirds in that city, but on 21 May 1857, in Bartrams Gardens in Philadelphia, he finally saw his first live one, a ruby-throated hummingbird. He then continued to Washington D.C. where he saw large numbers in the gardens of the Capitol. Gould attempted to return to England with live specimens, but, as he was not aware of the conditions necessary to keep them, they only lived for two months at most.
Gould published: A Monograph of the Trochilidae or Humming Birds with 360 plates (1849–61); The Mammals of Australia (1845–63), Handbook to the Birds of Australia (1865), The Birds of Asia (1850–83), The Birds of Great Britain (1862–73) and The Birds of New Guinea and the adjacent Papuan Islands (1875–88).
The University of Glasgow, which owns a copy of Birds of Great Britain, describes John Gould as the greatest figure in bird illustration after Audubon, and auctioneers Sotherans describe the work as Goulds pride and joy.
Gould had already published some of the illustrations in Birds of Europe, but Birds of Great Britain represents a development of his aesthetic style in which he adds illustrations of nests and young on a large scale.
Sotherans Co. reports that Gould published the book himself, producing 750 copies, which remain sought after both as complete volumes, and as individual plates, currently varying in price from £450 – £850. The University of Glasgow records that the volumes were issued in London in 25 parts, to make the complete set, between 1863 and 1873, and each set contained 367 coloured lithographs.
Gould undertook an ornithological tour of Scandinavia in 1856, in preparation for the work, taking with him the artist Henry Wolf who drew 57 of the plates from Goulds preparatory sketches. According to The University of Glasgow Goulds skill was in rapidly producing rough sketches from nature (a majority of the sketches were drawn from newly killed specimens) capturing the distinctiveness of each species. Gould then oversaw the process whereby his artists worked his sketches up into the finished drawings, which were made into coloured lithographs by engraver William Hart.
There were problems: the stone engraving of the snowy owl in volume I was dropped and broken at an early stage in the printing. Later issues of this plate show evidence of this damage and consequently the early issue – printed before the accident – are considered more desirable.
The lithographs were hand coloured. In the introduction for the work, Gould states every sky with its varied tints and every feather of each bird were coloured by hand; and when it is considered that nearly two hundred and eighty thousand illustrations in the present work have been so treated, it will most likely cause some astonishment to those who give the subject a thought.
The work has gathered critical acclaim: according to Mullens and Swann, Birds of Great Britain is the most sumptuous and costly of British bird books, whilst Wood describes it as a magnificent work. Isabella Tree writes that it was seen – perhaps partly because its subject was British, as the culmination of [his] ... genius
1735 Schubler & Steidlin Antique Baroque Print Musical Ball Regensburg Ger. 1717
- Title : Bal, welche den 26. Sept: 1717 in Sr Durchl: Eminens des Herrn Cardinals residens zu Regensburg, in dem so genamten Lowen-Saal, gehalten worden....NB das Bal Zimmer war mit rohten Tuch belegt
- Ref #: 93443
- Size: 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1735
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original Baroque copper plate engraved antique print, numbered three of three, of an early 18th century Ball, part of the celebrations at the Royal Court in the Cardinal Castle of Regensburg, on September 26, 1717, by Johann Schubler, was engraved by Johann Matthias Steidlin or Steudlin 1717-1754 and published by the Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1735.
A wonderful piece of Baroque art, engraved and published by some of the foremost art engravers and publishers at the beginning of the 18th century.
Professionally matted and can be easily removed if required.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair bottom right signature
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1245 Regensburg became a Free Imperial City and was a trade centre before the shifting of trade routes in the late Middle Ages. In 1486, Regensburg became part of the Duchy of Bavaria, but its independence was restored by the Holy Roman Emperor ten years later. In the city took place the Diet of 1541, was adopted the Protestant Reformation in 1542 and its Town Council remained entirely Lutheran. From 1663 to 1806, the city was the permanent seat of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire, which became known as the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. Thus, Regensburg was one of the central towns of the Empire, attracting visitors in large numbers.
A minority of the population remained Roman Catholic, and Roman Catholics were denied civic rights (Bürgerrecht). Although the Imperial city had adopted the Reformation, the town remained the seat of a Roman Catholic bishop and several abbeys. Three of these, St. Emmeram, Niedermünster and Obermünster, were free imperial estates within the Holy Roman Empire, meaning that they were granted a seat and a vote at the Imperial Diet (Reichstag). So there was the unique situation that the town of Regensburg comprised five independent states (in terms of the Holy Roman Empire): the Protestant city itself, the Roman Catholic bishopric, and the three monasteries. In addition, it was seen as the traditional capital of the region Bavaria (not the state), acted as functional co-capital of the Empire (second to the Emperors court at Vienna) due to the presence of the Perpetual Diet, and it was the residence of the Emperors Commissary-Principal to the same diet, who with one very brief exception was a prince himself (for many years the Prince of Thurn and Taxis, still resident in the town).
Schübler, Johann Jacob 1689 - 1741
Schübler was born in Nuremberg as was known as a versatile German baroque master builder , architectural theorist and writer and mathematician.
Schüblers father Johann Jacob was a braid maker and language teacher, and he also had medical knowledge, which he also used for a fee. He came to Nuremberg from Strasbourg and became resident there by marrying Maria Elisabeth Hengel, the daughter of an independent braid maker. The later master builder Johann Jacob Schübler was the fourth of the couples eight children. Through his father and private tutors, he received careful training, mainly in artistic subjects as well as in old and new languages. Architectural painter Johann Andreas Graff gave him his first drawing lessons . In 1698 he began his apprenticeship as a draftsman in the studio of the portraitist, engraver and art dealerJacob von Sandrart (1630-1708), in addition he was taught by Georg Christoph Eimmart (1638-1705), the long-time director of the important Nuremberg Academy of Painters , a representative of the mathematically oriented artists of the time and founder of the observatory at the Nuremberg castle .
At that time, extensive study trips were common for aspiring artists to complete their training. Between 1705 and 1713, Schüblers years of traveling took him through Germany, Denmark and Norway, the Netherlands and France - with a stopover in 1711 with his parents in Nuremberg. The time around 1700 in Europe was particularly intensive secular and church building activity, numerous elaborate, representative buildings. Schüblers travel destinations were primarily places where the current building activity was concentrated. However, Italy was missing from this program. He made longer stays for scholarly studies in Leipzig and Copenhagen .
After his return in 1713, Schübler remained settled in Nuremberg. Prominent colleagues such as Balthasar Neumann (1687–1753) visited him and he corresponded with well-known artists and scientists. He rejected various offers from foreign employers because they did not seem attractive enough to him. In 1717 he received the order for a gate of honor, which was built to celebrate a princely wedding in the main square of the residential city of Sulzbach . Schübler had an expansive triumphal arch with three stacked columns and niches for allegorical figures built, which was generally praised. A permanent position at the court of the Sulzbach Palatinate Countshowever, did not result from this. So he remained the prevented Builder. Great vocations only reached him towards the end of his life. In 1740 the Danish king invited him to Copenhagen, in 1741 negotiations for a move to Berlin followed to the court of the Prussian king Friedrich II. Both offers came too late for Schübler. He died in September 1741 from a clock-like illness.
Schübler only started his own family at an advanced age. In 1727 he married Margareta Maria Hemme, the daughter of a respected art dealer. At around 40, the bride was even a little older than Schübler herself; she died two years after the marriage, the marriage remained childless. In 1733 Schübler had a second marriage to 26-year-old Margaretha Setzmair. She also came from a long-established, wealthy middle-class family. The couple had two daughters, one of whom died very early, and a son who was born several months after Schüblers death.
In 1734 Schübler was accepted as an external member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin. The small Schüblerstrasse in Nuremberg reminds him of him.
Schüblers actual lifes work consisted of a large number of writings, the publication of which he began around 1715. With his later works in particular, he pursued the intention of scientifically examining the questions of the building industry based on proportion and perspective, thereby making them teachable and learnable for building theorists and practitioners of his time.
Initially, Schübler published smaller masterpieces that appeared in deliveries of six to twelve engravings and contained hardly any text. In it he showed architectural details (e.g. fireplaces , mansard windows , pulpits, altars, confessionals), furniture (beds, desks, clocks, night chairs) and technical objects such as pumping stations and fountains. He drew the originals himself, often with a light color, but hardly ever took over the transfer to the printing plates, even though he knew this technique. For this, he employed a large number of engravers, among them Johann August Corvinus, Johann Matthias Steidlin, Georg Lichtensteger and his own brother Georg Andreas. The objects depicted often appear grotesquely overloaded with decorative elements such as flower threads, sphinxes and the like, but were also not intended for direct implementation. Rather, the executing tradesmen were able to take very different suggestions from a single template. The templates appeared in the publisher Jeremias Wolff in Augsburg, which is renowned throughout Europe .
Schüblers more scientific and literary works were mostly published by Johann Christoph Weigel in Nuremberg. In 1719/20 Perspectiva Pes Picturae was published in two parts , a large-format work of art intended to provide the basis for architectural painting . 1723/24, again in two parts, came out a textbook on the column orders with practical aids for difficult problems, which was reprinted several times. This was followed by publications on the art of sundial (1726) and on the wood-fired parlor ovens(1728). Schüblers main works then appeared within five years. With them he wanted to provide a new, in-depth representation of the entire architecture, with the main areas of the Architectura Civilis and the Architectura Militaris . From the years 1732-35 are the five illustrated volumes of a Synopsis Architecturae Civilis eclecticae , to which the content of the theoretical work Ars inveniendi from 1734 on civil architecture can be assigned. The two volumes of carpentry (Ars Tignaria) date from 1731 and 1736 . The main works include Perspectiva Geometrica Practica .
Schüblers works were widespread, and individual writings had up to 20 editions. The last known new edition dates from 1786. The popularity of his practically applicable proposals ended with the domination of baroque and rococo in architecture. The new general artist lexicon by art historian Georg Kaspar Nagler (1801–1866) already discusses Schüblers works as examples of the aesthetic aberrations of an era that has been overcome and describes them as senseless outbursts of an unregulated imagination.
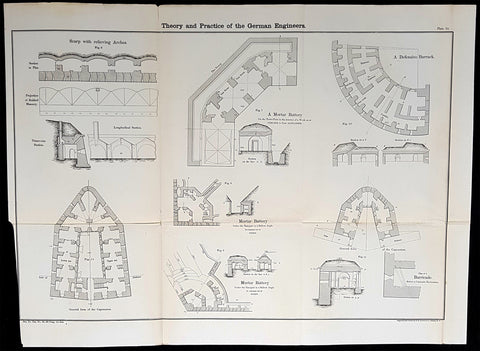
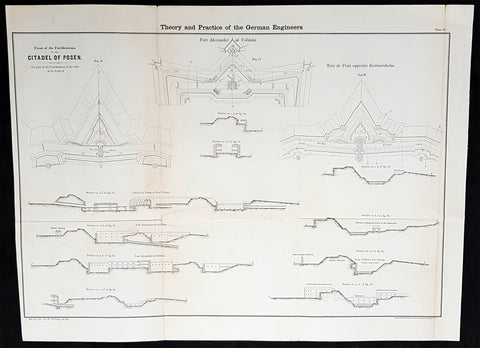
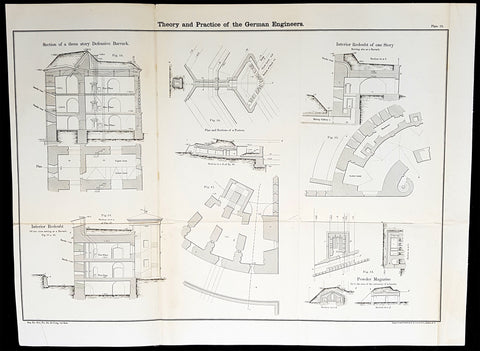
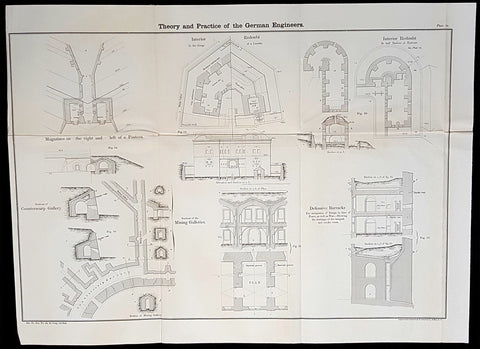
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90194
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
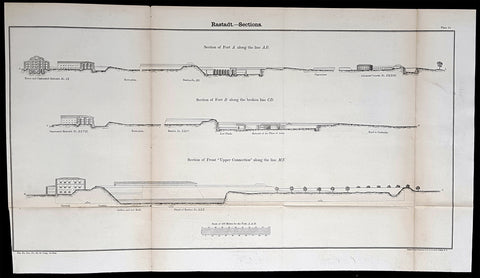
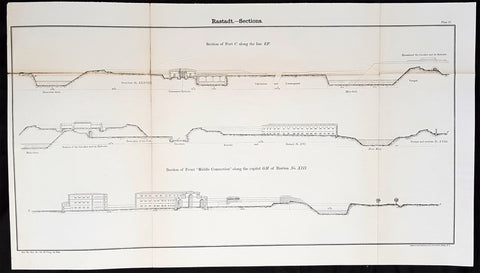
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
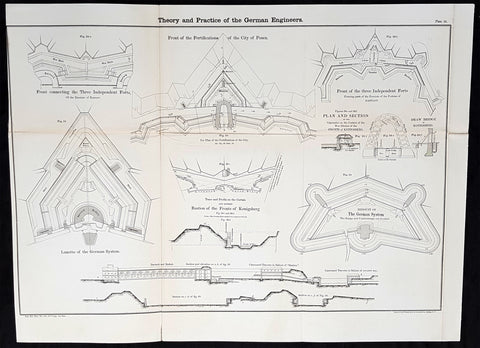
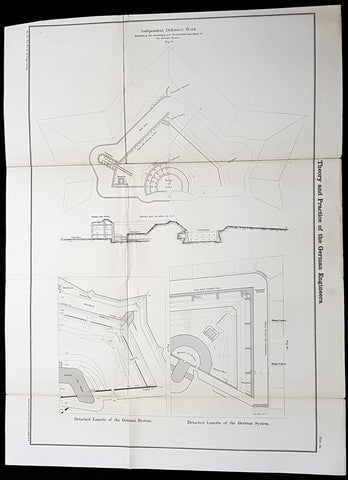
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90144
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
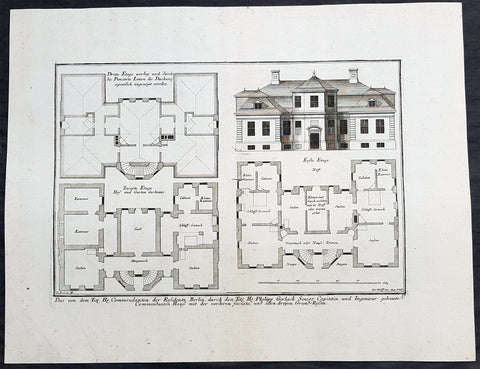
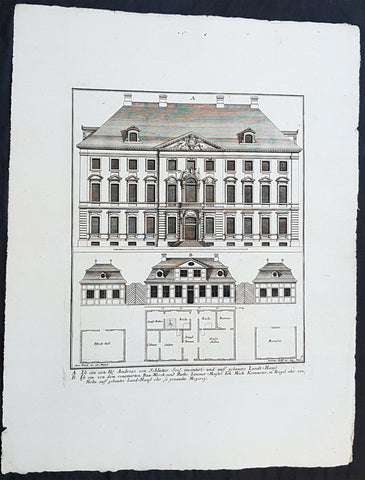
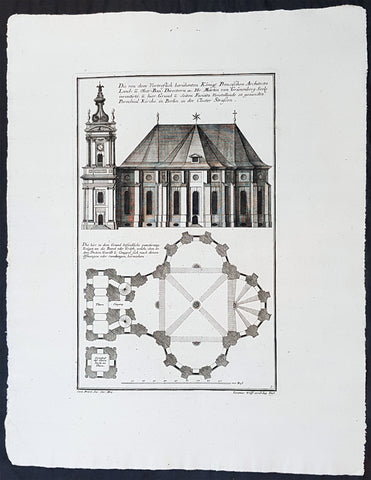
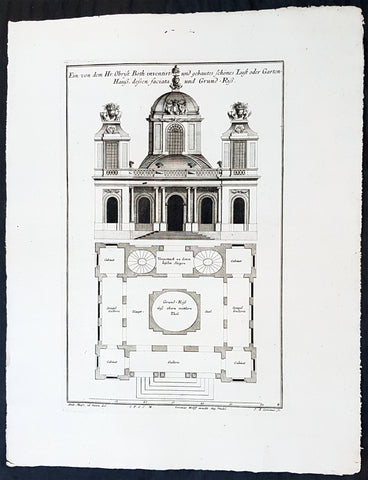
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Plan Officers Quarters, Royal Arsenal, Berlin
- Title : Das von dem Tit. H. Commendanten der Residentz Berlin, durch den Tit. H. Philipp Gerlach Senior Capitain und Ingenieur gebaute Commendaten Hauß mit der vorderen faciata und allen dreyen Grund-Rissen
- Ref #: 93449
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view & plan of officers quarters at the Royal Arsenal in Berlin - plate No.17 of 19 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
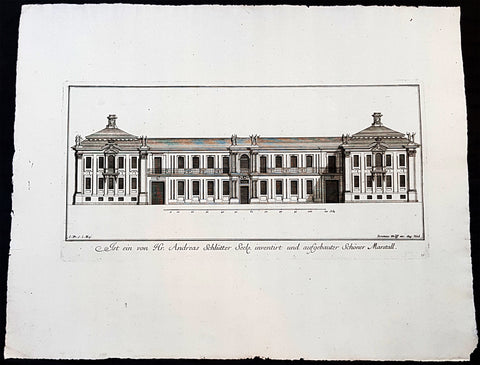
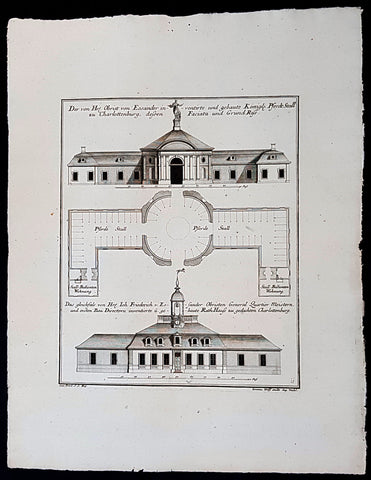
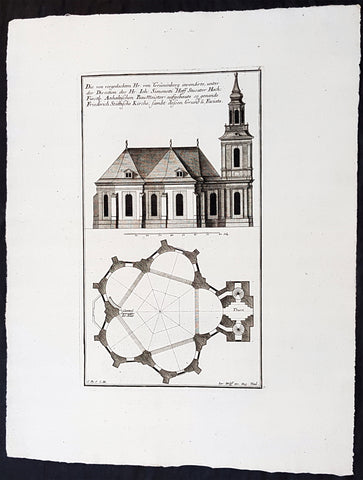
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Charlottenburg Palace Stables Berlin
- Title : Ist ein von Hr. Andreas Schlütter Seel. inventirt und aufgebauer Schöner Marstall Datierung
- Ref #: 93447
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view of the facade of the Charlottenburg Palace stables in Berlin - plate No.15 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
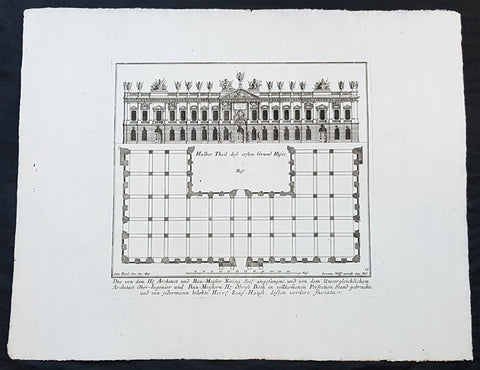
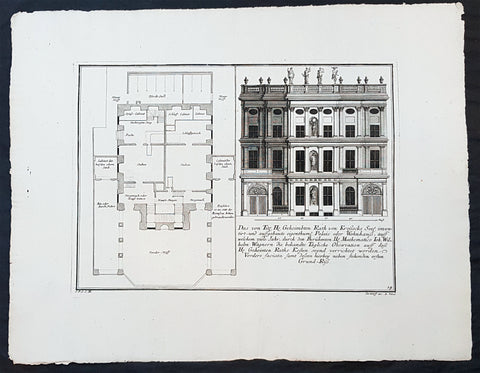
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of The Royal Arsenal in Berlin Germany
- Title : Das von dem H. Architect und Bau-Meister Nering Seel. angefangne, und von dem unvergleichlichen Architect Ober-Ingenier und Bau-Meistern H. Obrist Both in vollkommenen Perfection Stand gebrachte und von jedermann belobte Herr. Zeug-Haus, dessen vordere faciata
- Ref #: 93454
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view & plan of The Royal Arsenal in Berlin Houses - plate No.13 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
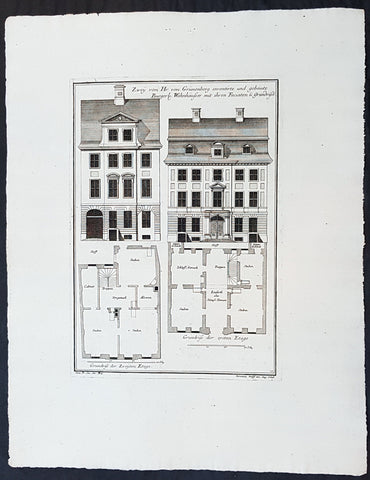
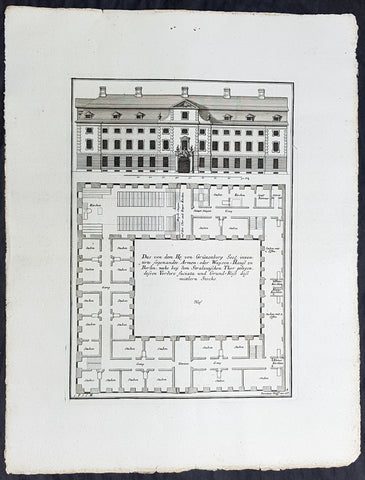
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print Plans of Residential Houses in Berlin
- Title : Zwey von Hr. von Grünenberg inventirte und gebaute Burgerl. Wohnhäusser mit ihren Faciaten u. Grundrissen
- Ref #: 93450
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print plans of Berlin Houses - plate No. 12 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Charlottenburg Palace Stables Berlin
- Title : Der von Hr. Obrist von Eosander inventirte und gebaute Königl. Pferdt Stall zu Charlottenburg, dessen Faciata und Grund Riss. - Das gleichfals von Hr. Joh. Friederich v. Eosander Obristen General Quartier Meistern, und ersten Bau Directorn inventierte und gebaute Rath Hauss zu gedachten Charlottenburg
- Ref #: 93453
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Royal Horse Stables at Charlottenburg Palace, Berlin - plate No. 11 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Berlin Mansions by A. von Schlütter
- Title : A. Ist ein von H. Andreas von Schlütter Seel. inventirt- und auff gebautes Landt-Hauss. B. Ist ein von dem renomirten Bau-Werck- und Raths Zimmer-Meister Joh. Mich. Kemmeter, in Riegel oder Holtz auff gebautes Land-Hauß oder so genandte Meyerey
- Ref #: 93445
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of 18th century Mansions in Berlin designed by Andreas von Schlütter - plate No. 9 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of a Poorhouse near Stralau Gate Berlin
- Title : Das von dem H. von Grünenberg Seel. inventirte sogenandte Armen- oder Waysen-Hauss zu Berlin, nache bey dem Stralauischen Thor gelegen, ....
- Ref #: 93455
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Poorhouse near the old Stralau Gate (Stralauer Tor) in Berlin - plate No. 8 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch. Print Jerusalem Church Friedrichstadt.Berlin
- Title : Die von vorgedachten Hr. von Grünenberg invendierte, unter der Direction des Hr. Ioh. Simonetti Hoff Stucator Hoch-Fürstl. Anhaltischen BauMeister aufgebaute so genande Friderich Stättische Kirche sampt dessen Grund u. Faciata.
- Ref #: 93458
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 7 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch. Print of the Parochialkirche in Mitte Berlin
- Title : Vordere faciata nebst dem halben Grund Riß der vorigen Parochial-Kirche mit verändertem Thurn wie solcher dermahlen sich würklich presentiert. Frontriß, darunter der halbe Grundriß.
- Ref #: 93459
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 6 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten.
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print Parochialkirche, Mitte, Berlin
- Title : Die Von dem Vortreslich beruhmten Konigl. Preusichen Architect Land u. Ober Bau Directorn etc. Hr. Martin von Grunenberg Seel. inventirte, u. hier Grund u. Seiten Faciata Vorstellende so genandte Parochial Kirche in Berlin in der Closter Strassen
- Ref #: 93451
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 5 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print of Berlin Gate, Leipziger Tor
- Title : Das von dem Herrn Baumeister Nering Seel. ausgefuhrte so genandte Leipziger Statt Thor in Berlin
- Ref #: 93452
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of buildings & gardens in 17th & 18th century Berlin - plate No. 3 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print Buildings, Gardens Berlin - No. 14
- Title : Das von Title Hr. Geheimbten Rath von Krossecks Seel. inventirt - und aussgebaute
- Ref #: 93448
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of buildings & gardens in the Charlottenburg suburb of Berlin & Charlottenburg Palace, - plate No. 14 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charlottenburg is an affluent locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a town in 1705 and named after late Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Prussia, it is best known for Charlottenburg Palace, the largest surviving royal palace in Berlin, and the adjacent museums.
Charlottenburg is located in Berlins inner city, west of the Großer Tiergarten park. Its historic core, the former village green of Alt Lietzow, is situated on the southern shore of the Spree River running through the Berlin glacial valley. The Straße des 17. Juni road, former Charlottenburger Chaussee, which runs eastwards from Charlottenburg Gate through the Tiergarten park to Brandenburg Gate, connects Charlottenburg with the historic centre of Berlin-Mitte.
In the north and west, the Berlin Ringbahn and the Bundesautobahn 100 (Stadtring) mark the border with the Charlottenburg-Nord and Westend suburbs. Adjacent in the south is the territory of Wilmersdorf. Charlottenburg also borders on the district of Halensee in the southwest, as well as on Moabit, Hansaviertel and Tiergarten (all part of the Mitte borough) in the east and on Schöneberg in the southeast.
In 1695, Sophia Charlotte of Hanover received Lietzow from her husband, Elector Frederick III of Brandenburg, in exchange for her estates in Caputh and Langerwisch near Potsdam. Frederick had a summer residence built there for Sophie Charlotte by the architect Johann Arnold Nering between 1695 and 1699. After he had crowned himself Frederick I, King in Prussia, the Lützenburg castle was extended into a stately building with a cour dhonneur. The Swedish master builder Johann Friedrich Eosander supervised this work. Sophie Charlotte died in February 1705; shortly afterwards the settlement facing the palace was called Charlottenburg - the palace itself became Schloss Charlottenburg - and chartered as a town on April 5, 1705. The king served as the towns mayor until the historic village of Lietzow was incorporated into Charlottenburg in 1720.
Fredericks successor as king, Frederick William I of Prussia, rarely stayed at the palace, which depressed the small town of Charlottenburg. Frederick William even tried to revoke the towns privileges. With the coronation of his successor Frederick II in 1740 the towns significance increased, as regular celebrations again took place at the palace. Between 1740 and 1747 Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff built the eastern New Wing as Fredericks residence. Later, Frederick II preferred the palace of Sanssouci, which he had partly designed himself.
When Frederick II died in 1786, his nephew Frederick William II succeeded him, and Charlottenburg became the favourite royal residence, and remained so for his son and successor Frederick William III (reigned 1797-1840). After the defeat of the Prussian army at Jena in 1806, the French occupied Berlin. Napoleon took over the palace, while his troops made a camp nearby. Charlottenburg became part of the new Prussian Province of Brandenburg in 1815 after the Napoleonic Wars.
In the late 18th century, Charlottenburgs development did not depend only on the crown. The town became a recreational area for the expanding city of Berlin. Its first true inn opened in the 1770s, in the street then called Berliner Straße (now Otto-Suhr-Allee), and many other inns and beer gardens were to follow, popular for weekend parties especially. Berliners seeking leisure and entertainment came by boat, by carriage and later by horse-drawn trams, above all to a large amusement park at the shore of the Spree river called Flora, that went into bankruptcy in 1904.
From the 1860s on the wealthy Bourgeoisie of Berlin discovered Charlottenburg as a residential area, among the first were Gerson von Bleichröder and Ernst Werner von Siemens, who had a villa built in the Berliner Straße in 1862. At the same time industrial companies like Siemens & Halske and Schering erected large factories in the north-east, at the border with the Moabit district of Berlin. In 1877 Charlottenburg received town privileges and until World War I saw an enormous increase of population with 100,000 inhabitants as of 1893 and a population of 306,000 in 1920, being the second largest city within the Province of Brandenburg, after Berlin. In the course of industrialization in the 19th century, much of Charlottenburg was incorporated in a network of streets laid out in the Hobrecht-Plan in an area that came to be known architecturally as the Wilhelmine Ring.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print Charlottenburg Palace, Gardens
- Title : Haupt Hof Grund Riss dess Marstalls...Jeremais Wolff exc Aug. Vind
- Ref #: 93446
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of buildings in the Charlottenburg suburb of Berlin & Charlottenburg Palace, - plate No. 4 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charlottenburg is an affluent locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a town in 1705 and named after late Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Prussia, it is best known for Charlottenburg Palace, the largest surviving royal palace in Berlin, and the adjacent museums.
Charlottenburg is located in Berlins inner city, west of the Großer Tiergarten park. Its historic core, the former village green of Alt Lietzow, is situated on the southern shore of the Spree River running through the Berlin glacial valley. The Straße des 17. Juni road, former Charlottenburger Chaussee, which runs eastwards from Charlottenburg Gate through the Tiergarten park to Brandenburg Gate, connects Charlottenburg with the historic centre of Berlin-Mitte.
In the north and west, the Berlin Ringbahn and the Bundesautobahn 100 (Stadtring) mark the border with the Charlottenburg-Nord and Westend suburbs. Adjacent in the south is the territory of Wilmersdorf. Charlottenburg also borders on the district of Halensee in the southwest, as well as on Moabit, Hansaviertel and Tiergarten (all part of the Mitte borough) in the east and on Schöneberg in the southeast.
In 1695, Sophia Charlotte of Hanover received Lietzow from her husband, Elector Frederick III of Brandenburg, in exchange for her estates in Caputh and Langerwisch near Potsdam. Frederick had a summer residence built there for Sophie Charlotte by the architect Johann Arnold Nering between 1695 and 1699. After he had crowned himself Frederick I, King in Prussia, the Lützenburg castle was extended into a stately building with a cour dhonneur. The Swedish master builder Johann Friedrich Eosander supervised this work. Sophie Charlotte died in February 1705; shortly afterwards the settlement facing the palace was called Charlottenburg - the palace itself became Schloss Charlottenburg - and chartered as a town on April 5, 1705. The king served as the towns mayor until the historic village of Lietzow was incorporated into Charlottenburg in 1720.
Fredericks successor as king, Frederick William I of Prussia, rarely stayed at the palace, which depressed the small town of Charlottenburg. Frederick William even tried to revoke the towns privileges. With the coronation of his successor Frederick II in 1740 the towns significance increased, as regular celebrations again took place at the palace. Between 1740 and 1747 Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff built the eastern New Wing as Fredericks residence. Later, Frederick II preferred the palace of Sanssouci, which he had partly designed himself.
When Frederick II died in 1786, his nephew Frederick William II succeeded him, and Charlottenburg became the favourite royal residence, and remained so for his son and successor Frederick William III (reigned 1797-1840). After the defeat of the Prussian army at Jena in 1806, the French occupied Berlin. Napoleon took over the palace, while his troops made a camp nearby. Charlottenburg became part of the new Prussian Province of Brandenburg in 1815 after the Napoleonic Wars.
In the late 18th century, Charlottenburgs development did not depend only on the crown. The town became a recreational area for the expanding city of Berlin. Its first true inn opened in the 1770s, in the street then called Berliner Straße (now Otto-Suhr-Allee), and many other inns and beer gardens were to follow, popular for weekend parties especially. Berliners seeking leisure and entertainment came by boat, by carriage and later by horse-drawn trams, above all to a large amusement park at the shore of the Spree river called Flora, that went into bankruptcy in 1904.
From the 1860s on the wealthy Bourgeoisie of Berlin discovered Charlottenburg as a residential area, among the first were Gerson von Bleichröder and Ernst Werner von Siemens, who had a villa built in the Berliner Straße in 1862. At the same time industrial companies like Siemens & Halske and Schering erected large factories in the north-east, at the border with the Moabit district of Berlin. In 1877 Charlottenburg received town privileges and until World War I saw an enormous increase of population with 100,000 inhabitants as of 1893 and a population of 306,000 in 1920, being the second largest city within the Province of Brandenburg, after Berlin. In the course of industrialization in the 19th century, much of Charlottenburg was incorporated in a network of streets laid out in the Hobrecht-Plan in an area that came to be known architecturally as the Wilhelmine Ring.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90140
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics of the 2nd Lancers Barracks, Berlin
- Title : Barrack of the Lancers of the Guard at Berlin...Barrack of the Second Regiment of the Lancers of the Guard at Berlin
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90143
- Size: 20 1/2in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of the 2nd German Lancer Regiment Barracks in Berlin - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
A lancer was a type of cavalryman who fought with a lance. Lances were used in mounted warfare by the Assyrians as early as 700 BC and subsequently by Greek, Persian, Gallic, Chinese, and Roman horsemen. The weapon was widely used in Asia and Europe during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance by armoured cavalry, before being adopted by light cavalry, particularly in Eastern Europe. In a modern context, a lancer regiment usually denotes an armoured unit.
The lancer (called ułan in Polish and Uhlan in German) had become a common sight in almost every European, Ottoman, and Indian army during this time, but, with the exception of the Ottoman troops, they increasingly discarded the heavy armour to give greater freedom of movement in combat. The Polish winged lancers were amongst the last to abandon the armour in Europe. There was debate over the value of the lance in mounted combat during the 18th century and most armies had few lancer units by the beginning of the 19th century. However, during the Napoleonic Wars, lancers were to be seen in many of the combatant nations as their value in shock tactics became clear. During the wars, the Poles became a ready source of recruitment for several armies, willingly or unwillingly. Polish lancers served with distinction in the Austrian, Prussian, Russian and French armies, most famously in Napoleons French Imperial Guard as the 1er Regiment de Chevau-Legers-Lanciers de la Garde Impériale.
At the Battle of Waterloo, French lances were nearly three meters (about nine feet, ten inches) long, weighed three kilograms (about six pounds, ten ounces), and had a steel point on a wooden staff, according to historian Alessandro Barbero. He adds that they were terrifyingly efficient. Commander of the French 1st Corps, 4th Division General Durutte, who saw the battle from the high ground in front of Papelotte, would write later, I had never before realized the great superiority of the lance over the sword.
In the Siege of Los Angeles (1846), during the war between Mexico and the United States, a company of Californio lancers temporarily recaptured the town, expelling a company of U.S. Marines.
Although having substantial impact in the charge, lancers could be vulnerable to other cavalry at close quarters, where the lance proved a clumsy and easily deflected weapon when employed against sabres. By the late 19th century, many cavalry regiments in the British and other European armies were composed of troopers with lances, as primary weapons, in the front rank and horsemen with sabres only in the second: the lances for the initial shock and sabres for the subsequent mêlée.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics of the 2nd Lancers Barracks, Berlin
- Title : Barrack of the Lancers of the Guard at Berlin...Barrack of the Second Regiment of the Lancers of the Guard at Berlin
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90152
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of the 2nd German Lancer Regiment Barracks in Berlin - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
A lancer was a type of cavalryman who fought with a lance. Lances were used in mounted warfare by the Assyrians as early as 700 BC and subsequently by Greek, Persian, Gallic, Chinese, and Roman horsemen. The weapon was widely used in Asia and Europe during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance by armoured cavalry, before being adopted by light cavalry, particularly in Eastern Europe. In a modern context, a lancer regiment usually denotes an armoured unit.
The lancer (called ułan in Polish and Uhlan in German) had become a common sight in almost every European, Ottoman, and Indian army during this time, but, with the exception of the Ottoman troops, they increasingly discarded the heavy armour to give greater freedom of movement in combat. The Polish winged lancers were amongst the last to abandon the armour in Europe. There was debate over the value of the lance in mounted combat during the 18th century and most armies had few lancer units by the beginning of the 19th century. However, during the Napoleonic Wars, lancers were to be seen in many of the combatant nations as their value in shock tactics became clear. During the wars, the Poles became a ready source of recruitment for several armies, willingly or unwillingly. Polish lancers served with distinction in the Austrian, Prussian, Russian and French armies, most famously in Napoleons French Imperial Guard as the 1er Regiment de Chevau-Legers-Lanciers de la Garde Impériale.
At the Battle of Waterloo, French lances were nearly three meters (about nine feet, ten inches) long, weighed three kilograms (about six pounds, ten ounces), and had a steel point on a wooden staff, according to historian Alessandro Barbero. He adds that they were terrifyingly efficient. Commander of the French 1st Corps, 4th Division General Durutte, who saw the battle from the high ground in front of Papelotte, would write later, I had never before realized the great superiority of the lance over the sword.
In the Siege of Los Angeles (1846), during the war between Mexico and the United States, a company of Californio lancers temporarily recaptured the town, expelling a company of U.S. Marines.
Although having substantial impact in the charge, lancers could be vulnerable to other cavalry at close quarters, where the lance proved a clumsy and easily deflected weapon when employed against sabres. By the late 19th century, many cavalry regiments in the British and other European armies were composed of troopers with lances, as primary weapons, in the front rank and horsemen with sabres only in the second: the lances for the initial shock and sabres for the subsequent mêlée.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics Internal Calvary Barracks, Quarters
- Title : Cavalry Barracks - Furniture of the Quarters...
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90191
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of the internals of cavalry barracks and quarters - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The arrival of explosive shells in the 19th century led to yet another stage in the evolution of fortification. Star forts did not fare well against the effects of high explosive and the intricate arrangements of bastions, flanking batteries and the carefully constructed lines of fire for the defending cannon could be rapidly disrupted by explosive shells.
Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the counter scarp. The ditch was extremely vulnerable to bombardment with explosive shells.
In response, military engineers evolved the polygonal style of fortification. The ditch became deep and vertically sided, cut directly into the native rock or soil, laid out as a series of straight lines creating the central fortified area that gives this style of fortification its name.
Wide enough to be an impassable barrier for attacking troops, but narrow enough to be a difficult target for enemy shellfire, the ditch was swept by fire from defensive blockhouses set in the ditch as well as firing positions cut into the outer face of the ditch itself.
The profile of the fort became very low indeed, surrounded outside the ditch covered by caponiers by a gently sloping open area so as to eliminate possible cover for enemy forces, while the fort itself provided a minimal target for enemy fire. The entrypoint became a sunken gatehouse in the inner face of the ditch, reached by a curving ramp that gave access to the gate via a rolling bridge that could be withdrawn into the gatehouse.
Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the blockhouses and firing points in the ditch to the fort proper, with magazines and machine rooms deep under the surface. The guns, however, were often mounted in open emplacements and protected only by a parapet; both in order to keep a lower profile and also because experience with guns in closed casemates had seen them put out of action by rubble as their own casemates were collapsed around them.
Gone were citadels surrounding towns: forts were to be moved to the outside of the cities some 12 km to keep the enemy at a distance so their artillery could not bombard the city center. From now on a ring of forts were to be built at a spacing that would allow them to effectively cover the intervals between them.
The new forts abandoned the principle of the bastion, which had also been made obsolete by advances in arms. The outline was a much simplified polygon, surrounded by a ditch. These forts, built in masonry and shaped stone, were designed to shelter their garrison against bombardment. One organizing feature of the new system involved the construction of two defensive curtains: an outer line of forts, backed by an inner ring or line at critical points of terrain or junctions (see, for example, Séré de Rivières system in France).
Traditional fortification however continued to be applied by European armies engaged in warfare in colonies established in Africa against lightly armed attackers from amongst the indigenous population. A relatively small number of defenders in a fort impervious to primitive weaponry could hold out against high odds, the only constraint being the supply of ammunition.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Print Fortifications of Rastatt Germany
- Title : Rastadt - Sections
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90192
- Size: 26 1/2in x 14in (675mm x 355mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print a plan of the fortifications around the city of Rastatt in Baden-Württemberg, Germany - during the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 14in (675mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 14in (675mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Rastatt is a town with a baroque core, District of Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located in the Upper Rhine Plain on the Murg river, 6 km above its junction with the Rhine. Rastatt was an important place of the War of the Spanish Succession (Treaty of Rastatt) and the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states.
Until the end of the 17th century, Rastatt held little influence, but after its destruction by the French in 1689, it was rebuilt on a larger scale by Louis William, margrave of Baden, the imperial general in the Habsburg-Ottoman War known popularly as Türkenlouis.
It then remained the residence of the margraves of Baden-Baden until 1771. It was the location of the First and Second Congress of Rastatt, the former giving rise to the Treaty of Rastatt while the second ended in failure in 1799. In the 1840s, Rastatt was surrounded by fortifications to form the fortress of Rastatt. For about 20 years previous to 1866, it was occupied by the troops of the German Confederation.
The Baden revolution of 1849 began with a mutiny of soldiers at Rastatt in May 1849 under Ludwik Mieroslawski and Gustav Struve, and ended there a few weeks later with the capture of the town by the Prussians. (See The Revolutions of 1848 in the German states and History of Baden.) For some years, Rastatt was one of the strongest fortresses of the German empire, but its fortifications were dismantled in 1890.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Print Fortifications of Rastatt Germany
- Title : Rastadt - Sections
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90134
- Size: 26 1/2in x 14in (675mm x 355mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print a plan of the fortifications around the city of Rastatt in Baden-Württemberg, Germany - during the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 14in (675mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 14in (675mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Rastatt is a town with a baroque core, District of Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located in the Upper Rhine Plain on the Murg river, 6 km above its junction with the Rhine. Rastatt was an important place of the War of the Spanish Succession (Treaty of Rastatt) and the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states.
Until the end of the 17th century, Rastatt held little influence, but after its destruction by the French in 1689, it was rebuilt on a larger scale by Louis William, margrave of Baden, the imperial general in the Habsburg-Ottoman War known popularly as Türkenlouis.
It then remained the residence of the margraves of Baden-Baden until 1771. It was the location of the First and Second Congress of Rastatt, the former giving rise to the Treaty of Rastatt while the second ended in failure in 1799. In the 1840s, Rastatt was surrounded by fortifications to form the fortress of Rastatt. For about 20 years previous to 1866, it was occupied by the troops of the German Confederation.
The Baden revolution of 1849 began with a mutiny of soldiers at Rastatt in May 1849 under Ludwik Mieroslawski and Gustav Struve, and ended there a few weeks later with the capture of the town by the Prussians. (See The Revolutions of 1848 in the German states and History of Baden.) For some years, Rastatt was one of the strongest fortresses of the German empire, but its fortifications were dismantled in 1890.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90130
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90163
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90150
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cpt R Delafield Large Antique Schematics 2nd Lancer Barracks Stables Berlin
- Title : Barrack and stables of the Lancers of the Guard at Berlin...Barrack of the Second Regiment of the Lancers of teh Guard at Berlin
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90142
- Size: 18 1/2in x 16in (470mm x 405mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of the 2nd German Lancer Regiment Barracks & Stables in Berlin - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 16in (470mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 16in (470mm x 405mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
A lancer was a type of cavalryman who fought with a lance. Lances were used in mounted warfare by the Assyrians as early as 700 BC and subsequently by Greek, Persian, Gallic, Chinese, and Roman horsemen. The weapon was widely used in Asia and Europe during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance by armoured cavalry, before being adopted by light cavalry, particularly in Eastern Europe. In a modern context, a lancer regiment usually denotes an armoured unit.
The lancer (called ułan in Polish and Uhlan in German) had become a common sight in almost every European, Ottoman, and Indian army during this time, but, with the exception of the Ottoman troops, they increasingly discarded the heavy armour to give greater freedom of movement in combat. The Polish winged lancers were amongst the last to abandon the armour in Europe. There was debate over the value of the lance in mounted combat during the 18th century and most armies had few lancer units by the beginning of the 19th century. However, during the Napoleonic Wars, lancers were to be seen in many of the combatant nations as their value in shock tactics became clear. During the wars, the Poles became a ready source of recruitment for several armies, willingly or unwillingly. Polish lancers served with distinction in the Austrian, Prussian, Russian and French armies, most famously in Napoleons French Imperial Guard as the 1er Regiment de Chevau-Legers-Lanciers de la Garde Impériale.
At the Battle of Waterloo, French lances were nearly three meters (about nine feet, ten inches) long, weighed three kilograms (about six pounds, ten ounces), and had a steel point on a wooden staff, according to historian Alessandro Barbero. He adds that they were terrifyingly efficient. Commander of the French 1st Corps, 4th Division General Durutte, who saw the battle from the high ground in front of Papelotte, would write later, I had never before realized the great superiority of the lance over the sword.
In the Siege of Los Angeles (1846), during the war between Mexico and the United States, a company of Californio lancers temporarily recaptured the town, expelling a company of U.S. Marines.
Although having substantial impact in the charge, lancers could be vulnerable to other cavalry at close quarters, where the lance proved a clumsy and easily deflected weapon when employed against sabres. By the late 19th century, many cavalry regiments in the British and other European armies were composed of troopers with lances, as primary weapons, in the front rank and horsemen with sabres only in the second: the lances for the initial shock and sabres for the subsequent mêlée.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.