Nicolas Tindal
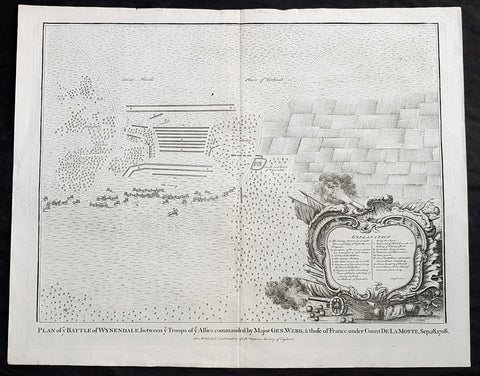
1745 N Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
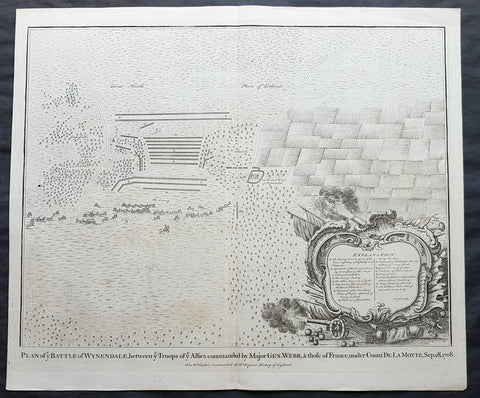
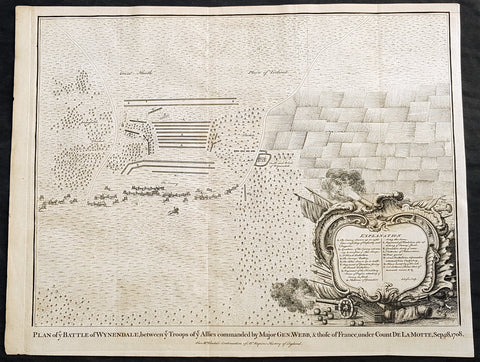
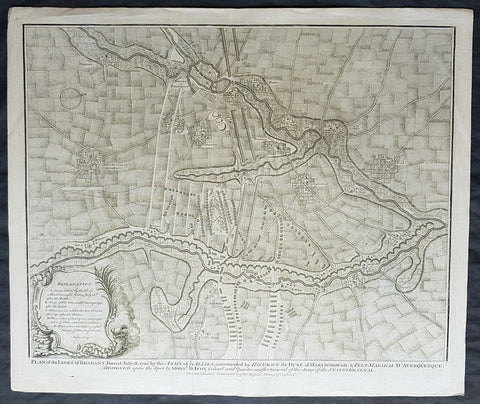
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 01-9034
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
1745 N Tindal Original Antique Map Siege of Douai, Flanders, North France in 1710
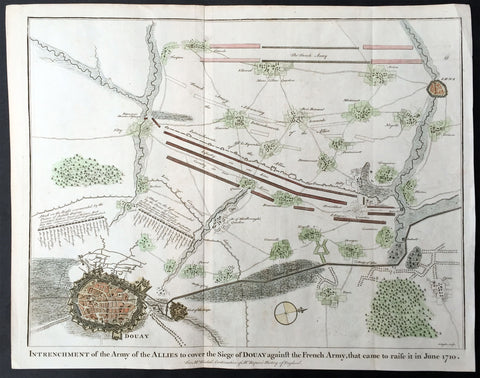
- Title : Intrenchment of the Army of the Allies to cover the Siege of Douay against the French Army that came to raise it in June 1710.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22212
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Siege of Douai, Flanders in Northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A large battle plan showing both siege and works against a fortified Douai, Flanders and the detailed dispositions and battle lines of Lord Marlborough\'s army against the French, and thier attempt to lift the siege in June 1710.
Successive sieges from 1710 to 1712 during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13), almost completely destroyed Douai by the British Army. By 1713, the town was fully integrated into France. Douai became the seat of the Parliament of Flanders.
1745 N Tindal Original Antique Map Siege of Douai, Flanders, North France in 1710
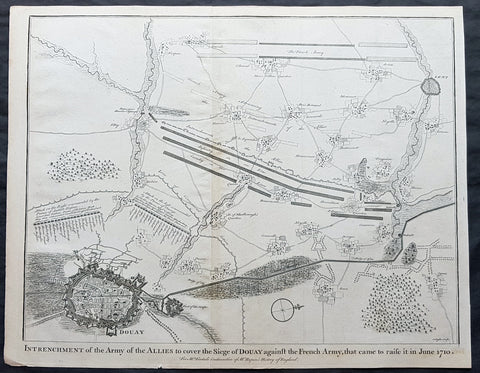
- Title : Intrenchment of the Army of the Allies to cover the Siege of Douay against the French Army that came to raise it in June 1710.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15654
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Siege of Douai, Flanders in Northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A large battle plan showing both siege and works against a fortified Douai, Flanders and the detailed dispositions and battle lines of Lord Marlborough\'s army against the French, and thier attempt to lift the siege in June 1710.
Successive sieges from 1710 to 1712 during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13), almost completely destroyed Douai by the British Army. By 1713, the town was fully integrated into France. Douai became the seat of the Parliament of Flanders.
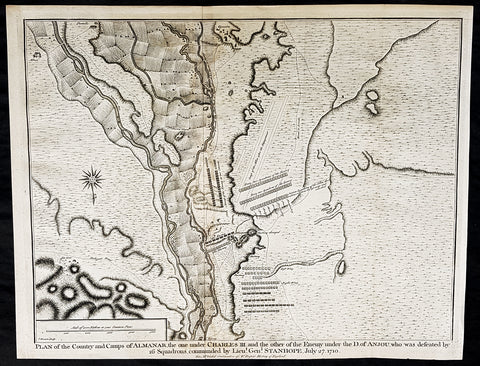
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map Battle of Almenar Balaguer, Catalonia, Spain
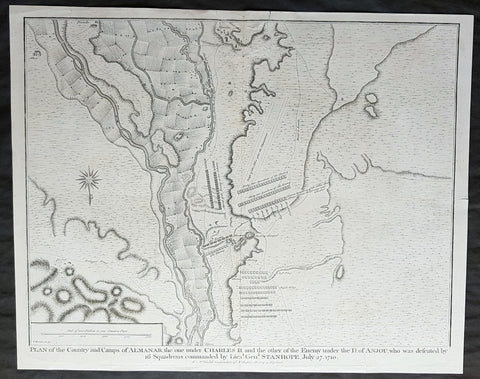
- Title : Plan of the Country and Camps of Almanar, the one under Charles II and the other of the Enemy under the D of Anjou who was defeated by 16 Squadrons commanded by Lieut. Gen. Stanhope, July 27 1710
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22174
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Almenar, near Balaguer, Catalonia, Spain in 1710 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - Repair to top of image, no loss
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Almenar took place on 27 July 1710 in the War of the Spanish Succession, between the troops of Phillip V and the Archduke Charles. Philip V\'s army having been defeated was forced to evacuate Catalonia and regroup behind the Ebro.
In spring of 1710, the Borbonic army had entered Catalonia from Aragón crossing the Segre river on March 15. On May 3, Philip V, the Borbon claimant to the throne, joined the army.
The opposing allied army, consisting of Austrian, British, and Dutch troops, was joined by Archduke Charles of Austria, the Habsburg claimant, in June.
In July, General Guido Starhemberg received reinforcements and decided to attack. He crossed the Noguera river taking up positions on the heights of Almenar.
Stanhope then crossed the Segre at Balaguer (north of Lerida) marching to the bridge of Alfarras, crossing it on 27 July.
Villadarias opened the battle with a cavalry attack which was initially successful, but the initiative was wasted by pursuing groups of fleeing enemies.
Then the British infantry attacked the left wing which fled, taking the second line with it. Then the Austrians attacked and destroyed the right wing, where Philip V risked his life fighting and was almost captured by the allies.
The Borbonic troops had to leave Catalonia and withdraw to Aragón, where the Battle of Saragossa took place on August 20.
Villadarias was relieved of his command and replaced by the Marquis de Bay.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map Battle of Almenar Balaguer, Catalonia, Spain
- Title : Plan of the Country and Camps of Almanar, the one under Charles II and the other of the Enemy under the D of Anjou who was defeated by 16 Squadrons commanded by Lieut. Gen. Stanhope, July 27 1710
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15653
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Almenar, near Balaguer, Catalonia, Spain in 1710 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - Repair to top of image, no loss
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Almenar took place on 27 July 1710 in the War of the Spanish Succession, between the troops of Phillip V and the Archduke Charles. Philip V\'s army having been defeated was forced to evacuate Catalonia and regroup behind the Ebro.
In spring of 1710, the Borbonic army had entered Catalonia from Aragón crossing the Segre river on March 15. On May 3, Philip V, the Borbon claimant to the throne, joined the army.
The opposing allied army, consisting of Austrian, British, and Dutch troops, was joined by Archduke Charles of Austria, the Habsburg claimant, in June.
In July, General Guido Starhemberg received reinforcements and decided to attack. He crossed the Noguera river taking up positions on the heights of Almenar.
Stanhope then crossed the Segre at Balaguer (north of Lerida) marching to the bridge of Alfarras, crossing it on 27 July.
Villadarias opened the battle with a cavalry attack which was initially successful, but the initiative was wasted by pursuing groups of fleeing enemies.
Then the British infantry attacked the left wing which fled, taking the second line with it. Then the Austrians attacked and destroyed the right wing, where Philip V risked his life fighting and was almost captured by the allies.
The Borbonic troops had to leave Catalonia and withdraw to Aragón, where the Battle of Saragossa took place on August 20.
Villadarias was relieved of his command and replaced by the Marquis de Bay.
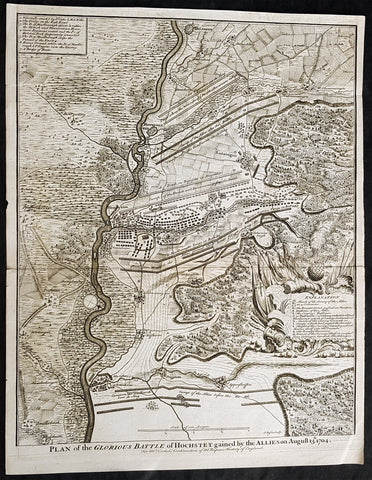
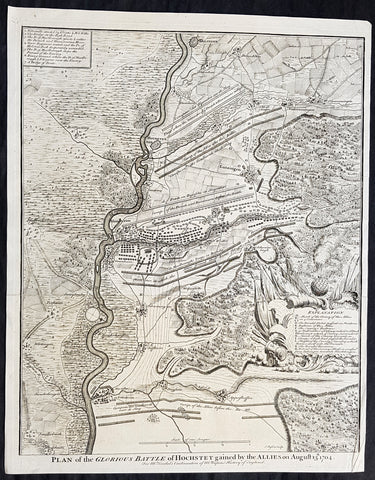
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map The Battle of Blenheim, Germany in 1704
- Title : Plan of the Glorious Battle of Hochstet gained by the Allies on August 13.th 1704.
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Ref #: 15692-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Blenheim or Hochstadt, fought in Bavaria, Germany in August 1704 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Blenheim (German: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt; French Bataille de Höchstädt), fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the Grand Alliance.
Louis XIV of France sought to knock the Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold out of the war by seizing Vienna, the Habsburg capital, and gain a favourable peace settlement. The dangers to Vienna were considerable: the Elector of Bavaria and Marshal Marsins forces in Bavaria threatened from the west, and Marshal Vendômes large army in northern Italy posed a serious danger with a potential offensive through the Brenner Pass. Vienna was also under pressure from Rákóczis Hungarian revolt from its eastern approaches. Realising the danger, the Duke of Marlborough resolved to alleviate the peril to Vienna by marching his forces south from Bedburg to help maintain Emperor Leopold within the Grand Alliance.
A combination of deception and skilled administration – designed to conceal his true destination from friend and foe alike – enabled Marlborough to march 400 kilometres (250 miles) unhindered from the Low Countries to the River Danube in five weeks. After securing Donauwörth on the Danube, Marlborough sought to engage the Electors and Marsins army before Marshal Tallard could bring reinforcements through the Black Forest. However, with the Franco-Bavarian commanders reluctant to fight until their numbers were deemed sufficient, the Duke enacted a policy of plundering in Bavaria designed to force the issue. The tactic proved unsuccessful, but when Tallard arrived to bolster the Electors army, and Prince Eugene arrived with reinforcements for the Allies, the two armies finally met on the banks of the Danube in and around the small village of Blindheim, from which the English Blenheim is derived.
Blenheim was one of the battles that altered the course of the war, which until then was leaning for Louis coalition, and ended French plans of knocking the Emperor out of the war. France suffered as many as 38,000 casualties including the commander-in-chief, Marshal Tallard, who was taken captive to England. Before the 1704 campaign ended, the Allies had taken Landau, and the towns of Trier and Trarbach on the Moselle in preparation for the following years campaign into France itself. The offensive never materialised as the Grand Alliances army had to depart the Moselle to defend Liège from a French counteroffensive. The war would rage on for another decade.
Tindal, Nicolas 1687 – 1774
Nicolas Tindal was the translator and continuer of the History of England published by Paul de Rapin (1661-1725) in 1724. De Rapins publication chronicles the History of Britain from the invasion of the Romans to the death of Charles I. Very few comprehensive histories of England existed at the time and Tindal added his three-volume Continuation, of the Kingdom, from the reigns of James II to George II.
Tindal\\\'s translation of de Rapins History, was first published in 1727. Tindal enlarged the volumes in their second edition (1732) to contain notes, genealogical tables and maps of his own composition. In 1745 Tindal published Tindal’s Continuation of Mr. Rapin’s History of England. Included with this edition was an atlas containing 45 maps, battle and town plans from the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) that were engraved by Richard William Seale and John Basire.
These maps represent battles that took place during the War of Spanish Succession, concluded by the Treaties of Utrecht. The war resulted from a dispute over who should inherit Spain and its possessions after its Habsburg rulers in 1700. The last Habsburg king of Spain, Charles II (d. 1700) had left the throne to his closest relative in female line: Philippe de France, duke of Anjou, grandson of Louis XIV (Felipe V of Spain). The closest relatives in male line, the Habsburgs of Austria, disputed this claim, and many European nations did not want to see French princes reigning over both kingdoms. The Utrecht treaties recognized Felipe V of Spain, but transferred the Spanish possessions in the Netherlands and Italy to Austria and to Savoy. To reach the goal of separating the crowns of France and Spain, the treaties required Felipe V to relinquish all claims to the French throne, and the remaining French princes to relinquish all claims to the Spanish throne.
The War of the Spanish Succession, was also known as Marlboroughs Wars, that was fought in Europe and the Mediterranean, and were the last and the bloodiest of the Wars between England and France under Louis XIV, and the first in which Britain played a major military role in European military affairs.
Paul de Rapin 1661-1725 was born in Castes and educated at the Protestant academy of Saumur. In 1685 after the death of his father he moved to England but after being unable to find employment moved to Holland and enlisted in French volunteers at Utrecht commanded by his cousin Daniel de Rapin. He accompanied the prince of Orange to England in 1688 and participated in the Irish campaigns of the siege of Carrickfergus, Battle of the Boyne and Limerick. Rapin resigned to become tutor to the Earl of Portlands son. He settled in Holland where he began work on The History of England. It was published in Holland in 1724 in 8 volumes. The work was an attempt to be exhaustive in the spirit of the eighteenth century philosophies by treating the subject from prehistoric times up to the date of publication.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map The Battle of Blenheim, Germany in 1704
- Title : Plan of the Glorious Battle of Hochstet gained by the Allies on August 13.th 1704.
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Ref #: 22178
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Blenheim or Hochstadt, fought in Bavaria, Germany in August 1704 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Blenheim (German: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt; French Bataille de Höchstädt), fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the Grand Alliance.
Louis XIV of France sought to knock the Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold out of the war by seizing Vienna, the Habsburg capital, and gain a favourable peace settlement. The dangers to Vienna were considerable: the Elector of Bavaria and Marshal Marsins forces in Bavaria threatened from the west, and Marshal Vendômes large army in northern Italy posed a serious danger with a potential offensive through the Brenner Pass. Vienna was also under pressure from Rákóczis Hungarian revolt from its eastern approaches. Realising the danger, the Duke of Marlborough resolved to alleviate the peril to Vienna by marching his forces south from Bedburg to help maintain Emperor Leopold within the Grand Alliance.
A combination of deception and skilled administration – designed to conceal his true destination from friend and foe alike – enabled Marlborough to march 400 kilometres (250 miles) unhindered from the Low Countries to the River Danube in five weeks. After securing Donauwörth on the Danube, Marlborough sought to engage the Electors and Marsins army before Marshal Tallard could bring reinforcements through the Black Forest. However, with the Franco-Bavarian commanders reluctant to fight until their numbers were deemed sufficient, the Duke enacted a policy of plundering in Bavaria designed to force the issue. The tactic proved unsuccessful, but when Tallard arrived to bolster the Electors army, and Prince Eugene arrived with reinforcements for the Allies, the two armies finally met on the banks of the Danube in and around the small village of Blindheim, from which the English Blenheim is derived.
Blenheim was one of the battles that altered the course of the war, which until then was leaning for Louis coalition, and ended French plans of knocking the Emperor out of the war. France suffered as many as 38,000 casualties including the commander-in-chief, Marshal Tallard, who was taken captive to England. Before the 1704 campaign ended, the Allies had taken Landau, and the towns of Trier and Trarbach on the Moselle in preparation for the following years campaign into France itself. The offensive never materialised as the Grand Alliances army had to depart the Moselle to defend Liège from a French counteroffensive. The war would rage on for another decade.
Tindal, Nicolas 1687 – 1774
Nicolas Tindal was the translator and continuer of the History of England published by Paul de Rapin (1661-1725) in 1724. De Rapins publication chronicles the History of Britain from the invasion of the Romans to the death of Charles I. Very few comprehensive histories of England existed at the time and Tindal added his three-volume Continuation, of the Kingdom, from the reigns of James II to George II.
Tindal\\\'s translation of de Rapins History, was first published in 1727. Tindal enlarged the volumes in their second edition (1732) to contain notes, genealogical tables and maps of his own composition. In 1745 Tindal published Tindal’s Continuation of Mr. Rapin’s History of England. Included with this edition was an atlas containing 45 maps, battle and town plans from the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) that were engraved by Richard William Seale and John Basire.
These maps represent battles that took place during the War of Spanish Succession, concluded by the Treaties of Utrecht. The war resulted from a dispute over who should inherit Spain and its possessions after its Habsburg rulers in 1700. The last Habsburg king of Spain, Charles II (d. 1700) had left the throne to his closest relative in female line: Philippe de France, duke of Anjou, grandson of Louis XIV (Felipe V of Spain). The closest relatives in male line, the Habsburgs of Austria, disputed this claim, and many European nations did not want to see French princes reigning over both kingdoms. The Utrecht treaties recognized Felipe V of Spain, but transferred the Spanish possessions in the Netherlands and Italy to Austria and to Savoy. To reach the goal of separating the crowns of France and Spain, the treaties required Felipe V to relinquish all claims to the French throne, and the remaining French princes to relinquish all claims to the Spanish throne.
The War of the Spanish Succession, was also known as Marlboroughs Wars, that was fought in Europe and the Mediterranean, and were the last and the bloodiest of the Wars between England and France under Louis XIV, and the first in which Britain played a major military role in European military affairs.
Paul de Rapin 1661-1725 was born in Castes and educated at the Protestant academy of Saumur. In 1685 after the death of his father he moved to England but after being unable to find employment moved to Holland and enlisted in French volunteers at Utrecht commanded by his cousin Daniel de Rapin. He accompanied the prince of Orange to England in 1688 and participated in the Irish campaigns of the siege of Carrickfergus, Battle of the Boyne and Limerick. Rapin resigned to become tutor to the Earl of Portlands son. He settled in Holland where he began work on The History of England. It was published in Holland in 1724 in 8 volumes. The work was an attempt to be exhaustive in the spirit of the eighteenth century philosophies by treating the subject from prehistoric times up to the date of publication.
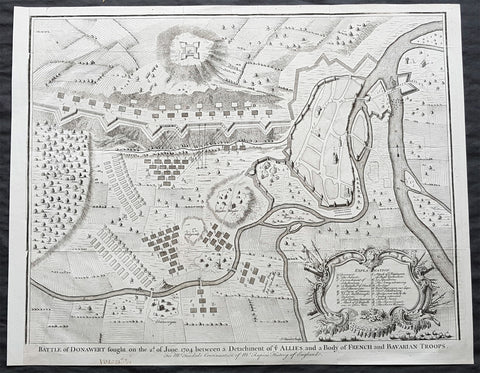
1745 Nicolas Tindal Large Antique Map The Battle of Schellenberg, Germany 1704
- Title : Battle of Donawert fought on the 2nd of June 1704 between a detachment of ye Allies and a body of French and Bavarian Troops
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 22160
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved military map of the Battle of Schellenberg, also known as the Battle of Donauwörth in the Donau-Ries district of Swabia, in Bavaria, Germany - during the Spanish War of Succession - was engraved by John Basire and published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
The Battle of Schellenberg, also known as the Battle of Donauwörth, was fought on 2 July 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The engagement was part of the Duke of Marlboroughs campaign to save the Habsburg capital of Vienna from a threatened advance by King Louis XIVs Franco-Bavarian forces ranged in southern Germany. Marlborough had commenced his 400 km march from Bedburg, near Cologne, on 19 May; within five weeks he had linked his forces with those of the Margrave of Baden, before continuing on to the river Danube. Once in southern Germany, the Allies task was to induce Max Emanuel, the Elector of Bavaria, to abandon his allegiance to Louis XIV and rejoin the Grand Alliance; but to force the issue, the Allies first needed to secure a fortified bridgehead and magazine on the Danube, through which their supplies could cross to the south of the river into the heart of the Electors lands. For this purpose, Marlborough selected the town of Donauwörth.
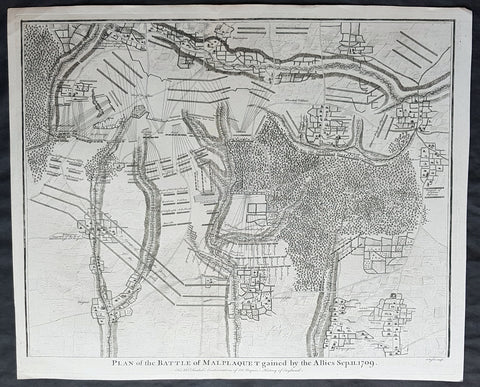
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22173
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
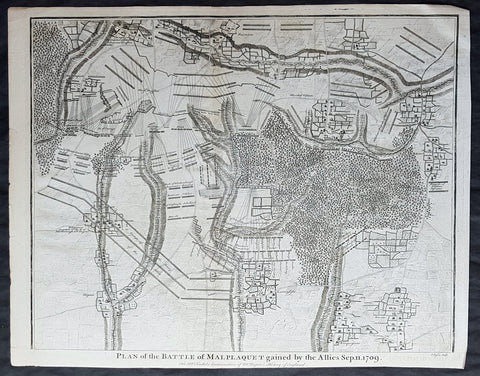
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15659
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
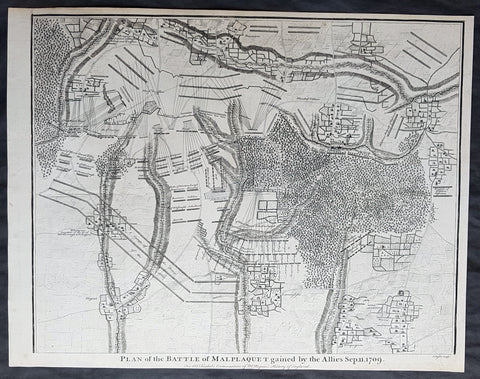
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22154
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22165
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15662
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
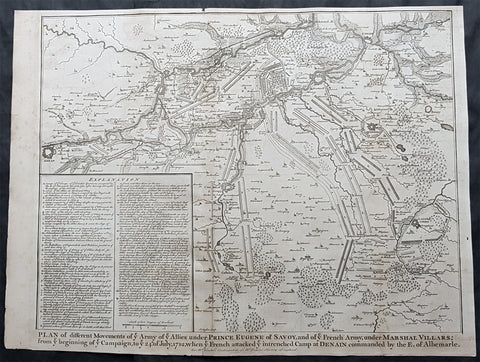
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle Plan of Denain, France in 1712
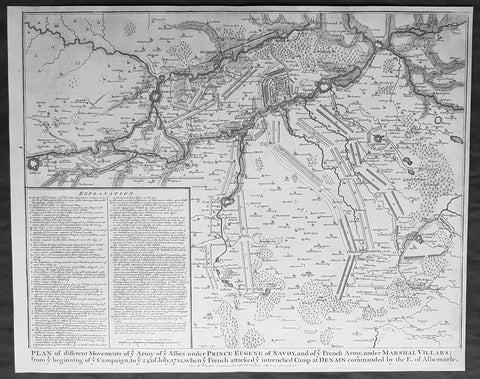
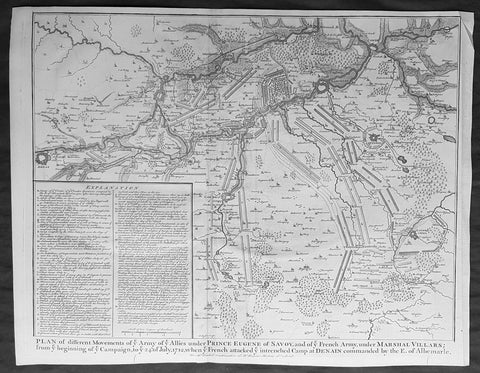
- Title : Plan of the movements of ye Armies of ye Allies under Prince Eugene of Savoy and of ye French Army under Marshal Villars; from ye beginning of ye campaign to ye 24th July 1712, when ye French attacked ye intrenchement Camp at Denain commanded by the E. of Albemarle
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22155
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan of the Battle of Denain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - centering on the cities of Douai & Bouchain in northern France, was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Denain was fought on 24 July 1712, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in a French victory under Marshal Villars against Dutch and Austrian forces under Prince Eugene of Savoy.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle Plan of Denain, France in 1712
- Title : Plan of the movements of ye Armies of ye Allies under Prince Eugene of Savoy and of ye French Army under Marshal Villars; from ye beginning of ye campaign to ye 24th July 1712, when ye French attacked ye intrenchement Camp at Denain commanded by the E. of Albemarle
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15689
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan of the Battle of Denain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - centering on the cities of Douai & Bouchain in northern France, was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Denain was fought on 24 July 1712, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in a French victory under Marshal Villars against Dutch and Austrian forces under Prince Eugene of Savoy.
1745 Tindal Antique Battle Map of Oudenaarde, Belgium in 1708 - Britain & France
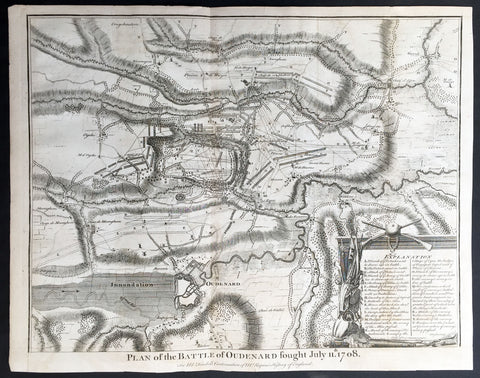
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Oudenard fought July 11th 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15661
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the Battle of Oudenard or Oudenaarde, in Flemish Belgium, in 1708 between Britain & its allies and France and its allies - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Oudenarde (or Oudenaarde) was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 11 July 1708 between the forces of Great Britain, the Dutch Republic and the Holy Roman Empire on the one side and those of France on the other. It took place at Oudenaarde (now in Belgium) and was a great victory for the allies.
Great Britain, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire were horrified at the thought of a union between Spain and France which caused them to ally against France, beginning the War of the Spanish Succession. The commander of the allied armies was John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, whose chief deputy was the commander of the Empire\'s army Prince Eugène of Savoy, who was his close friend.
Meanwhile, the two French army commanders were very quarrelsome. Louis Joseph, duc de Vendôme was a seasoned, experienced soldier. The Duke of Burgundy had considerably less experience and owed his position to the fact he was the grandson of the King, Louis XIV of France.
Marlborough\'s army consisted of about 80,000 men (113 infantry battalions and 180 cavalry squadrons) just south of Brussels. Eugène\'s forces were assembled at Coblenz. These two areas were somewhat far apart, while the French army\'s 85,000 soldiers (139 battalions and 204 squadrons) were concentrated near Mons.
At this time, the French commanders began quarrelling. Vendôme wanted to attack the city of Huy, which could draw Marlborough in pursuit. The eventual plan adopted, however, (under orders from Louis XIV) was to attack Flanders. The army moved eastward, until they reached the city of Braine-l\'Alleud, which was about 25 km south of Brussels, and also threatened the nearby city of Leuven. Marlborough placed his forces a few miles south of Leuven, in order to cover both threatened cities.
The French army then remained inactive for more than a month. This apparently allowed the extremely behind schedule Eugène to bring his army from the Rhine River. On 5 July, however, the French unexpectedly moved west, taking the cities of Bruges and Ghent (although about 300 British soldiers held out in Ghent for a few days). This extremely demoralized Marlborough and his army, and he did not recover until Eugène was at his side.
The French army had the entire length of the Scheldt River from the French border to the newly taken city of Ghent. Only one British fortress remained: Oudenaarde. If they took that city, Marlborough\'s army would be cut off from the coast, causing them to lose communications with England.
Marlborough detected this objective, and also correctly guessed the method by which the French troops would attempt to take it. They would march down the east bank of the Scheldt (closer to Marlborough\'s troops), while leaving a large covering force between the two opposing armies. The French army marched on 8 July, toward the city of Lessines. However, Marlborough made one of the most inspired forced marches in history, taking the city on 10 July. This forced the French commanders to attempt simply to march across the Scheldt and thereby take the city of Oudenaarde.
Again Marlborough ordered a forced march. This time, though, he ordered 11,000 troops to hold the main crossing point across the Scheldt, under the command of his Quartermaster General, William Cadogan. Cadogan\'s force built 5 additional pontoon bridges to allow Marlborough to get his 80,000-strong army across the river, until French foragers discovered the allied presence around 09:00 AM.
Cadogan, a superb Irish cavalry commander, ordered some dragoons, under Danish General Jørgen Rantzau, to take prisoners from the French advance guard. Many of those troops escaped and alerted Lieutenant General Charles-Armand de Gontaut, duc de Biron, who commanded the vanguard, of the presence of Allied troops on the west bank.
When de Biron advanced, he was disagreeably surprised by the large number of Allied cavalry already across the river, along with the approaching Allied infantry. Although he was ordered to attack by Vendôme, he hesitated upon seeing the reinforced line of 20 battalions (including the four that had been left to guard the pontoon bridges). Biron\'s own forces comprised only 7 battalions and 20 squadrons. He had been given reliable advice that cavalry could not negotiate the marshy terrain in the area and decided not to attempt a crossing. At this time, Eugène, along with 20 squadrons of Prussian cavalry, moved across the river and occupied crucial positions.
While Biron\'s troops were manoeuvring, the leading British infantry brigade had arrived, under the inexperienced but gifted John Campbell, 2nd Duke of Argyll. Cadogan, with authority from Marlborough, attacked Biron\'s 7 battalions (of Swiss mercenaries) with his soldiers (mainly cavalry). The isolated Swiss mercenaries were immediately pushed back and the Allied force destroyed Biron\'s squadrons, until they reached a large mass of French cavalry, at which point they were forced to retire, outnumbered. The force which performed this action was Rantzau\'s cavalry, with the future King George II of England among them.
Burgundy, making another mistake, decided to attack (over protests by Vendôme). The French right wing began to attack the Allied positions near Eine, while the left wing (for an unknown reason) remained stationary near Huise. A very strong position was held by the Allied left wing. 28 cavalry squadrons protected the right flank of Cadogan\'s infantry, which would receive the attack (which proceeded at about 4:00 p.m.).
Burgundy ordered the assault, which landed on Prussian cavalry squadrons under Dubislav Gneomar von Natzmer. Although hard fighting ensued, the attack was dispersed. Then, Vendôme made a dubious decision and led an attack of twelve regiments, fighting hand-to-hand with a half-pike. This meant that while one commander (Burgundy) was in his headquarters, with no view of the battle, the other was fighting, with no possibility of control.
Most historians agree that the weakened Allied right flank would have been destroyed, had the French left wing attacked. Vendôme realized this, asking Burgundy for permission to attack with the left wing. Burgundy sent a messenger with a refusal but the messenger failed to deliver the message. The situation worsened with Vendôme believing that an attack would support his troops, who were lengthening their line, threatening to envelop the Allied left flank. As Argyll\'s regiments approached, they lengthened the Allied line but too slowly and not great enough in extent, to prevent the French from threatening such an envelopment.
Marlborough moved his headquarters to the left flank, giving Eugène command of the right flank (which still checked the left wing of the French army). While the right was under pressure, Marlborough made a brilliant command decision: he placed 18 newly arrived Hessian and Hanoverian battalions in the left flank, while replacing 20 of Prussian General Carl von Lottum\'s battalions, moving them to Eugène\'s support. This moved fresh troops to the critical left, while reinforcing the right flank (and resting Lottum\'s troops). Marlborough then began formulating a new plan of double encirclement. He had the entire Dutch Army, under Field Marshal Count Hendrik Overkirk, an experienced military officer. His force was unable to cross the collapsed pontoon bridges near Oudenaarde, forcing him to use the stone bridges in the city, delaying him for an hour. Marlborough went ahead with his plan, having Eugène\'s cavalry charge towards Burgundy\'s headquarters. The French Household Cavalry, the Maison du Roi, were able to turn them back and Marlborough, with only the 18 Hessian and Hanoverian battalions, was unable to do much other than keep the French right in check. At about 20:30, Overkirk\'s troops had arrived and flanked the French right wing. This was in conjunction with a dual attack by Marlborough and Eugène. Overkirk\'s manoeuvre was successful, with much of the French army being routed or captured but there was not enough daylight to complete the manoeuvre.
The French army retired to Ghent, with its commanders quarreling; only darkness and a few broken pontoon bridges saved the army from destruction. For unknown reasons, about half of the French army was kept in reserve, without participating at all. There was a great mass of French cavalry and infantry in some raised ground north of the Norken River and many of Burgundy\'s troops remained inactive. There were many bad decisions in the French army. The cavalry had remained in reserve, mainly because of the advice that the ground was impassable. The entire left wing (the troops under Burgundy and the large mass north of the Norken) was kept in reserve. They could easily have destroyed the rather weak right wing of the Allied army. Had a concerted attack been carried out, with Vendôme attacking with his main body to envelop the Allied right, while Burgundy attacked with the left (before Overkirk and the rest of Argyll\'s troops arrived), the French army could have easily won. The French army lost about 14–15,000 soldiers (about 8,000 of whom were prisoners) and 25 guns, while the Allies lost fewer than 3,000.
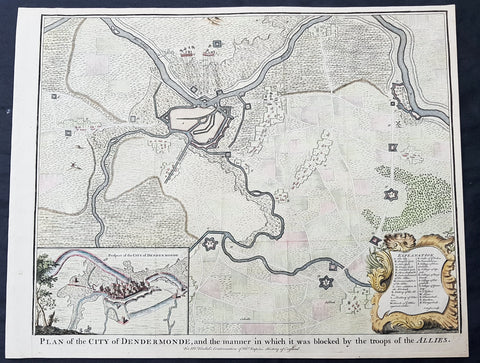
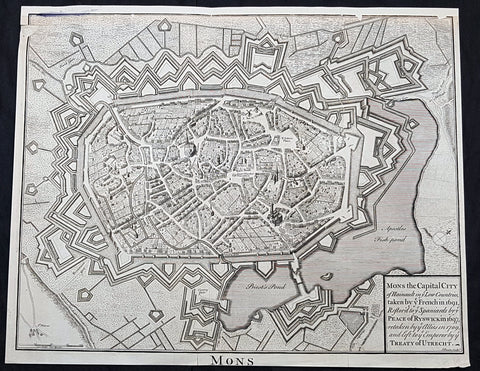
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan & View Siege of Dendermonde, Belgium in 1706
- Title : Plan of the City of Dendermonde, and the manner in which it was blocked by the troops of the Allies
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22157
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the Belgium city of Dendermonde and surrounding regions during the siege of Dendermonde in 1706 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Dendermonde is a Belgian city and municipality located in the Flemish province of East Flanders in the Denderstreek. The municipality comprises the city of Dendermonde proper and the towns of Appels, Baasrode, Grembergen, Mespelare, Oudegem, Schoonaarde, and Sint-Gillis-bij-Dendermonde. Dendermonde is located at the mouth of the river Dender, where it flows into the Scheldt. The town has a long-standing (folkloric) feud with Aalst (situated south along the same river), which dates back from the Middle Ages.
The city is an administrative, commercial, educational, and medical centre for the surrounding region. The current Mayor of Dendermonde is Piet Buyse (Christian Democratic and Flemish).
Some interesting La-Tène artifacts were found in Appels, proof that this region of the Scheldt was inhabited in prehistory. Grave sites from the 2nd and 6th century also attest to dense settlement in Gallo-Roman and Merovingian times. In 843, the Treaty of Verdun placed Dendermonde in Lotharingia. After the Norman invasions of 883, however, Baldwin II took over the region and incorporated it into the German part of the newly founded County of Flanders.
Otto II built a fort here in the 10th century, encouraging further settlements in the area. The town received its city charter in 1233 and grew quickly after that thanks to a thriving cloth industry. Several cloisters, chapels and churches, and a fortified defensive wall were built as well. A cloth hall and belfry were erected on the market square in the mid 14th century. The town’s prosperity, however, gave rise to severe competition with cities such as Ghent and to occasional attacks and plunders by neighbours. In 1384, the whole area came under the control of the Valois dukes of Burgundy.
The 16th century saw a decline in Dendermonde’s fortunes. In 1572 Dendermonde was conquered by William the Silent. The same year however Spanish troops under Duke Alexander Farnese of Parma, took over the city, looted and mostly destroyed it. A decade later, the Spaniards built their own fortress between the Dender and the Scheldt. In 1667, it was France’s turn to advance on the city, but the allied troops of the Netherlands and England, under the Duke of Marlborough, caused the heaviest damage in 1706. The city was then fortified by the Austrians against further French ambitions. After a last siege by Louis XV, the city could finally breathe to the point that the fortifications were dismantled a few decades later.
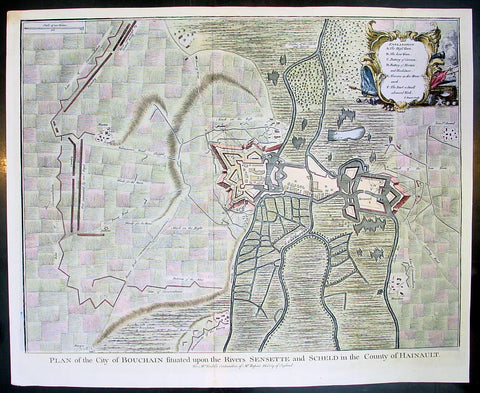
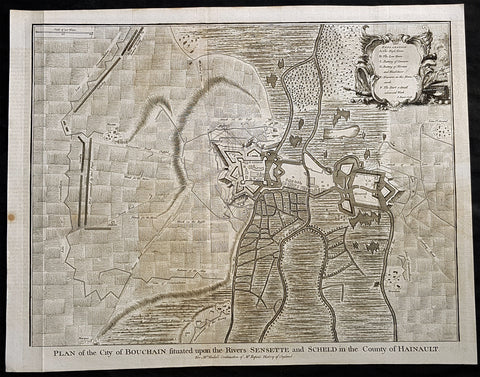
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22198
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
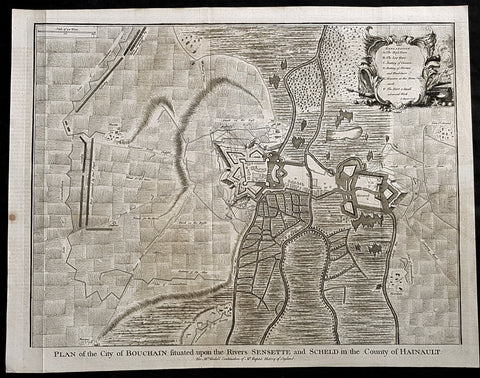
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22198
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
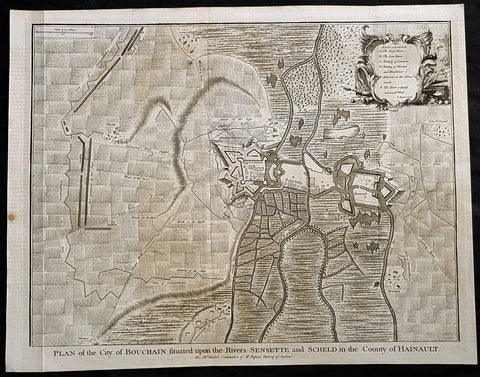
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22156-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22156-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
1745 Tindal Antique Map of France during the Spanish War of Succession 1701-13
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Oudenard fought July 11th 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15661
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the Battle of Oudenard or Oudenaarde, in Flemish Belgium, in 1708 between Britain & its allies and France and its allies - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Oudenarde (or Oudenaarde) was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 11 July 1708 between the forces of Great Britain, the Dutch Republic and the Holy Roman Empire on the one side and those of France on the other. It took place at Oudenaarde (now in Belgium) and was a great victory for the allies.
Great Britain, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire were horrified at the thought of a union between Spain and France which caused them to ally against France, beginning the War of the Spanish Succession. The commander of the allied armies was John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, whose chief deputy was the commander of the Empire\'s army Prince Eugène of Savoy, who was his close friend.
Meanwhile, the two French army commanders were very quarrelsome. Louis Joseph, duc de Vendôme was a seasoned, experienced soldier. The Duke of Burgundy had considerably less experience and owed his position to the fact he was the grandson of the King, Louis XIV of France.
Marlborough\'s army consisted of about 80,000 men (113 infantry battalions and 180 cavalry squadrons) just south of Brussels. Eugène\'s forces were assembled at Coblenz. These two areas were somewhat far apart, while the French army\'s 85,000 soldiers (139 battalions and 204 squadrons) were concentrated near Mons.
At this time, the French commanders began quarrelling. Vendôme wanted to attack the city of Huy, which could draw Marlborough in pursuit. The eventual plan adopted, however, (under orders from Louis XIV) was to attack Flanders. The army moved eastward, until they reached the city of Braine-l\'Alleud, which was about 25 km south of Brussels, and also threatened the nearby city of Leuven. Marlborough placed his forces a few miles south of Leuven, in order to cover both threatened cities.
The French army then remained inactive for more than a month. This apparently allowed the extremely behind schedule Eugène to bring his army from the Rhine River. On 5 July, however, the French unexpectedly moved west, taking the cities of Bruges and Ghent (although about 300 British soldiers held out in Ghent for a few days). This extremely demoralized Marlborough and his army, and he did not recover until Eugène was at his side.
The French army had the entire length of the Scheldt River from the French border to the newly taken city of Ghent. Only one British fortress remained: Oudenaarde. If they took that city, Marlborough\'s army would be cut off from the coast, causing them to lose communications with England.
Marlborough detected this objective, and also correctly guessed the method by which the French troops would attempt to take it. They would march down the east bank of the Scheldt (closer to Marlborough\'s troops), while leaving a large covering force between the two opposing armies. The French army marched on 8 July, toward the city of Lessines. However, Marlborough made one of the most inspired forced marches in history, taking the city on 10 July. This forced the French commanders to attempt simply to march across the Scheldt and thereby take the city of Oudenaarde.
Again Marlborough ordered a forced march. This time, though, he ordered 11,000 troops to hold the main crossing point across the Scheldt, under the command of his Quartermaster General, William Cadogan. Cadogan\'s force built 5 additional pontoon bridges to allow Marlborough to get his 80,000-strong army across the river, until French foragers discovered the allied presence around 09:00 AM.
Cadogan, a superb Irish cavalry commander, ordered some dragoons, under Danish General Jørgen Rantzau, to take prisoners from the French advance guard. Many of those troops escaped and alerted Lieutenant General Charles-Armand de Gontaut, duc de Biron, who commanded the vanguard, of the presence of Allied troops on the west bank.
When de Biron advanced, he was disagreeably surprised by the large number of Allied cavalry already across the river, along with the approaching Allied infantry. Although he was ordered to attack by Vendôme, he hesitated upon seeing the reinforced line of 20 battalions (including the four that had been left to guard the pontoon bridges). Biron\'s own forces comprised only 7 battalions and 20 squadrons. He had been given reliable advice that cavalry could not negotiate the marshy terrain in the area and decided not to attempt a crossing. At this time, Eugène, along with 20 squadrons of Prussian cavalry, moved across the river and occupied crucial positions.
While Biron\'s troops were manoeuvring, the leading British infantry brigade had arrived, under the inexperienced but gifted John Campbell, 2nd Duke of Argyll. Cadogan, with authority from Marlborough, attacked Biron\'s 7 battalions (of Swiss mercenaries) with his soldiers (mainly cavalry). The isolated Swiss mercenaries were immediately pushed back and the Allied force destroyed Biron\'s squadrons, until they reached a large mass of French cavalry, at which point they were forced to retire, outnumbered. The force which performed this action was Rantzau\'s cavalry, with the future King George II of England among them.
Burgundy, making another mistake, decided to attack (over protests by Vendôme). The French right wing began to attack the Allied positions near Eine, while the left wing (for an unknown reason) remained stationary near Huise. A very strong position was held by the Allied left wing. 28 cavalry squadrons protected the right flank of Cadogan\'s infantry, which would receive the attack (which proceeded at about 4:00 p.m.).
Burgundy ordered the assault, which landed on Prussian cavalry squadrons under Dubislav Gneomar von Natzmer. Although hard fighting ensued, the attack was dispersed. Then, Vendôme made a dubious decision and led an attack of twelve regiments, fighting hand-to-hand with a half-pike. This meant that while one commander (Burgundy) was in his headquarters, with no view of the battle, the other was fighting, with no possibility of control.
Most historians agree that the weakened Allied right flank would have been destroyed, had the French left wing attacked. Vendôme realized this, asking Burgundy for permission to attack with the left wing. Burgundy sent a messenger with a refusal but the messenger failed to deliver the message. The situation worsened with Vendôme believing that an attack would support his troops, who were lengthening their line, threatening to envelop the Allied left flank. As Argyll\'s regiments approached, they lengthened the Allied line but too slowly and not great enough in extent, to prevent the French from threatening such an envelopment.
Marlborough moved his headquarters to the left flank, giving Eugène command of the right flank (which still checked the left wing of the French army). While the right was under pressure, Marlborough made a brilliant command decision: he placed 18 newly arrived Hessian and Hanoverian battalions in the left flank, while replacing 20 of Prussian General Carl von Lottum\'s battalions, moving them to Eugène\'s support. This moved fresh troops to the critical left, while reinforcing the right flank (and resting Lottum\'s troops). Marlborough then began formulating a new plan of double encirclement. He had the entire Dutch Army, under Field Marshal Count Hendrik Overkirk, an experienced military officer. His force was unable to cross the collapsed pontoon bridges near Oudenaarde, forcing him to use the stone bridges in the city, delaying him for an hour. Marlborough went ahead with his plan, having Eugène\'s cavalry charge towards Burgundy\'s headquarters. The French Household Cavalry, the Maison du Roi, were able to turn them back and Marlborough, with only the 18 Hessian and Hanoverian battalions, was unable to do much other than keep the French right in check. At about 20:30, Overkirk\'s troops had arrived and flanked the French right wing. This was in conjunction with a dual attack by Marlborough and Eugène. Overkirk\'s manoeuvre was successful, with much of the French army being routed or captured but there was not enough daylight to complete the manoeuvre.
The French army retired to Ghent, with its commanders quarreling; only darkness and a few broken pontoon bridges saved the army from destruction. For unknown reasons, about half of the French army was kept in reserve, without participating at all. There was a great mass of French cavalry and infantry in some raised ground north of the Norken River and many of Burgundy\'s troops remained inactive. There were many bad decisions in the French army. The cavalry had remained in reserve, mainly because of the advice that the ground was impassable. The entire left wing (the troops under Burgundy and the large mass north of the Norken) was kept in reserve. They could easily have destroyed the rather weak right wing of the Allied army. Had a concerted attack been carried out, with Vendôme attacking with his main body to envelop the Allied right, while Burgundy attacked with the left (before Overkirk and the rest of Argyll\'s troops arrived), the French army could have easily won. The French army lost about 14–15,000 soldiers (about 8,000 of whom were prisoners) and 25 guns, while the Allies lost fewer than 3,000.
1745 Tindal Antique Map of Spanish & Austrian Armies in Catalonia Spain in 1711
- Title : Plan of the Incampment of the Allies at Prats Del Rey. under the command of Count Staremberg and of ye Enemy under the Duke of Vendsome: wher ye two Armies lay from ye 17th of September to ye 25th of December 1711 N.S. when ye Enemy decamped and ye Allies the 27th.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15687
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the encampments of the Spanish army under Louis-Joseph, duke de Vendome & the Austrian Army under Count Guido Starhemberg in Prado Del Rey in Catalonia, Spain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Duke Louis-Joseph de Vendome , 1654 — 1712 was one of King Louis XIV’s leading generals during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–14).
Vendome was the son of Louis de Vendome, Duke de Mercoeur, by his marriage to Cardinal Jules Mazarin’s niece, Laure Mancini. Vendôme entered the French Army in 1672 and had risen to the rank of lieutenant general by the outbreak of the War of the Grand Alliance (1689–97) between France and the other major powers. He distinguished himself in the victory over the Allies at Steenkirke (1692) and was made commander in Catalonia in 1695; two years later he captured Barcelona.
The dispute over the succession to the Spanish throne brought France and Spain to war with the British, the Austrians, and the Dutch in 1701. Appointed to the command in northern Italy in 1702, Vendôme fought the Austrian commander, Prince Eugene of Savoy, in the bloody but indecisive Battle of Luzzara on August 15. He took Vercelli in 1704 and defeated Prince Eugene at Cassano in August 1705. In May 1706 Vendôme was transferred to the Flanders front, where the British commander John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, had just won an overwhelming victory at Ramillies. Vendôme made limited gains until he was severely defeated by Marlborough and Prince Eugene at Oudenaarde on July 11, 1708. Vendôme subsequently failed to relieve besieged Lille (in northern France), which fell to the Allies in October. Recalled by Louis XIV, he was temporarily disgraced.
Guido Wald Rüdiger, count of Starhemberg1657 – 1737 was an Austrian military officer.
He was a cousin of Ernst Rudiger von Starhemberg (1638-1701), the famous commander of Vienna during the Turkish siege of 1683, and acted as his aide-de-camp during that siege. Guido followed his cousin, and later Prince Eugene of Savoy, in battles against the Turks.
In the War of the Spanish Succession, Starhemberg fought in Italy and Spain. Between 1706 and 1708 he was the commander-in-chief of the imperial army in Hungary, leading military operations against the insurgents of Francis II Rákóczi. In 1708, he was appointed Supreme Commander of the Austrians in Spain.
Together with James Stanhope he succeeded in conquering Madrid in 1710, after previously gaining victories at Almenar and Saragossa. In December, however, he was forced to leave the city by the lack of support by its inhabitants for the Habsburg pretender. After the subsequent defeats at the Battle of Brihuega and the Battle of Villaviciosa (1710), he had to pull back to Catalonia, where he was made viceroy when Archduke Charles returned to Austria.
After the Peace of Utrecht (1713), archduke Charles, now Emperor Charles VI, ordered him to abandon Catalonia. He pulled back with his troops to Genoa on English ships.
When he died in 1737, he was Governor of Slavonia
1745 Tindal Antique Map of Spanish & Austrian Armies in Catalonia Spain in 1711
- Title : Plan of the Incampment of the Allies at Prats Del Rey. under the command of Count Staremberg and of ye Enemy under the Duke of Vendsome: wher ye two Armies lay from ye 17th of September to ye 25th of December 1711 N.S. when ye Enemy decamped and ye Allies the 27th.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15657
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the encampments of the Spanish army under Louis-Joseph, duke de Vendome & the Austrian Army under Count Guido Starhemberg in Prado Del Rey in Catalonia, Spain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Duke Louis-Joseph de Vendome , 1654 — 1712 was one of King Louis XIV’s leading generals during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–14).
Vendome was the son of Louis de Vendome, Duke de Mercoeur, by his marriage to Cardinal Jules Mazarin’s niece, Laure Mancini. Vendôme entered the French Army in 1672 and had risen to the rank of lieutenant general by the outbreak of the War of the Grand Alliance (1689–97) between France and the other major powers. He distinguished himself in the victory over the Allies at Steenkirke (1692) and was made commander in Catalonia in 1695; two years later he captured Barcelona.
The dispute over the succession to the Spanish throne brought France and Spain to war with the British, the Austrians, and the Dutch in 1701. Appointed to the command in northern Italy in 1702, Vendôme fought the Austrian commander, Prince Eugene of Savoy, in the bloody but indecisive Battle of Luzzara on August 15. He took Vercelli in 1704 and defeated Prince Eugene at Cassano in August 1705. In May 1706 Vendôme was transferred to the Flanders front, where the British commander John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, had just won an overwhelming victory at Ramillies. Vendôme made limited gains until he was severely defeated by Marlborough and Prince Eugene at Oudenaarde on July 11, 1708. Vendôme subsequently failed to relieve besieged Lille (in northern France), which fell to the Allies in October. Recalled by Louis XIV, he was temporarily disgraced.
Guido Wald Rüdiger, count of Starhemberg1657 – 1737 was an Austrian military officer.
He was a cousin of Ernst Rudiger von Starhemberg (1638-1701), the famous commander of Vienna during the Turkish siege of 1683, and acted as his aide-de-camp during that siege. Guido followed his cousin, and later Prince Eugene of Savoy, in battles against the Turks.
In the War of the Spanish Succession, Starhemberg fought in Italy and Spain. Between 1706 and 1708 he was the commander-in-chief of the imperial army in Hungary, leading military operations against the insurgents of Francis II Rákóczi. In 1708, he was appointed Supreme Commander of the Austrians in Spain.
Together with James Stanhope he succeeded in conquering Madrid in 1710, after previously gaining victories at Almenar and Saragossa. In December, however, he was forced to leave the city by the lack of support by its inhabitants for the Habsburg pretender. After the subsequent defeats at the Battle of Brihuega and the Battle of Villaviciosa (1710), he had to pull back to Catalonia, where he was made viceroy when Archduke Charles returned to Austria.
After the Peace of Utrecht (1713), archduke Charles, now Emperor Charles VI, ordered him to abandon Catalonia. He pulled back with his troops to Genoa on English ships.
When he died in 1737, he was Governor of Slavonia
1745 Tindal Antique Map of Spanish & Austrian Armies in Catalonia Spain in 1711
- Title : Plan of the Incampment of the Allies at Prats Del Rey. under the command of Count Staremberg and of ye Enemy under the Duke of Vendsome: wher ye two Armies lay from ye 17th of September to ye 25th of December 1711 N.S. when ye Enemy decamped and ye Allies the 27th.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 16430
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the encampments of the Spanish army under Louis-Joseph, duke de Vendome & the Austrian Army under Count Guido Starhemberg in Prado Del Rey in Catalonia, Spain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Duke Louis-Joseph de Vendome , 1654 — 1712 was one of King Louis XIV’s leading generals during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–14).
Vendome was the son of Louis de Vendome, Duke de Mercoeur, by his marriage to Cardinal Jules Mazarin’s niece, Laure Mancini. Vendôme entered the French Army in 1672 and had risen to the rank of lieutenant general by the outbreak of the War of the Grand Alliance (1689–97) between France and the other major powers. He distinguished himself in the victory over the Allies at Steenkirke (1692) and was made commander in Catalonia in 1695; two years later he captured Barcelona.
The dispute over the succession to the Spanish throne brought France and Spain to war with the British, the Austrians, and the Dutch in 1701. Appointed to the command in northern Italy in 1702, Vendôme fought the Austrian commander, Prince Eugene of Savoy, in the bloody but indecisive Battle of Luzzara on August 15. He took Vercelli in 1704 and defeated Prince Eugene at Cassano in August 1705. In May 1706 Vendôme was transferred to the Flanders front, where the British commander John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, had just won an overwhelming victory at Ramillies. Vendôme made limited gains until he was severely defeated by Marlborough and Prince Eugene at Oudenaarde on July 11, 1708. Vendôme subsequently failed to relieve besieged Lille (in northern France), which fell to the Allies in October. Recalled by Louis XIV, he was temporarily disgraced.
Guido Wald Rüdiger, count of Starhemberg1657 – 1737 was an Austrian military officer.
He was a cousin of Ernst Rudiger von Starhemberg (1638-1701), the famous commander of Vienna during the Turkish siege of 1683, and acted as his aide-de-camp during that siege. Guido followed his cousin, and later Prince Eugene of Savoy, in battles against the Turks.
In the War of the Spanish Succession, Starhemberg fought in Italy and Spain. Between 1706 and 1708 he was the commander-in-chief of the imperial army in Hungary, leading military operations against the insurgents of Francis II Rákóczi. In 1708, he was appointed Supreme Commander of the Austrians in Spain.
Together with James Stanhope he succeeded in conquering Madrid in 1710, after previously gaining victories at Almenar and Saragossa. In December, however, he was forced to leave the city by the lack of support by its inhabitants for the Habsburg pretender. After the subsequent defeats at the Battle of Brihuega and the Battle of Villaviciosa (1710), he had to pull back to Catalonia, where he was made viceroy when Archduke Charles returned to Austria.
After the Peace of Utrecht (1713), archduke Charles, now Emperor Charles VI, ordered him to abandon Catalonia. He pulled back with his troops to Genoa on English ships.
When he died in 1737, he was Governor of Slavonia
1745 Tindal Large Original Antique Map Battle Plan of Denain, France in 1712
- Title : Plan of the movements of ye Armies of ye Allies under Prince Eugene of Savoy and of ye French Army under Marshal Villars; from ye beginning of ye campaign to ye 24th July 1712, when ye French attacked ye intrenchement Camp at Denain commanded by the E. of Albemarle
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 15655
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan of the Battle of Denain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - centering on the cities of Douai & Bouchain in northern France, was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
The Battle of Denain was fought on 24 July 1712, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in a French victory under Marshal Villars against Dutch and Austrian forces under Prince Eugene of Savoy.
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Birds Eye View City of Mons, Walloon, Belgium
- Title : Mons the capital city of Hainault in ye French in 1691,restor.d to ye Spaniards by ye Peace of Ryswick in 1697,retaken by ye Allies in 1709 and left to ye Emperor by ye Treaty of Utrecht
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 91299
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map a Bird Eye View of the city of Mons, Belgium - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin restored, smudge along top left border
Plate area: - Small loss to left of image
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Mons is a Walloon city and municipality, and the capital of the Belgian province of Hainaut. The Mons municipality includes the former communes of Cuesmes, Flénu, Ghlin, Hyon, Nimy, Obourg, Jemappes, Ciply, Harmignies, Harveng, Havré, Maisières, Mesvin, Nouvelles, Saint-Denis, Saint-Symphorien, Spiennes and Villers-Saint-Ghislain.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. The population grew quickly, trade flourished, and several commercial buildings were erected near the GrandPlace. In 1814, King William I of the Netherlands increased the fortifications, following the fall of the First French Empire. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry. In 1830, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle the fortifications, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects.
In 1515, Charles V took an oath in Mons as Count of Hainaut. In this period of its history, the city became the target of various occupations, starting in May 1572 with the Protestant takeover by Louis of Nassau, who had hoped to clear the way for the French Protestant leader Gaspard de Coligny to oppose Spanish rule. After the murder of de Coligny during the St. Bartholomews Day massacre, the Duke of Alba took control of Mons in September 1572 in the name of the Catholic King of Spain. This spelled the ruin of the city and the arrest of many of its inhabitants; from 1580 to 1584, Mons became the capital of the Southern Netherlands.
On 8 April 1691, after a nine-month siege, Louis XIVs army stormed the city, which again suffered heavy casualties. From 1697 to 1701, Mons was alternately French or Austrian. After being under French control from 1701 to 1709, the Dutch army gained the upper hand in the Battle of Malplaquet. In 1715, Mons returned to Austria under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht (1713). But the French did not give up easily; Louis XV besieged the city again in 1746. After the Battle of Jemappes (1792), the Hainaut area was annexed to France and Mons became the capital of the Jemappes district.
Following the fall of the First French Empire in 1814, King William I of the Netherlands fortified the city heavily. In 1830, however, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle fortified cities such as Mons, Charleroi, and Namur. The actual removal of fortifications only happened in the 1860s, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry, which strongly influenced the culture and image of the Borinage region as a whole. It was to become an integral part of the sillon industriel, the industrial backbone of Wallonia.
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Birds Eye View City of Namur, Walloon, Belgium
- Title : The City of Namur with the Castle and other Fortifications
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 15970
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map a Bird Eye View of the city of Namur, Belgium - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin restored
Plate area: - Small loss to left of image
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Mons is a Walloon city and municipality, and the capital of the Belgian province of Hainaut. The Mons municipality includes the former communes of Cuesmes, Flénu, Ghlin, Hyon, Nimy, Obourg, Jemappes, Ciply, Harmignies, Harveng, Havré, Maisières, Mesvin, Nouvelles, Saint-Denis, Saint-Symphorien, Spiennes and Villers-Saint-Ghislain.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. The population grew quickly, trade flourished, and several commercial buildings were erected near the GrandPlace. In 1814, King William I of the Netherlands increased the fortifications, following the fall of the First French Empire. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry. In 1830, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle the fortifications, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects.
In 1515, Charles V took an oath in Mons as Count of Hainaut. In this period of its history, the city became the target of various occupations, starting in May 1572 with the Protestant takeover by Louis of Nassau, who had hoped to clear the way for the French Protestant leader Gaspard de Coligny to oppose Spanish rule. After the murder of de Coligny during the St. Bartholomews Day massacre, the Duke of Alba took control of Mons in September 1572 in the name of the Catholic King of Spain. This spelled the ruin of the city and the arrest of many of its inhabitants; from 1580 to 1584, Mons became the capital of the Southern Netherlands.
On 8 April 1691, after a nine-month siege, Louis XIVs army stormed the city, which again suffered heavy casualties. From 1697 to 1701, Mons was alternately French or Austrian. After being under French control from 1701 to 1709, the Dutch army gained the upper hand in the Battle of Malplaquet. In 1715, Mons returned to Austria under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht (1713). But the French did not give up easily; Louis XV besieged the city again in 1746. After the Battle of Jemappes (1792), the Hainaut area was annexed to France and Mons became the capital of the Jemappes district.
Following the fall of the First French Empire in 1814, King William I of the Netherlands fortified the city heavily. In 1830, however, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle fortified cities such as Mons, Charleroi, and Namur. The actual removal of fortifications only happened in the 1860s, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry, which strongly influenced the culture and image of the Borinage region as a whole. It was to become an integral part of the sillon industriel, the industrial backbone of Wallonia.
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map of Aire-sur-la-Lys, Fort St Francis & St Venant, France
-
Title : Plan of the City of Aire and Fort of St. Francis with a view of St.Venant
Sep. 28, 1708 - Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22218
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan & birds eye view of the French city of Aire-sur-la-Lys, a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France along with Fort St Francis and Fort St Venant - used by Lord Marlborough during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Aire-sur-la-Lys is located 10 miles (16 km) southeast of Saint-Omer, by the banks of the Leie and the Laquette rivers.
It is mentioned for the first time in 857 and developed around a fort or castrum built by Baldwin II, Count of Flanders in response to the Norman invasions. More growth followed with the establishment of the Collegiate church of Saint-Pierre by Baldwin V, Count of Flanders.
The town was laid siege ten times between 1127 and 1710. It was separated from the County of Flanders and attached to the County of Artois in 1196. Subsequently ruled by the Burgundians then by the Spanish.
The town was besieged in 1676 by Vauban and retaken for France, although it remained a Spanish possession until 14 April 1713, when, by the Treaty of Utrecht, it finally became a part of France.
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Plan of the Battle of Elixheim, Brabant in 1705
- Title : Plan of the Battle lines of Brabant Forced July 18 1705 by the Army of ye Allies commanded by His Grace the Duke of Marlborough & Felt-Marshall D Averquerque Designed upon the spot by Mons D Ivoy Colonel and Quater master General of the Army of the States General
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 01-8714
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Elixheim, in 1705, also known as the Passage of the Lines of Brabant - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Elixheim, 18 July 1705, also known as the Passage of the Lines of Brabant was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The Duke of Marlborough successfully broke through the French Lines of Brabant, an arc of defensive fieldworks stretching in a seventy-mile arc from Antwerp to Namur. Although he was unable to bring about a decisive battle, the breaking and subsequent razing of the lines would prove critical to the allied victory at Ramillies the next year.
Early in the campaigning season, Marlborough attempted to launch an invasion of France up the Moselle valley. This effort was halted by a combination of supply shortages and an excellent French defensive position in front of Sierck, and Marlborough and his army were recalled by the Dutch States General when Marshall Villeroi attacked and took the fortress of Huy and threatened Liege. Having rushed back to the Low Countries (and forcing Villeroi to retreat behind his defenses), Marlborough retook Huy, and then planned to break through the lines to bring Villeroi to battle.
On the evening of 17 July Marlborough sent the Dutch troops under Marshal Overkirk in a feint southwards towards Namur, drawing Villeroi and 40,000 men after them. Overnight he marched with his own English and Scottish troops northwards to the small village of Eliksem (Elixheim), and there broke through the lines without resistance. Early the next day, as Overkirk\'s men countermarched northwards to join with Marlborough, a French detachment attacked the small force of allied troops drawn up to the west of the lines, facing south. Following a short but intense cavalry battle, in which Marlborough was often personally engaged, they were driven off, and Villeroi withdrew his army to the west, behind the river Dyle.
Unable to pursue the French with any vigour on the day of the battle due to the exhaustion of his men, who had marched all night and then fought an intense battle, Marlborough nonetheless still hoped to bring Villeroi to battle. He was frustrated in manoeuvering to the west of the lines in the month immediately following the breakthrough. A final effort in early August, using wagons loaded with supplies to remove his dependency on his lines of communication, while successful in forcing Villeroi\'s army to make a stand close to Waterloo, ultimately failed to bring about a battle due to the veto exercised by the Dutch Field Deputies, notably Slangenburg. The Duke was forced to content himself with the capture of the fortress of Leau and the levelling of the Lines of Brabant between Leau and the Meuse.