Antonio Zatta
Antonio Zatta (fl. 1757-1797) was a prominent Italian cartographer, engraver, and publisher in Venice during the late 18th century. He is best known for his series of maps and atlases of Italy, Europe, and the world, which were renowned for their high quality and accuracy.
Zatta was born in Venice around 1757 and initially trained as an engraver. He established his own printing and publishing company in Venice in the late 18th century and began producing maps and atlases. His first major work was the "Atlante Novissimo" in 1779, a comprehensive atlas of the world that contained 57 maps and was widely acclaimed for its accuracy and detail.
Over the next two decades, Zatta produced numerous other maps and atlases, including the "Atlante Veneto" in 1784, a comprehensive atlas of the Venetian Republic that included detailed maps of each province, and the "Atlante di Toscana" in 1792, a detailed atlas of the Tuscany region of Italy. Zatta's maps were known for their accurate depictions of geography, topography, and political boundaries, as well as their beautiful engravings and elaborate ornamentation.
Zatta's work was highly regarded by his contemporaries and he was awarded numerous honors and titles throughout his career, including being named an official geographer to the Republic of Venice. Today, his maps and atlases are highly prized by collectors and are regarded as some of the finest examples of cartography from the 18th century.
Antonio Zatta (1)
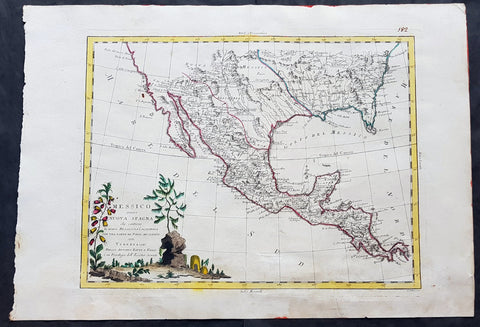
1785 Antonio Zatta Large Antique Map of Mexico, Texas, California, SW & SE USA
- Title : Messico ouvero Nuova Spagna che contiene Il Nuovo Messico La Californoa Con Una Partie de Paesi Adjacenti Venezi 1785
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1785
- Ref #: 93006
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Mexico including Texas, California, and the SE USA was engraved in 1785 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Antonio Zatta in his Atlas Atlante Novissimo. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The capture of Tenochtitlan and refounding of Mexico City in 1521 was the beginning of a 286-year-long colonial era during which Mexico was known as Nueva España (New Spain). The Kingdom of New Spain was created from the remnants of the Aztec hegemonic empire. Subsequent enlargements, such as the conquest of the Tarascan state, resulted in the creation of the Viceroyalty of New Spain in 1535. The Viceroyalty at its greatest extent included the territories of modern Mexico, Central America as far south as Costa Rica, and the western United States. The Viceregal capital Mexico City also administrated the Spanish West Indies (the Caribbean), the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines), and Spanish Florida.
The indigenous population stabilized around one to one and a half million individuals in the 17th century from the most commonly accepted five to ten million pre-contact population. The population decline was primarily the result of communicable diseases, particularly smallpox, introduced during the Columbian Exchange. During the three hundred years of the colonial era, Mexico received between 400,000 and 500,000 Europeans, between 200,000 and 250,000 Africans and between 40,000 and 120,000 Asians. The 18th century saw a great increase in the percentage of mestizos.
Colonial law with Spanish roots was introduced and attached to native customs creating a hierarchy between local jurisdiction (the Cabildos) and the Spanish Crown. Upper administrative offices were closed to native-born people, even those of pure Spanish blood (criollos). Administration was based on the racial separation, among Republics of Spaniards, Amerindians and castas, autonomous and directly dependent on the king himself.
The Council of Indies and the mendicant religious orders, which arrived in Mesoamerica as early as 1524, labored to generate capital for the crown of Spain and convert the Amerindian populations to Catholicism. The 1531 Marian apparitions to Saint Juan Diego gave impetus to the evangelization of central Mexico. The Virgin of Guadalupe became a symbol of criollo patriotism and was used by the insurgents that followed Miguel Hidalgo during the War of Independence. Some Crypto-Jewish families emigrated to Mexico to escape the Spanish Inquisition.
The rich deposits of silver, particularly in Zacatecas and Guanajuato, resulted in silver extraction dominating the economy of New Spain. Taxes on silver production became a major source of income for Spain. Other important industries were the haciendas (functioning under the encomienda and repartimiento systems) and mercantile activities in the main cities and ports. Wealth created during the colonial era spurred the development of New Spanish Baroque.
As a result of its trade links with Asia, the rest of the Americas, Africa and Europe and the profound effect of New World silver, central Mexico was one of the first regions to be incorporated into a globalized economy. Being at the crossroads of trade, people and cultures, Mexico City has been called the first world city. The Nao de China (Manila Galleons) operated for two and a half centuries and connected New Spain with Asia. Goods were taken from Veracruz to Atlantic ports in the Americas and Spain. Veracruz was also the main port of entry in mainland New Spain for European goods, immigrants, and African slaves. The Camino Real de Tierra Adentro connected Mexico City with the interior of New Spain. Mexican silver pesos became the first globally used currency and the silver mined in Mexico were used to run commerce and wage crusades in two sides of globe, at the Mediterranean were Spain fought against the Ottoman Caliphate and at Southeast Asia where the Philippines fought against the Brunei Sultanate.
Due to the importance of New Spain administrative base, Mexico was the location of the first printing shop (1539), first university (1551), first public park (1592), and first public library (1646) in the Americas, amongst other institutions. Important artists of the colonial period, include the writers Juan Ruiz de Alarcón and Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, painters Cristóbal de Villalpando and Miguel Cabrera, and architect Manuel Tolsá. The Academy of San Carlos was the first major school and museum of art in the Americas. Scientist Andrés Manuel del Río Fernández discovered the element vanadium.
Spanish forces, sometimes accompanied by native allies, led expeditions to conquer territory or quell rebellions through the colonial era. Notable Amerindian revolts in sporadically populated northern New Spain include the Chichimeca War (1576–1606), Tepehuán Revolt (1616–1620) and the Pueblo Revolt (1680). To protect Mexico from the attacks of English, French and Dutch pirates and protect the Crowns monopoly of revenue, only two ports were open to foreign trade—Veracruz on the Atlantic and Acapulco on the Pacific. Among the best-known pirate attacks are the 1663 Sack of Campeche and 1683 Attack on Veracruz.
Many Mexican cultural features including tequila, first distilled in the 16th century, charreria (17th), mariachi (18th) and Mexican cuisine, a fusion of American and European (particularly Spanish) cuisine, arose during the colonial era.
On September 16, 1810, a loyalist revolt against the ruling junta was declared by priest Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, in the small town of Dolores, Guanajuato. This event, known as the Cry of Dolores (Spanish: Grito de Dolores) is commemorated each year, on September 16, as Mexicos independence day. The first insurgent group was formed by Hidalgo, the Spanish viceregal army captain Ignacio Allende, the militia captain Juan Aldama and La Corregidora Josefa Ortiz de Domínguez. Hidalgo and some of his soldiers were captured and executed by firing squad in Chihuahua, on July 31, 1811. Following his death, the leadership was assumed by priest José María Morelos, who occupied key southern cities.
In 1813 the Congress of Chilpancingo was convened and, on November 6, signed the Solemn Act of the Declaration of Independence of Northern America. Morelos was captured and executed on December 22, 1815.
In subsequent years, the insurgency was near collapse, but in 1820 Viceroy Juan Ruiz de Apodaca sent an army under the criollo general Agustín de Iturbide against the troops of Vicente Guerrero. Instead, Iturbide approached Guerrero to join forces, and on August 24, 1821 representatives of the Spanish Crown and Iturbide signed the Treaty of Córdoba and the Declaration of Independence of the Mexican Empire, which recognized the independence of Mexico under the terms of the Plan of Iguala.
Mexicos short recovery after the War of Independence was soon cut short again by the civil wars and institutional instability of the 1850s, which lasted until the government of Porfirio Díaz reestablished conditions that paved the way for economic growth. The conflicts that arose from the mid-1850s had a profound effect because they were widespread and made themselves perceptible in the vast rural areas of the countries, involved clashes between castes, different ethnic groups and haciendas, and entailed a deepening of the political and ideological divisions between republicans and monarchists.
Agustín de Iturbide became constitutional emperor of the First Mexican Empire in 1822. A revolt against him in 1823 established the United Mexican States. In 1824, a Republican Constitution was drafted and Guadalupe Victoria became the first president of the newly born country. Central America, including Chiapas, left the union. In 1829 president Guerrero abolished slavery. The first decades of the post-independence period were marked by economic instability, which led to the Pastry War in 1836. There was constant strife between Liberals, supporters of a federal form of government, and Conservatives, who proposed a hierarchical form of government.
During this period, the frontier borderlands to the north became quite isolated from the government in Mexico City, and its monopolistic economic policies caused suffering. With limited trade, the people had difficulty meeting tax payments and resented the central governments actions in collecting customs. Resentment built up from California to Texas. Both the mission system and the presidios had collapsed after the Spanish withdrew from the colony, causing great disruption especially in Alta California and New Mexico. The people in the borderlands had to raise local militias to protect themselves from hostile Native Americans. These areas developed in different directions from the center of the country.
Wanting to stabilize and develop the frontier, Mexico encouraged immigration into present-day Texas, as they were unable to persuade people from central Mexico to move into those areas. They allowed for religious freedom for the new settlers, who were primarily Protestant English speakers from the United States. Within several years, the Anglos far outnumbered the Tejano in the area. Itinerant traders traveled through the area, working by free market principles. The Tejano grew more separate from the government and due to its neglect, many supported the idea of independence and joined movements to that end, collaborating with the English-speaking Americans.
General Antonio López de Santa Anna, a centralist and two-time dictator, approved the Siete Leyes in 1836, a radical amendment that institutionalized the centralized form of government. When he suspended the 1824 Constitution, civil war spread across the country. Three new governments declared independence: the Republic of Texas, the Republic of the Rio Grande and the Republic of Yucatán.
The 1846 United States annexation of the Republic of Texas and subsequent American military incursion into territory that was part of Coahuila (also claimed by Texas) instigated the Mexican–American War. The war was settled in 1848 via the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Mexico was forced to give up more than one-third of its land to the U.S., including Alta California, Santa Fe de Nuevo México and the territory claimed by Texas. A much smaller transfer of territory in what is today southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico—known as the Gadsden Purchase—occurred in 1854.
The Caste War of Yucatán, the Maya uprising that began in 1847, was one of the most successful modern Native American revolts. Maya rebels, or Cruzob, maintained relatively independent enclaves in the peninsula until the 1930s.
Dissatisfaction with Santa Annas return to power led to the liberal Plan of Ayutla, initiating an era known as La Reforma. The new Constitution drafted in 1857 established a secular state, federalism as the form of government, and several freedoms. As the Conservatives refused to recognize it, the Reform War began in 1858, during which both groups had their own governments. The war ended in 1861 with victory by the Liberals, led by president Benito Juárez, who was an ethnic Zapotec.
In the 1860s Mexico was occupied by France, which established the Second Mexican Empire under the rule of the Habsburg Archduke Ferdinand Maximilian of Austria with support from the Roman Catholic clergy and the Conservatives. The latter switched sides and joined the Liberals. Maximilian surrendered, was tried on June 14, 1867, and was executed a few days later on June 19 in Querétaro.