Recent Acquisitions (4)
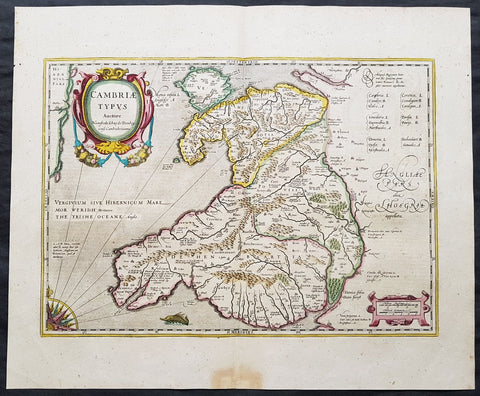
1639 Mercator & Hondius Large Old, Antique Map of Wales, GB - Humphrey Llwyd
- Title : Cambriae Typus Auctore Humfredo Lhuydo Denbigiense Cambrobritanno
- Date : 1639
- Size: 23in x 19in (590mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 43139
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Wales - dedicated to its original creator the Welsh cartographer Lhuyd Humphrey - by Gerard Mercator was published by Jodocus Hondius in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas.
One of the best examples I seen of this map to date, beautiful original hand colour with strong sturdy paper with a deep strong impression.
Humphrey Llwyd (also spelled Lhuyd) (1527–1568) was a Welsh cartographer , author, antiquary and Member of Parliament. He was a leading member of the Renaissance period in Wales along with other such men as Thomas Salisbury and William Morgan.
Llwyd was born in Denbigh, the county seat of the then county of Denbighshire at Foxhall, his family's estate. His father, Robert Llwyd, was descended from Harry Rossendale, henchman and grantee of the Earl of Lincoln. The first of the family that came to Wales from England appears to have been Foulk Rosindale, from whom Foxhall, or Foulk's Hall, was called. He married into the family of the Llwyd's of Aston, and probably from where his descendants derived their name, as well as their extraction from Einion Evell of the 12th Century. Einion Evell, Lord of part of Cynllaith, resided at Llwyn y Macn, in the parish of Oswestry. He and his twin brother, Cynwrig Evell, Lord of Y Glwyegl in Maelor Gymraeg, were the illegitimate sons of Madog ab Maredydd, Prince of Powys, by Eva, daughter of Madog (ab Einion Hael) ab Urien of Macn Gwynedd, ab Eginirab Lies ab Idnerth Benvras, Lord of Maesbrwg.
As a young man, he was educated at Brasenose College, Oxford and fared so well in the sciences and engineering that he was given a position as a physician to the Earl of Arundel during the Earl's tenure as Chancellor of the university. He was MP for East Grinstead during Elizabeth I's first parliament (1559).
In 1563, Llwyd returned to Denbigh and lived at Denbigh Castle at the permission of Sir John Salusbury who was then the Lord of the Manor of Denbigh. That year, he was elected MP for Denbigh Boroughs during Elizabeth's second Parliament where he promoted an act allowing the translation of the Bible into Welsh.
From 1566 he toured Europe, including Brussels, Augsburg, Milan, Padua and Venice. In Antwerp, he learnt from, and collaborated with, map maker Abraham Ortelius. In 1567, when Llwyd returned to Denbigh, he was given a stipend from the Crown to create the first printed map of Wales.
Llwyd died in 1568 and is buried in Whitchurch, a small chapel on the outskirts of Denbigh
Jodocus Hondius (1563 - 1612), one of the most notable engravers of his time, is known for his work in association with many of the cartographers and publishers prominent at the end of the sixteenth and the beginning of the seventeenth century.
In 1604 Hondius bought the plates of Mercator's Atlas which, in spite of its excellence, had not competed successfully with the continuing demand of the Ortelius Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
To meet this competition Hondius added about 40 maps to Mercator's original number and from 1606 published enlarged editions in many languages, still under Mercator's name but with his own name as publisher. These atlases have become known as the Mercator/Hondius series. The following year the maps were re-engraved in miniature form and issued as a pocket Atlas Minor.
After the death of Jodocus Hondius the Elder in 1612, work on the two atlases, folio and miniature, was carried on by his widow and sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, and eventually in conjunction with Jan Jansson in Amsterdam. In all, from 1606 onwards, nearly 50 editions with increasing numbers of maps with texts in the main European languages were printed. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (590mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14in (500mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning to bottom of margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
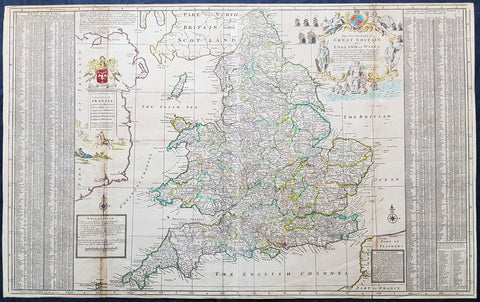
1710 Herman Moll Large Antique Map of England & Wales - extensive Details
- Title : The South Part of Great Britain called England & Wales...by Herman Moll 1710
- Size: 39in x 24in (1.0m x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1710
- Ref #: 80662
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of England & Wales was engraved in 1710 by Herman Moll - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by John Bowles of London.
Striking large format, one off published, map of England and Wales. The map is embellished with two large cartouches and an extensive table locating all ye Cities, Market Towns, Boroughs and whateve Places in South Britain have ye Election of Members of Parliament.
The map is elaborately colored by counties, with 5 sailing ships to the right of Northumberland. Includes a dedication to Right Honourable FRANCIS, Lord Viscount Rialton in the cartouche at the right side of the map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39in x 24in (1.0m x 610mm)
Plate size: - 38in x 23in (970mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds
Verso: - None
Background:
English Cartography: When considering the work of English map makers we tend, perhaps, to think too much in terms of county maps, dominated by the names of Saxton and Speed, but we should not underrate the contribution to the sum of geographical knowledge made in other spheres, such as the sea charts of Edward Wright, Robert Dudley and Greenvile Collins, the discoveries of James Cook, the road maps of Ogilby and Cary, the meteorological and magnetic charts compiled by Edmund Halley, to mention only a few.
In 1558 Queen Elizabeth came to the throne in the midst of a fast changing world. In 1563 a nineteen sheet map, copies of which survive only in manuscript form, was completed by Laurence Nowell, and no doubt, the issue of Mercators large-scale map of the British Isles in 1564 had an important influence on the thought of the period. A few years later a national survey was commissioned privately, although probably at the instigation of Lord Burghley, the Lord Treasurer, but subsequently was completed with royal encouragement. The outcome was Christopher Saxtons Atlas of EngIand and Wales, started about 1570 and published in 1579 - the first printed set of county maps and the first countrywide atlas on such a splendid scale produced anywhere. A Welsh antiquarian, Humphrey Lhuyd completed a set of surveys that were even more successful than Saxton in which he had produced fine manuscript maps of England and Wales which were used by Ortelius in editions of his Atlas from 1573 onwards.
The earliest maps of the 17th century, attributed to William Smith of the College of Heralds, covered only twelve counties based on Saxton/Norden and were presumably intended to be part of a complete new atlas. They were printed in the Low Countries in 1602-3 and were soon followed by maps for the Latin edition of Camdens Britannia dated 1607. In 1610-11 the first edition of John Speeds famous county Atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published and immediately replaced Saxtons in popular appeal. Although Speed assembled much of his material from the earlier works of Saxton, Norden and others, a considerable part of the up-to-date information, especially relating to the inset town plans depicted on his maps, was obtained first hand. The maps undoubtedly owed much of their popularity to the splendid engravings of high quality made in the workshops in Amsterdam of Jodocus Hondius to whom Speed sent his manuscripts, the plates subsequently being returned to London for printing.
In 1645, Volume IV of the famous Blaeu World Atlas covering the counties of England and Wales was published in Amsterdam. These maps have always been esteemed as superb examples of engraving and design, the calligraphy being particularly splendid, but nevertheless they were nearly all based on Saxton and Speed and added little to geographical knowledge.
Not until the latter part of the century do we find an English map maker of originality with the capacity to put new ideas into practice. John Ogilby, one of the more colourful figures associated with cartography, started life as a dancing master and finished as Kings Cosmographer and Geographic Printer. After publishing a small number of county maps, somewhat on the lines of John Norden he issued in 1675 the Britannia, the first practical series of detailed maps of the post roads of England and Wales on a standard scale of 1,760 yards to the mile. Up to the end of the century and beyond, reprints and revisions of Saxtons and Speeds atlases continued to appear and the only other noteworthy county maps were Richard Blomes Britannia (1673), John Overtons Atlas (c. 1670) and Robert Mordens maps for an English translation of Camdens Britannia published in 1695.
Another noted cartographer of the day was Captain Greenvile Collins, and of his work in surveying the coasts of Great Britain culminating in the issue in 1693 of the Great Britains Coasting Pilot. Apart from these charts, English cartographers published during the century a number of world atlases. Speed was the first Englishman to produce a world atlas with the issue in 1627 of his A Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World. Other atlases appeared later in the century by Peter Heylin, John Seller, William Berry, Moses Pitt and Richard Blome, whilst Ogilby found time to issue maps of Africa, America and Asia. Far more important, from the purely scientific point of view, was the work of Edmund Halley, Astronomer Royal, who compiled and issued meteorological and magnetic charts in 1688 and 1701 respectively.
At the beginning of the eighteenth century the Dutch map trade was finally in decline, the French in the ascendant and the English to a great extent still dominated by Saxton and Speed except, as we have shown, in the spheres of sea charts and road maps. There were atlases by John Senex, the Bowles family, Emanuel and Thomas Bowen, Thomas Badeslade and the unique birds-eye perspective views of the counties, The British Monarchy by George Bickham. In 1750-60 Bowen and Kitchins The Large English Atlas containing maps on a rather larger scale than hitherto was published.
In 1759 the Society for the encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce offered an award of £100 for the best original surveys on this scale and by the end of the century about thirty counties had been re-surveyed. These maps, many of which formed, in later years, the basis for the first issues of county maps by the Ordnance Survey Office were not only decorative but a tremendous improvement geographically on earlier local maps. As a consequence, the skills and expertise of the new-style cartographers soon enabled them to cover the world as well as the domestic market. Thomas Jefferys was such a man; he was responsible for a number of the new 1 in. to 1 mile county surveys and he issued an edition of Saxtons much battered 200-year-old plates of the county maps, but he is better known for many fine maps of North America and the West Indies. His work was continued on the same lines by William Faden, trading as Faden and Jefferys. Other publishers such as Sayer and Bennett and their successors Laurie and Whittle published a prodigious range of maps, charts and atlases in the second half of the century. A major influence at this time was John Cary who, apart from organizing the first re-survey of post roads since Ogilby and subsequently printing the noted Travellers Companion, was a prolific publisher of atlases and maps of every kind of all parts of the world. After starting work with Cary, and taking part in the new road survey, Aaron Arrowsmith set up in his own business and went on to issue splendid large-scale maps of many parts of the world. Both Carys and Arrowsmiths plates were used by other publishers until far into the next century and, in turn, their work was taken up and developed by James Wyld (Elder and Younger) and Tallis and Co.
Later into the 19th century some of the better known cartographers and publishers were by Henry Teesdale (1829-30), Christopher and John Greenwood, surveyors, Thomas Moule, a writer on heraldry and antiques (1830-36) and John Walker (1837) but by about the middle of the century few small-scale publishers survived and their business passed into the hands of large commercial concerns such as Bartholomews of Edinburgh and Philips of London who continue to this day. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
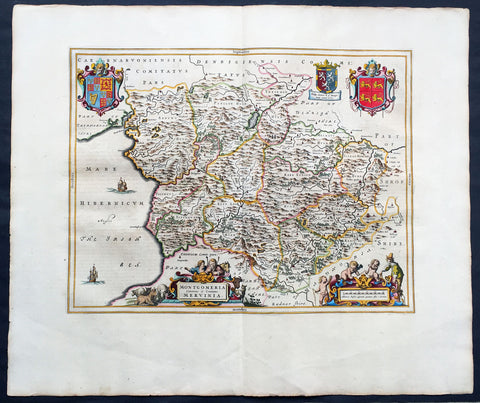
1664 Joan Blaeu Large Antqiue Map The Welsh County of Montgomery
-
Title : Montgomeria Comitatus et Comitatus Mervinia
- Date : 1664
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 01-4004
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Welsh County of Montgomery was published in the 1664 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Major.
Blaeus reference for the topographical data is from John Speeds maps from the 1611 Empire of Great Britaine - the beautiful decoration, though, is distinctly Blaeus. (Ref: Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16 1/2in (510mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
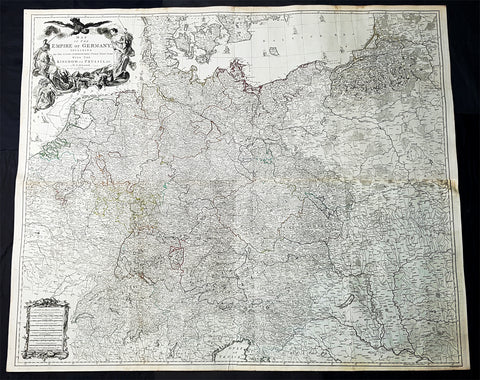
1759 Delarochette & Kitchin 1st Edition Antique Map of Germany Central Europe - Rare
- Titles: Map of the Empire of Germany, Including All the States Comprehend under that name: with the Kingdom of Priussia &c.
Sizes: 48 1/2in x 41in (1.230m x 1.040m) - Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date: 1759
- Ref #: 93418
Description:
This stunning very large, scare and original copper-plate engraved antique 1st edition wall map of Germany, Bohemia, Austria, Prussia, Poland, Hungary, Netherlands and Northern Italy by the English cartographers Louis d arcy Delarochette & Thomas Kitchin (engraver) was published by Robert Sayer in 1759.
Incredibly detailed map of central Europe showing political boundaries as they were in the mid 18th century. Much detail noting roadways, towns, castles, monasteries, forests, swamps, rivers, towns, cities, mountains and much more. An incredible insight into mid 18th century Europe.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 48 1/2in x 41in (1.230m x 1.040m)
Plate size: - 48 1/2in x 41in (1.230m x 1.040m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Louis d Arcy Delarochette 1731 - 1802 was a British cartographer active in the mid to late 18th century. Collaborated with many famous British cartographers including Kitchin, Faden, Laurie & Whittle and Thomas Jefferies. Well know for his large scale maps.
Robert Sayers 1724 - 1794 was an important English map publisher and engraver active from the mid to late 18th century. Sayer was born in Sunderland, England, in 1725. He may have clerked as a young man with the Bank of England, but this is unclear. His brother, James Sayer, married Mary Overton, daughter-in-law of John Overton and widow of Philip Overton. Sayer initially worked under Mary Overton, but by December of 1748 was managing the Overton enterprise and gradually took it over, transitioning the plates to his own name. When Thomas Jefferys went bankrupt in 1766, Sayer offered financial assistance to help him stay in business and, in this way, acquired rights to many of the important Jefferys map plates as well as his unpublished research. From about 1774, he began publishing with his apprentice, John Bennett (fl. 1770-1784), as Sayer and Bennett, but the partnership was not formalized until 1777. Bennett retired in 1784 following a mental collapse and the imprint reverted to Robert Sayer. From 1790, Sayer added Robert Laurie and James Whittle to his enterprise, renaming the firm Robert Sayer and Company. Ultimately, Laurie and Whittle partnered to take over his firm. Sayer retired to Bath, where, after a long illness, he died. During most of his career, Sayer was based at 53 Fleet Street, London. His work is particularly significant for its publication of many British maps relating to the American Revolutionary War. Unlike many map makers of his generation, Sayer was a good businessman and left a personal fortune and great estate to his son, James Sayer, who never worked in the publishing business.