Recent Acquisitions (6)
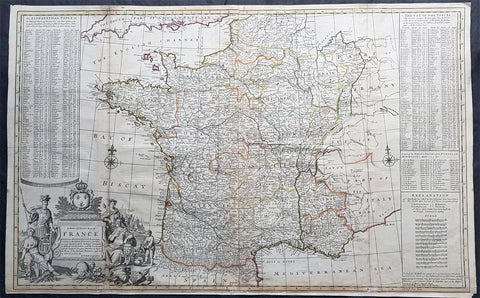
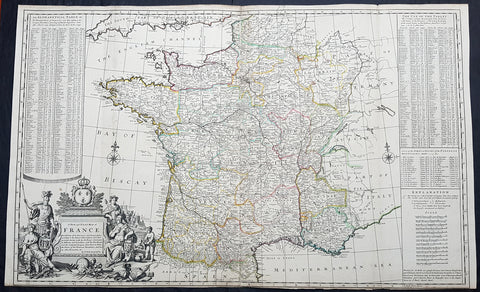
1720 Herman Moll Large Antique Pre Revolutionary Map of France in Provinces
- Title : A New and Exact Map of France Divided into all its Provinces...by H Moll Geographer
- Size: 39 1/2in x 25in (1.00m x 630mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1720
- Ref #: 43196
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of France by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39 1/2in x 25in (1.00m x 630mm)
Plate size: - 39 1/2in x 25in (1.00m x 630mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, bottom margin extended from plate-mark
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds
Verso: - Re-enforced along folds
Background:
The Carolingian dynasty ruled France until 987, when Hugh Capet, Duke of France and Count of Paris, was crowned King of the Franks. His descendants—the Capetians, the House of Valois, and the House of Bourbon—progressively unified the country through wars and dynastic inheritance into the Kingdom of France, which was fully declared in 1190 by Philip II Augustus. The French nobility played a prominent role in most Crusades in order to restore Christian access to the Holy Land. French knights made up the bulk of the steady flow of reinforcements throughout the two-hundred-year span of the Crusades, in such a fashion that the Arabs uniformly referred to the crusaders as Franj caring little whether they really came from France. The French Crusaders also imported the French language into the Levant, making French the base of the lingua franca (litt. Frankish language) of the Crusader states. French knights also made up the majority in both the Hospital and the Temple orders. The latter, in particular, held numerous properties throughout France and by the 13th century were the principal bankers for the French crown, until Philip IV annihilated the order in 1307. The Albigensian Crusade was launched in 1209 to eliminate the heretical Cathars in the southwestern area of modern-day France. In the end, the Cathars were exterminated and the autonomous County of Toulouse was annexed into the crown lands of France. Later kings expanded their domain to cover over half of modern continental France, including most of the north, centre and west of France. Meanwhile, the royal authority became more and more assertive, centred on a hierarchically conceived society distinguishing nobility, clergy, and commoners.
From the 11th century, the House of Plantagenet, the rulers of the County of Anjou, succeeded in establishing its dominion over the surrounding provinces of Maine and Touraine, then progressively built an empire that spanned from England to the Pyrenees and covering half of modern France. Tensions between the kingdom of France and the Plantagenet empire would last a hundred years, until Philip Augustus of France conquered between 1202 and 1214 most of the continental possessions of the empire, leaving England and Aquitaine to the Plantagenets. Following the Battle of Bouvines, the Angevin court retreated to England, but persistent Capetian–Plantagenet rivalry would paved the way for another conflict.
Charles IV the Fair died without an heir in 1328. Under the rules of the Salic law the crown of France could not pass to a woman nor could the line of kingship pass through the female line. Accordingly, the crown passed to Philip of Valois, a cousin of Charles, rather than through the female line to Charles nephew, Edward of Plantagenet, who would soon become Edward III of England. During the reign of Philip of Valois, the French monarchy reached the height of its medieval power. Philips seat on the throne was contested by Edward III of England and in 1337, on the eve of the first wave of the Black Death, England and France went to war in what would become known as the Hundred Years War. The exact boundaries changed greatly with time, but French landholdings of the English Kings remained extensive for decades. With charismatic leaders, such as Joan of Arc and La Hire, strong French counterattacks won back English continental territories. Like the rest of Europe, France was struck by the Black Death; half of the 17 million population of France died.
The French Renaissance saw a spectacular cultural development and the first standardisation of the French language, which would become the official language of France and the language of Europes aristocracy. It also saw a long set of wars, known as the Italian Wars, between France and the House of Habsburg. French explorers, such as Jacques Cartier or Samuel de Champlain, claimed lands in the Americas for France, paving the way for the expansion of the First French colonial empire. The rise of Protestantism in Europe led France to a civil war known as the French Wars of Religion, where, in the most notorious incident, thousands of Huguenots were murdered in the St. Bartholomews Day massacre of 1572. The Wars of Religion were ended by Henry IVs Edict of Nantes, which granted some freedom of religion to the Huguenots. Spanish troops, the terror of Western Europe, assisted the Catholic side during the Wars of Religion in 1589–1594, and invaded northern France in 1597; after some skirmishing in the 1620s and 1630s, Spain and France returned to all-out war between 1635 and 1659. The war cost France 300,000 casualties.
Under Louis XIII, the energetic Cardinal Richelieu promoted the centralisation of the state and reinforced the royal power by disarming domestic power holders in the 1620s. He systematically destroyed castles of defiant lords and denounced the use of private violence (dueling, carrying weapons, and maintaining private army). By the end of 1620s, Richelieu established the royal monopoly of force as the doctrine. During Louis XIVs minority and the regency of Queen Anne and Cardinal Mazarin, a period of trouble known as the Fronde occurred in France. This rebellion was driven by the great feudal lords and sovereign courts as a reaction to the rise of royal absolute power in France.
The monarchy reached its peak during the 17th century and the reign of Louis XIV. By turning powerful feudal lords into courtiers at the Palace of Versailles, Louis XIVs personal power became unchallenged. Remembered for his numerous wars, he made France the leading European power. France became the most populous country in Europe and had tremendous influence over European politics, economy, and culture. French became the most-used language in diplomacy, science, literature and international affairs, and remained so until the 20th century. France obtained many overseas possessions in the Americas, Africa and Asia. Louis XIV also revoked the Edict of Nantes, forcing thousands of Huguenots into exile.
Under Louis XV, Louis XIVs great-grandson, France lost New France and most of its Indian possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years War (1756–63). Its European territory kept growing, however, with notable acquisitions such as Lorraine (1766) and Corsica (1770). An unpopular king, Louis XVs weak rule, his ill-advised financial, political and military decisions – as well as the debauchery of his court– discredited the monarchy, which arguably paved the way for the French Revolution 15 years after his death.
Louis XVI, Louis XVs grandson, actively supported the Americans, who were seeking their independence from Great Britain (realised in the Treaty of Paris (1783)). The financial crisis aggravated by Frances involvement in the American Revolutionary War was one of many contributing factors to the French Revolution. Much of the Enlightenment occurred in French intellectual circles, and major scientific breakthroughs and inventions, such as the discovery of oxygen (1778) and the first hot air balloon carrying passengers (1783), were achieved by French scientists. French explorers, such as Bougainville and Lapérouse, took part in the voyages of scientific exploration through maritime expeditions around the globe. The Enlightenment philosophy, in which reason is advocated as the primary source for legitimacy and authority, undermined the power of and support for the monarchy and helped pave the way for the French Revolution.
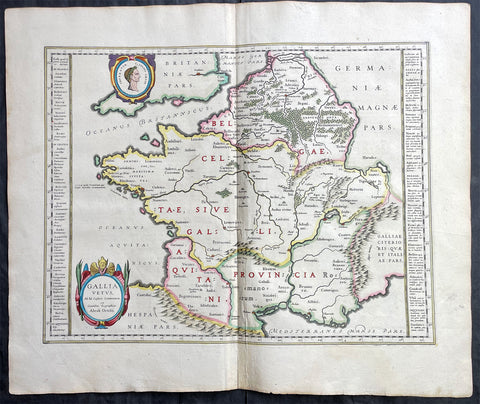
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of France
- Title : Galliae supera omnes in hac...auctore Henrico Hondio
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 17039
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of France was published by Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
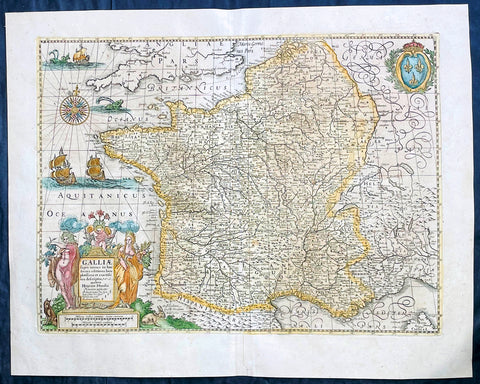
1638 Joan Blaeu & Abraham Ortelius Antiue Map of France
- Title : Gallia Vetus...Abrah Ortelii
- Date : 1638
- Size: 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70606
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of France, after Abraham Ortelius, was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1638 French edition of Atlas Nouvs,.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
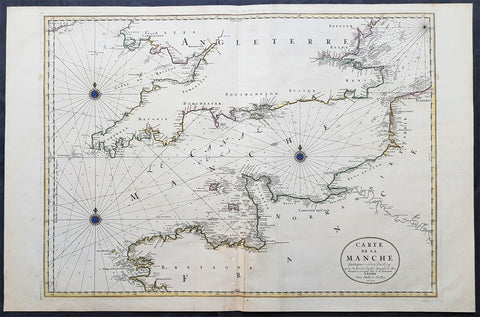
1692 Jaillot Large Antique Map Sea Chart The English Channel during 9 Years War
- Title : Carte De La Manche faite par ordre du Roy. pour le Service de les Armees de Mer.....a Paris...1692
- Size: 38in x 25in (960m x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1692
- Ref #: 16371
Description:
This very large, beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, a large Sea Chart of The English Channel - produced for the French Navy during the Nine Years War and specifically the Battle of Beachy Head - was engraved in 1692, dated in the cartouche, and was published for Alexis Hubert Jaillots 1698 edition of his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 38in x 25in (960m x 635mm)
Plate size: - 32 1/2in x 23 1/2in (825mm x 595mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Nine Years War (1688–97)—often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg—was a conflict between Louis XIV of France and a European coalition of the Holy Roman Empire, led by Austria, the Dutch Republic, Spain, England and Savoy. It was fought in Europe and the surrounding seas, North America and in India. It is sometimes considered the first global war. The conflict encompassed the Williamite war in Ireland and Jacobite risings in Scotland, where William III and James II struggled for control of England and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Indigenous allies, today called King Williams War by Americans.
Louis XIV of France had emerged from the Franco-Dutch War in 1678 as the most powerful monarch in Europe, an absolute ruler who had won numerous military victories. Using a combination of aggression, annexation, and quasi-legal means, Louis XIV set about extending his gains to stabilize and strengthen France\'s frontiers, culminating in the brief War of the Reunions (1683–84). The Truce of Ratisbon guaranteed France\'s new borders for twenty years, but Louis XIV\'s subsequent actions—notably his Edict of Fontainebleau (the revocation of the Edict of Nantes) in 1685— led to the deterioration of his military and political dominance. Louis XIVs decision to cross the Rhine in September 1688 was designed to extend his influence and pressure the Holy Roman Empire into accepting his territorial and dynastic claims. Leopold I and the German princes resolved to resist, and when the States General and William III brought the Dutch and the English into the war against France, the French King faced a powerful coalition aimed at curtailing his ambitions.
The main fighting took place around Frances borders in the Spanish Netherlands, the Rhineland, the Duchy of Savoy and Catalonia. The fighting generally favoured Louis XIV\'s armies, but by 1696 his country was in the grip of an economic crisis. The Maritime Powers (England and the Dutch Republic) were also financially exhausted, and when Savoy defected from the Alliance, all parties were keen to negotiate a settlement. By the terms of the Treaty of Ryswick (1697) Louis XIV retained the whole of Alsace but was forced to return Lorraine to its ruler and give up any gains on the right bank of the Rhine. Louis XIV also accepted William III as the rightful King of England, while the Dutch acquired a Barrier fortress system in the Spanish Netherlands to help secure their borders. With the ailing and childless Charles II of Spain approaching his end, a new conflict over the inheritance of the Spanish Empire embroiled Louis XIV and the Grand Alliance in the War of the Spanish Succession.
The Battle of Beachy Head (Bévéziers) was a naval engagement fought on 10 July 1690 during the Nine Years\' War. The battle was the greatest French tactical naval victory over their English and Dutch opponents during the war. The Dutch lost six ships of the line (sources vary) and three fireships; their English allies also lost one ship of the line, whereas the French did not lose a vessel. Control of the English Channel temporarily fell into French hands but Vice-Admiral Tourville failed to pursue the Allied fleet with sufficient vigour, allowing it to escape to the River Thames.
Tourville was criticised for not following up his victory and was relieved of his command. The English Admiral Arthur Herbert, 1st Earl of Torrington – who had advised against engaging the superior French fleet but had been overruled by Queen Mary and her ministers – was court-martialled for his performance during the battle. Although he was acquitted, King William dismissed him from the service.
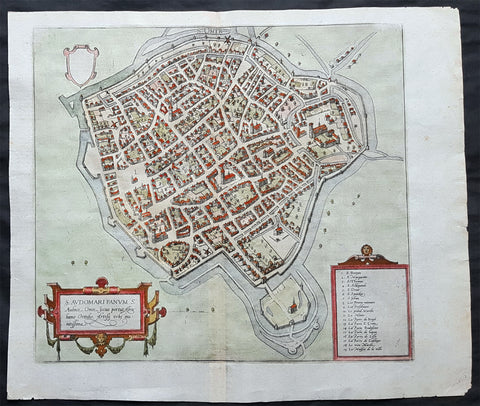
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Original Antique Birds Eye View of St Omer, Calais France
- Title : S. Audomari Fanum. S. Ausmer, Omer, Iccius portus Abrahamo Orttelio, Artesii urbs munitissima
- Date : 1575
- Size: 25in x 21 1/4in (635mm x 540mm)
- Ref #: 30268
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original 1572 antique birds eye view of the Northern French Town of St Omer in the Pas-de-Calais department, was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
This is a bird's-eye view from the south of the town, which is fortified with moats, walls and bastions. Numerous churches stand out, including the Gothic cathedral of Notre-Dame in the lower left-hand corner, with its 50-m-high clock tower. The town goes back to the Benedictine monastery established in AD 657 by Bishop Audomar of Thérouanne. Initially a religious centre, it quickly developed various commercial activities. At the beginning of the 14th century the town was one of the largest in France, the wealthiest in Artois and a centre of European trade.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 15 1/2in (470mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/2in (385mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This is a bird's-eye view from the south of the town, which is fortified with moats, walls and bastions. Numerous churches stand out, including the Gothic cathedral of Notre-Dame in the lower left-hand corner, with its 50-m-high clock tower. The town goes back to the Benedictine monastery established in AD 657 by Bishop Audomar of Thérouanne. Initially a religious centre, it quickly developed various commercial activities. At the beginning of the 14th century the town was one of the largest in France, the wealthiest in Artois and a centre of European trade.
Saint-Omer, is a city in France in the sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department 68 km. The town is named after Saint Audomar, who brought Christianity to the area.
Saint Audomar (died c. 670), better known as Saint Omer, was a Burgundy-born bishop of Thérouanne, after whom nearby Saint-Omer in northern France was named
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN (on verso): "Saint-Audomar, commonly known as Saint-Audmar, and, in the mutilated form read by some, Saint-Omer, a small town in Artois, gets its name from St Audomar, a German, a priest born not far from Constance [...]. Through the recommendation of King Pippin and the bishop of Noyon, he was appointed bishop to the Morini or Flemings. Because he was a man of pious conduct, Adroaldus, a rich and noble man, was later persuaded to present him with the hamlet of Sithieu and the surrounding area to build a monastery there. [...] Through the teachings of these men a large number of people came to the little village of Sithieu and began to build a town, which was later named St Audomar or St Omer in honour of this excellent bishop."
CARTOUCHE LEFT: S. Audomari Fanum, S. Aulmer, Saint-Omer. Iccius portus according to Abraham Ortelius; well-fortified town in Artois.
1720 Herman Moll Large Antique Map of France in Provinces - Pre Revolution
- Title : A New and Exact Map of France Divided into all its Provinces...by H Moll Geographer
- Ref #: 93416
- Size: 40in x 24 1/2in (1.010m x 625mm)
- Date : 1720
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of France by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 40in x 24 1/2in (1.010m x 625mm)
Plate size: - 39 1/2in x 24in (1.00m x 620mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin cropped to plate mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The Carolingian dynasty ruled France until 987, when Hugh Capet, Duke of France and Count of Paris, was crowned King of the Franks. His descendants—the Capetians, the House of Valois, and the House of Bourbon—progressively unified the country through wars and dynastic inheritance into the Kingdom of France, which was fully declared in 1190 by Philip II Augustus. The French nobility played a prominent role in most Crusades in order to restore Christian access to the Holy Land. French knights made up the bulk of the steady flow of reinforcements throughout the two-hundred-year span of the Crusades, in such a fashion that the Arabs uniformly referred to the crusaders as Franj caring little whether they really came from France. The French Crusaders also imported the French language into the Levant, making French the base of the lingua franca (litt. Frankish language) of the Crusader states. French knights also made up the majority in both the Hospital and the Temple orders. The latter, in particular, held numerous properties throughout France and by the 13th century were the principal bankers for the French crown, until Philip IV annihilated the order in 1307. The Albigensian Crusade was launched in 1209 to eliminate the heretical Cathars in the southwestern area of modern-day France. In the end, the Cathars were exterminated and the autonomous County of Toulouse was annexed into the crown lands of France. Later kings expanded their domain to cover over half of modern continental France, including most of the north, centre and west of France. Meanwhile, the royal authority became more and more assertive, centred on a hierarchically conceived society distinguishing nobility, clergy, and commoners.
From the 11th century, the House of Plantagenet, the rulers of the County of Anjou, succeeded in establishing its dominion over the surrounding provinces of Maine and Touraine, then progressively built an empire that spanned from England to the Pyrenees and covering half of modern France. Tensions between the kingdom of France and the Plantagenet empire would last a hundred years, until Philip Augustus of France conquered between 1202 and 1214 most of the continental possessions of the empire, leaving England and Aquitaine to the Plantagenets. Following the Battle of Bouvines, the Angevin court retreated to England, but persistent Capetian–Plantagenet rivalry would paved the way for another conflict.
Charles IV the Fair died without an heir in 1328. Under the rules of the Salic law the crown of France could not pass to a woman nor could the line of kingship pass through the female line. Accordingly, the crown passed to Philip of Valois, a cousin of Charles, rather than through the female line to Charles nephew, Edward of Plantagenet, who would soon become Edward III of England. During the reign of Philip of Valois, the French monarchy reached the height of its medieval power. Philips seat on the throne was contested by Edward III of England and in 1337, on the eve of the first wave of the Black Death, England and France went to war in what would become known as the Hundred Years War. The exact boundaries changed greatly with time, but French landholdings of the English Kings remained extensive for decades. With charismatic leaders, such as Joan of Arc and La Hire, strong French counterattacks won back English continental territories. Like the rest of Europe, France was struck by the Black Death; half of the 17 million population of France died.
The French Renaissance saw a spectacular cultural development and the first standardisation of the French language, which would become the official language of France and the language of Europes aristocracy. It also saw a long set of wars, known as the Italian Wars, between France and the House of Habsburg. French explorers, such as Jacques Cartier or Samuel de Champlain, claimed lands in the Americas for France, paving the way for the expansion of the First French colonial empire. The rise of Protestantism in Europe led France to a civil war known as the French Wars of Religion, where, in the most notorious incident, thousands of Huguenots were murdered in the St. Bartholomews Day massacre of 1572. The Wars of Religion were ended by Henry IVs Edict of Nantes, which granted some freedom of religion to the Huguenots. Spanish troops, the terror of Western Europe, assisted the Catholic side during the Wars of Religion in 1589–1594, and invaded northern France in 1597; after some skirmishing in the 1620s and 1630s, Spain and France returned to all-out war between 1635 and 1659. The war cost France 300,000 casualties.
Under Louis XIII, the energetic Cardinal Richelieu promoted the centralisation of the state and reinforced the royal power by disarming domestic power holders in the 1620s. He systematically destroyed castles of defiant lords and denounced the use of private violence (dueling, carrying weapons, and maintaining private army). By the end of 1620s, Richelieu established the royal monopoly of force as the doctrine. During Louis XIVs minority and the regency of Queen Anne and Cardinal Mazarin, a period of trouble known as the Fronde occurred in France. This rebellion was driven by the great feudal lords and sovereign courts as a reaction to the rise of royal absolute power in France.
The monarchy reached its peak during the 17th century and the reign of Louis XIV. By turning powerful feudal lords into courtiers at the Palace of Versailles, Louis XIVs personal power became unchallenged. Remembered for his numerous wars, he made France the leading European power. France became the most populous country in Europe and had tremendous influence over European politics, economy, and culture. French became the most-used language in diplomacy, science, literature and international affairs, and remained so until the 20th century. France obtained many overseas possessions in the Americas, Africa and Asia. Louis XIV also revoked the Edict of Nantes, forcing thousands of Huguenots into exile.
Under Louis XV, Louis XIVs great-grandson, France lost New France and most of its Indian possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years War (1756–63). Its European territory kept growing, however, with notable acquisitions such as Lorraine (1766) and Corsica (1770). An unpopular king, Louis XVs weak rule, his ill-advised financial, political and military decisions – as well as the debauchery of his court– discredited the monarchy, which arguably paved the way for the French Revolution 15 years after his death.
Louis XVI, Louis XVs grandson, actively supported the Americans, who were seeking their independence from Great Britain (realised in the Treaty of Paris (1783)). The financial crisis aggravated by Frances involvement in the American Revolutionary War was one of many contributing factors to the French Revolution. Much of the Enlightenment occurred in French intellectual circles, and major scientific breakthroughs and inventions, such as the discovery of oxygen (1778) and the first hot air balloon carrying passengers (1783), were achieved by French scientists. French explorers, such as Bougainville and Lapérouse, took part in the voyages of scientific exploration through maritime expeditions around the globe. The Enlightenment philosophy, in which reason is advocated as the primary source for legitimacy and authority, undermined the power of and support for the monarchy and helped pave the way for the French Revolution.