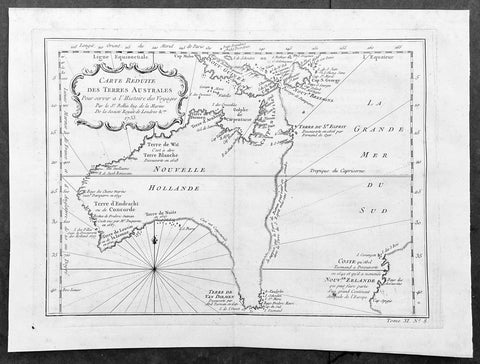
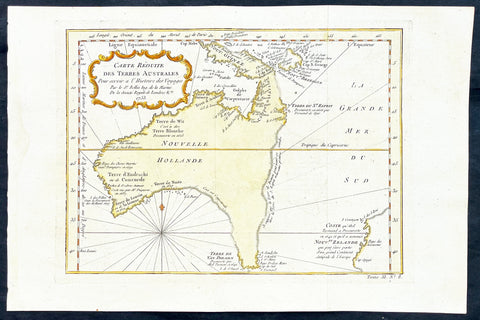
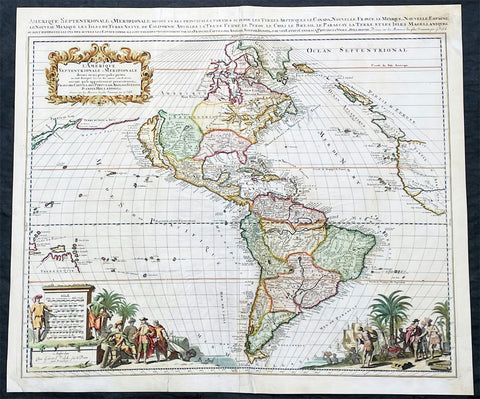
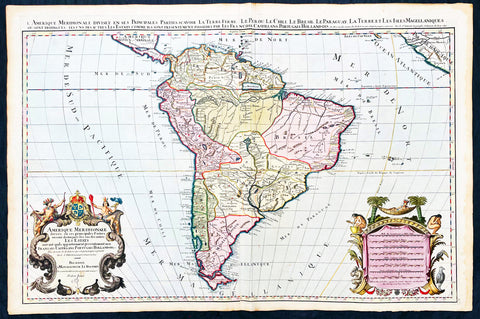
Maps (899)
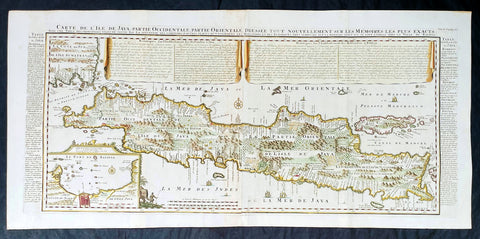
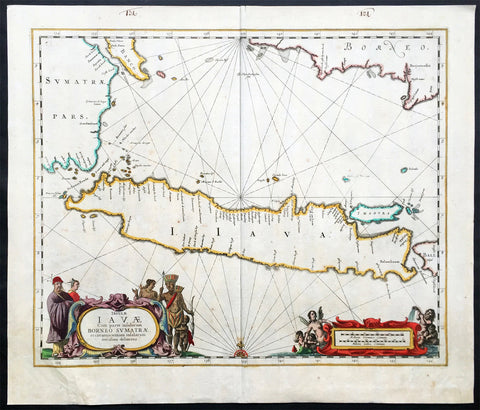
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map of Java Indonesia - EIC Dutch East Indies
Antique Map
- Title : Carte de L ' Isle de Java; Partie Occidentale, Partie Orientale, Dresee tout Nouvellement
- Date : 1719
- Size: 36 3/4in x 17 1/2in (980mm x 445mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35643
Description:
This large fine beautifully hand coloured highly detailed original antique map of the Indonesian Island of Java was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1718 was published in his famous Atlas Historique.
This is a landmark map at a time when the Dutch East India Company still had stranglehold on the trade of the East Indies with bright hand colouring, clean strong sturdy paper and a heavy clear impression donating an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36 3/4in x 17 1/2in (980mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 15 1/2in (900mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
A beautiful example of Henri Chatelain's important 1718 map of Java. Covers the island in full as well as adjacent parts of Sumatra and Bali. Offers beautiful engraving and extraordinary detail throughout, noting rice plantations, mountain ranges, grazing lands, forests, and in many places, elephants and gazelle. The previously unknown southern shore is mapped both correctly and in considerable detail. Also shows some offshore reefs and other dangers. The volcanic island of Krakatau, here identified as Cracatao, which nearly 150 years later would erupt with devastating consequences, appears in the Strait of Sunda between Java and Sumatra. In the lower left quadrant an inset details the city and port of Batavia, then the center of Dutch East Indian Company's activity in the region. Appearing in tapestry style windows at the top of the map is an area of extensive text. Composed by Gueudeville, this is a discussion of the history of the lands and countries depicted. Additional textual data referencing the cities and villages of Java, appears to the left and right of the map proper.
In its day Chatelain's map of Java was by far the most sophisticated study of the island yet published. Previous to this map, the most advanced cartographic rendering of Java was Van der Aa's 1714 mapping of the region, which though it correctly identified general form of Java's northern shore, identified the southern shore as "Parte Incognita". Of course the Dutch were active in this region since the 17th century and had no doubt produced accurate manuscript charts of the island, but these were carefully guarded trade secrets controlled by the powerful Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie (V.O.C. or Dutch East India Company). The publication of Chatelain's map of Java, offered here, suggests that Chatelain somehow obtained his data from a source outside of the V.O.C. That Chatelain's map was copied by Johannes Van Keulen II, the V.O.C.'s own cartographer, nine years later suggests that even the V.O.C., who maintained an active presence on the island, did not possess more accurate data. It is highly likely that Chatelain extracted much of his cartographic information on Java from Hadrien Reland, a Dutch scholar and philologist who composed a number of works on the Indonesian Archipelago in the early 18th century.
A highly important map of the region and a must for an serious collection focusing on the East Indies.
The Atlas Historique published by Henri Chatelain was part of a major work of its time, an encyclopedia in seven volumes, including geography as one of its main subjects. The text was by Nicholas Gueudeville and the maps by Chatelain. The Atlas included one of the finest map of America (four sheets) surrounded by vignettes and decorative insets. The Atlas Historique was completed between 1705 and 1720, further issues were published up to 1739. The series was published in Amsterdam, with Chatelain’s maps based on those of G. Delisle. (Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden; AMPR)
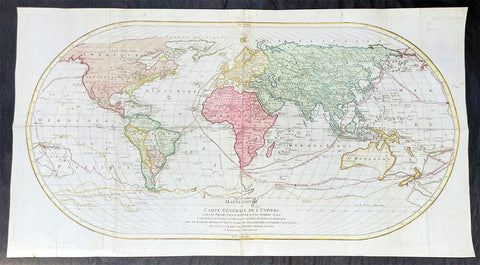
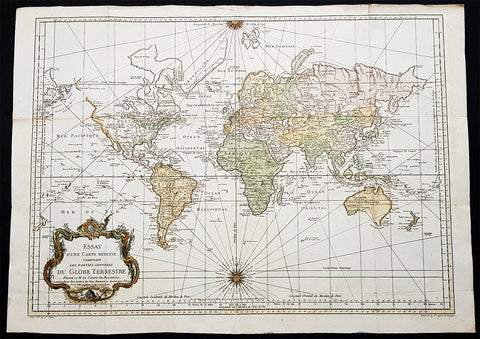
1782 Matthaus Lotter Large World Map Tracking of Cooks Voyages 1768, 1772 & 1776
- Title : Mappe Monde ou carte generale de l`Univers sur une projection nouvelle d`une sphere ovale pour mieux entendre les distances entre l`Europe et Amerique avec le tour du monde du Lieut Cook et Tous Les Decouvertes Nouvelles...MDCCLXXXII
- Date : 1782 (2nd edition)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35646
- Size: 38 1/2in x 21in (985mm x 535mm)
Description:
This very large, impressive original copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on an Ortelius Oval Projection, was engraved and published by Matthäus Albrecht Lotter in 1782, dated in title.
The map was first issued in 1778 and re-issued in 1782 & 1787 and included all three of Cooks voyages of discovery.
This map was one of the first world maps published to cash in on the publicity over Captain James Cooks Circumnavigation of the world and the first European survey of New Zealand and the East Coast of Australia. Beautifully executed and dominated by New Holland, Australia, for the first time almost complete on a world map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 38 1/2in x 21in (985mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 37 1/2in x 19 1/4in (955mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issue, light soiling
Plate area: - Folds as issue, light soiling
Verso: - Folds as issue, light soiling
Background:
This large world map was one of the first to show the discoveries of the east coast of Australia and New Zealand by James Cook on his first voyage of Discovery. The shadow line from Tasmania west to Western Australia was not filled in until the later discoveries of Bass Strait by Bass and Matthew Flinders in 1797 and the southern coast by Baudin and Flinders in 1803. Also included along the New Holland coastline is the earlier Dutch discoveries of Hartog 1616, the van Leeuwin 1619, Nuyts 1627, de Wit 1628 and Tasman 1642-44. The Trial Islands near present-day Dampier, named after the English ship the Trial, which were incorrectly charted by Gerritsz after the false reports provided by Captain Brookes, are also noted.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cook\\\\\\\'s command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth\\\\\\\'s distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
Cooks Second Voyage (1772-1775)
Based on the success of his first voyage, Cook was appointed by the Admiralty to lead a second expedition. Two ships were employed with Cook commanding the Resolution and Captain Tobias Furneaux in charge of the Adventure. The purpose was to circumnavigate the globe as far south as possible to confirm the location of a southern continent. Cook proved that there was no Terra Australis, which supposedly was located between New Zealand and South America. Cook was convinced, however, that there was land beyond the southern ice fields. In his pursuit of this idea, this expedition was the first European voyage to cross the Antarctic Circle. In addition, in two great sweeps through the Southern latitudes, Cook made an incredible number of landfalls including New Zealand, Easter Island, the Marquesas, Tahiti and the Society Islands, the Tonga Islands, the New Hebrides, New Caledonia, and a number of smaller islands.
In addition to these navigational accomplishments and the accompanying expansion of geographical knowledge, the expedition also recorded a vast amount of information regarding the Pacific islands and peoples, proved the value of the chronometer as an instrument for calculating longitude, and improved techniques for preventing scurvy.
Cooks Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cooks third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\\\\\\\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cooks death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cooks death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
The Ortelius Oval Projection is a map projection used for world maps largely in the late 16th and early 17th century. It is neither conformal nor equal-area but instead offers a compromise presentation. It is similar in structure to a pseudocylindrical projection but does not qualify as one because the meridians are not equally spaced along the parallels. The projection\'s first known use was by Battista Agnese (flourished 1535–1564) around 1540, although whether the construction method was truly identical to Ortelius\'s or not is unclear because of crude drafting and printing. The front hemisphere is identical to Petrus Apianus\'s 1524 globular projection.
The projection reached a wide audience via the popular map Typus Orbis Terrarum by Abraham Ortelius beginning in 1570. The projection (and indeed Ortelius maps) were widely copied by other mapmakers such as Giovanni Pietro Maffei, Fernando de Solis, and Matteo Ricci.
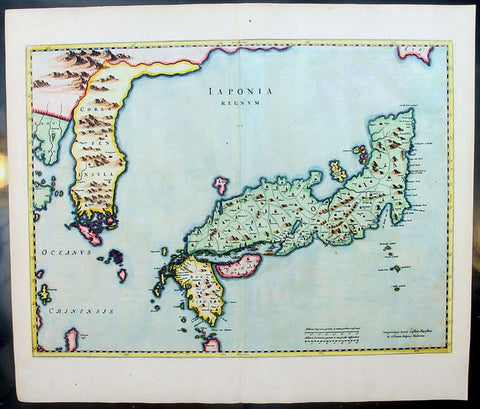
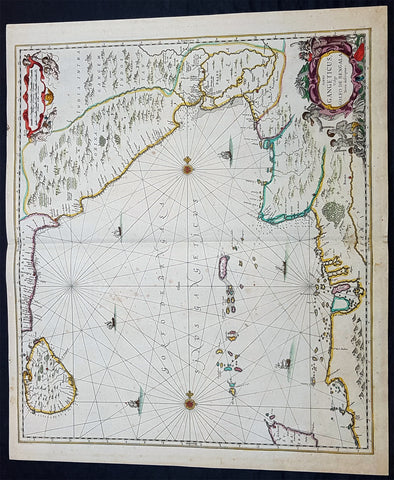
1655 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Japan, Korea & parts of China - Beautiful
- Title : Japonia Regnum
- Date : 1655
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92811
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Japan & Korea - the seventeenth and last of the maps provided by the Jesuit priest Martino Martini to Joan Blaeu - was published by Joan Blaeu in his 1665 edition of Atlas Simenis.
Martinis map was to provide the most accurate depiction of the general outlines of the principle islands of Japan - Honshu, Kyushu and Shikoku - for more than a century. The map was copied extensively by other mapmakers throughout the remainder of the seventeenth century and was replaced during the eighteenth century by maps that were in nearly all respects considerably inferior, albeit rather more flamboyant in design. Martinis first hand knowledge of the Chinese mainland enabled him to draw Korea correctly, for the first time on a printed map, as a peninsular even though little interior detail is shown. However what lay to the north of Japan was a mystery, not only Europeans, but also to the Japanese and Chinese as well. Even as early as 1613, William Adams, an Englishman living in Japan for many years, had written back to England recommending Japan as a base for "discouerie to the northward...never hath bin better menes to discouer". As with his general map of China, Martini here provides information on the internal administrative divisions in Japan; each of the feudal fiefdoms is shown, with the chief town in each, while some evidence of the activity of Jesuit missions, since the arrival of Francis Xavier in 1549, can be gathered from the town symbols surmounted by a small cross. This is one of the finest maps of Japan ever published, the engraving is strong, paper excellent and clean with beautiful original hand colour. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early color
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic & beautiful
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 16 3/4in (570mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
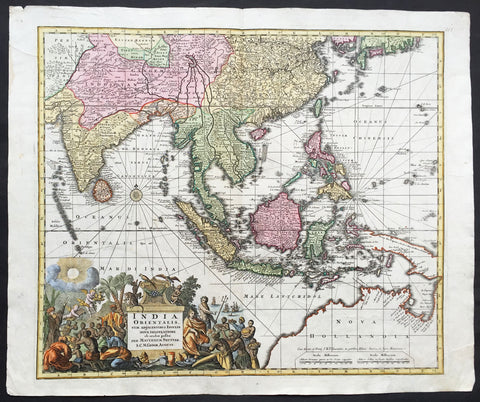
1730 George Seutter Large Antique Map of Australia, East Indies, SE Asia, China
- Title: India Orientalis cum Adjacentibus Insulis Nova Delineatione ob oculos posita ..Matth. Suettro.
- Date: 1730
- Condition: (A+) Condition
- Ref: 43155
- Size: 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Description: This large, scarce & beautifully hand coloured original map of Australia & SE Asia was published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730. This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen, especially with the colouring. In excellent condition, a must in any Australian or SE Asian collection.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/4in (580mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: The map extends from China, Japan and Persia in the North and in the south stretching from The Maldives east to Northern Australia. Of note, Australia continues to be attached to Nova Guinea, albeit with some hesitation, as the image extends outside the inner neat-line to convey this information - even though 20+ names are confidently engraved around Northern Australia Coastline. The detail throughout Southeast Asia is informative and up-to-date and the print style typically strong. The cartouche is one of Seutter's most ornate, with elaborate scenes from sea, land, jungle and mythology. This map rarely appears on the market, as it was only included in select copies of Seutters atlas. (Ref: Norwich; M&B; Tooley)
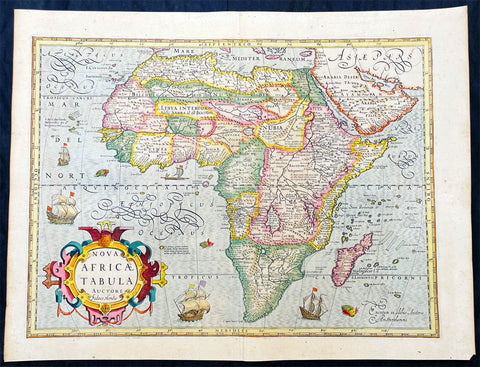
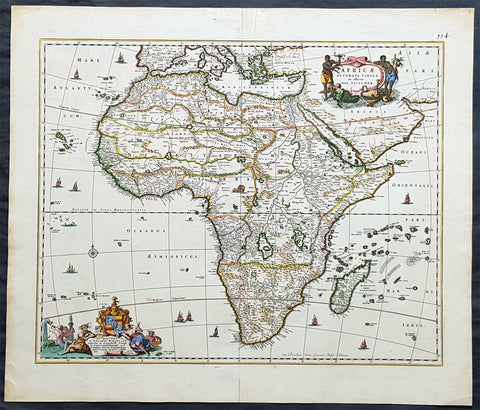
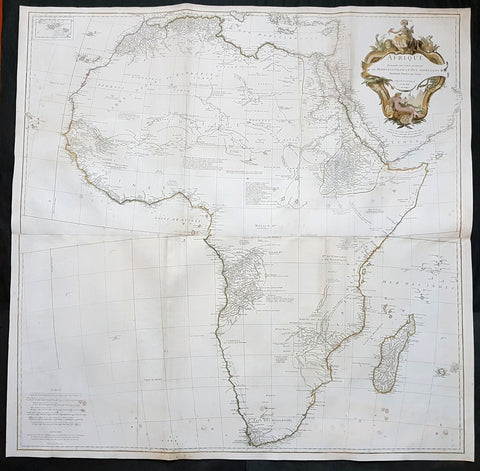
1628 Jodocus Hondius & Gerard Mercator Antique Map of Africa - Beautiful
- Title : Nova Africae Tabula. Auctore Jodoco Hondio Excusum in aedibus Auctoris Amsterodami.
- Ref #: 35626
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 22 1/2in x 17 1/4in (615mm x 530mm)
- Date: 1628
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Africa by Jodocus Hondius, after Gerard Mercator, was published in the 1628 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes De Fabrica Mundi
This is a beautiful map with original hand colouring, heavy age toned paper with a deep impression. Beautiful map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 17 1/4in (615mm x 530mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
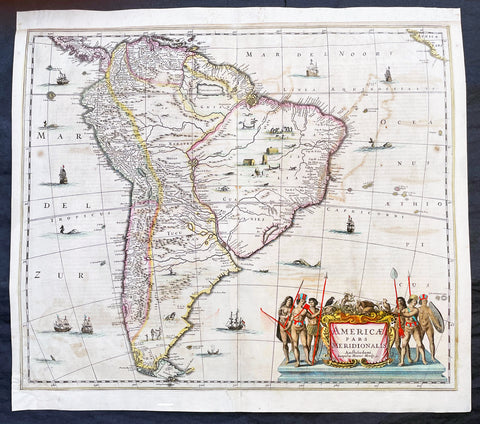
1639 Henricus Hondius Large Antique Map of South America - Beautiful
- Title : Americae Pars Meridionalis Henrici Hony...
- Ref #: 43162
-
Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1639
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique copper plate engraved antique map of South America by Henricus Hondius was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Beautiful large map, the second by Hondius, with original hand colouring and strong sturdy paper.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 18 1/4in (545mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin extended from plate-mark, small repair to bottom margin
Plate area: - Offsetting
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
Background:
Between 1452 and 1493, a series of papal bulls (Dum Diversas, Romanus Pontifex, and Inter caetera) paved the way for the European colonization and Catholic missions in the New World. These authorized the European Christian nations to \"take possession\" of non-Christian lands and encouraged subduing and converting the non-Christian people of Africa and the Americas.
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime powers of that time, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas in the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west. Through the treaty they agreed that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries. The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (which is now known to include most of the South American soil), would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. Because accurate measurements of longitude were not possible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus sailed near the Orinoco Delta and then landed in the Gulf of Paria (Actual Venezuela). Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in his moving letter to Isabella I and Ferdinand II that he must have reached heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
Great signs are these of the Terrestrial Paradise, for the site conforms to the opinion of the holy and wise theologians whom I have mentioned. And likewise, the [other] signs conform very well, for I have never read or heard of such a large quantity of fresh water being inside and in such close proximity to salt water; the very mild temperateness also corroborates this; and if the water of which I speak does not proceed from Paradise then it is an even greater marvel, because I do not believe such a large and deep river has ever been known to exist in this world.
Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it into colonies.
European diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles and typhus) to which the native populations had no resistance were the overwhelming cause of the depopulation of the Native American population. Cruel systems of forced labor (such as encomiendas and mining industry\'s mita) under Spanish control also contributed to depopulation. Lower bound estimates speak of a decline in the population of around 20–50 per cent, whereas high estimates arrive at 90 per cent.[42] Following this, African slaves, who had developed immunity to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their American subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end. However, most initial attempts at this were only partially successful; American groups simply blended Catholicism with their traditional beliefs. The Spaniards did not impose their language to the degree they did their religion. In fact, the missionary work of the Roman Catholic Church in Quechua, Nahuatl, and Guarani actually contributed to the expansion of these American languages, equipping them with writing systems.
Eventually the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a Mestizo class. Mestizos and the Native Americans were often forced to pay unfair taxes to the Spanish government (although all subjects paid taxes) and were punished harshly for disobeying their laws. Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers. This included a great number of gold and silver sculptures, which were melted down before transport to Europe.
In 1616, the Dutch, attracted by the legend of El Dorado, founded a fort in Guayana and established three colonies: Demerara, Berbice, and Essequibo.
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area of modern-day French Guiana, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne along with some small-scale plantations.
Since the sixteenth century there were some movements of discontent to Spanish and Portuguese colonial system. Among these movements, the most famous being that of the Maroons, slaves who escaped their masters and in the shelter of the forest communities organized free communities. Attempts to subject them by the royal army was unsuccessful, because the Maroons had learned to master the South American jungles. In a royal decree of 1713, the king gave legality to the first free population of the continent: Palenque de San Basilio in Colombia today, led by Benkos Bioho. Brazil saw the formation of a genuine African kingdom on their soil, with the Quilombo of Palmares.
Between 1721 and 1735, the Revolt of the Comuneros of Paraguay arose, because of clashes between the Paraguayan settlers and the Jesuits, who ran the large and prosperous Jesuit Reductions and controlled a large number of Christianized Indians.
Between 1742 and 1756, was the insurrection of Juan Santos Atahualpa in the central jungle of Peru. In 1780, the Viceroyalty of Peru was met with the insurrection of curaca Condorcanqui or Tupac Amaru II, which would be continued by Tupac Catari in Upper Peru.
In 1763, the African Cuffy led a revolt in Guyana which was bloodily suppressed by the Dutch. In 1781, the Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada), an insurrection of the villagers in the Viceroyalty of New Granada, was a popular revolution that united indigenous people and mestizos. The villagers tried to be the colonial power and despite the capitulation were signed, the Viceroy Manuel Antonio Flores did not comply, and instead ran to the main leaders José Antonio Galán. In 1796, Essequibo (colony) of the Dutch was taken by the British, who had previously begun a massive introduction of slaves.
During the eighteenth century, the figure of the priest, mathematician and botanist José Celestino Mutis (1732–1808), was delegated by the Viceroy Antonio Caballero y Gongora to conduct an inventory of the nature of the Nueva Granada, which became known as the Botanical Expedition, which classified plants, wildlife and founded the first astronomical observatory in the city of Santa Fé de Bogotá.
On August 15, 1801, the Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt reached Fontibón where Mutis, and began his expedition to New Granada, Quito. The meeting between the two scholars are considered the brightest spot of the botanical expedition. Humboldt also visited Venezuela, Mexico, United States, Chile, and Peru. Through his observations of temperature differences between the Pacific Ocean between Chile and Peru in different periods of the year, he discovered cold currents moving from south to north up the coast of Peru, which was named the Humboldt Current in his honour.
Between 1806 and 1807, British military forces tried to invade the area of the Rio de la Plata, at the command of Home Riggs Popham and William Carr Beresford, and John Whitelocke. The invasions were repelled, but powerfully affected the Spanish authority
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
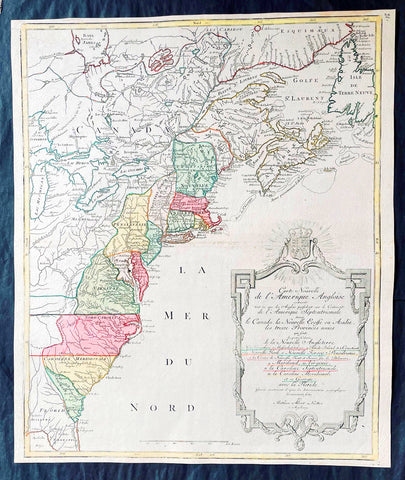
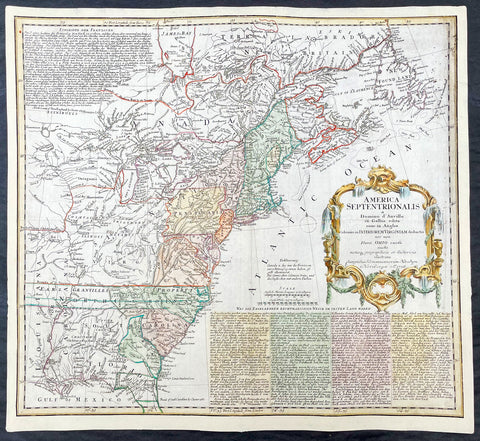
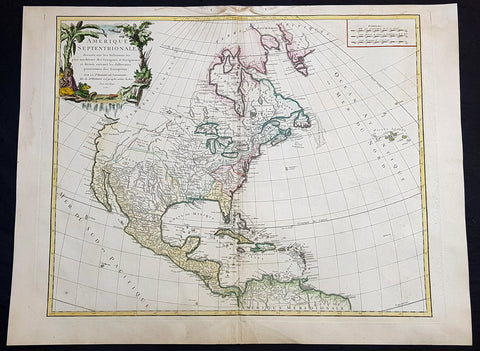
1776 Tobias Lotter Large Antique Post Revolutionary North America Map 13 Colonies
- Title : Carte Nouvelle de l Amerique Angloise Contenant Tout ce que les Anglois Possedent sur le Continent de l'Amerique Septentrionale Savior le Canada, la Nouvelle Ecosse ou Acadie, les Treize Provinces Unies ... avec la Floride
- Ref #: 27009
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1776
Description:
This is possibly one of the last significant maps, of the original 13 American colonies, published prior to the American Revolution for Independence from Britain, beginning in 1763 and ending with the signing of the Declaration of Independence in 1776.
Published in Augsberg, Germany in 1776 by Conrad Tobias Lotter, this large original antique map reflects both the French & German interests in North America just prior to the outbreak of hostilities.
The map covers the area from the James Bay to the Gulf of Mexico and west to Lake Michigan. It shows provinces, towns and cities, some forts and trails, as well as Indian villages and tribal territory. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Each of the thirteen Colonies is identified by name both on the map, and in the title. The title is placed within an attractive decorative border surmounted by the British Royal arms. The French title and nomenclature indicates that Lotter, a leading German mapmaker, intended this for the French market, as does the fact that he limits the claims of the British to the regions east of the Appalachian Mountains. The delineation of the thirteen Provinces unies is generally well done (although Maryland and Georgia are both strangely shaped): a number of locations are named in the Ohio Valley, including Logs Town, Twictwees, Ft. Du Quesne, Allegheny, Vinango, Buffaloons, Sandoski and Mingos. Some interesting details are also shown in the region of the Great Lakes.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
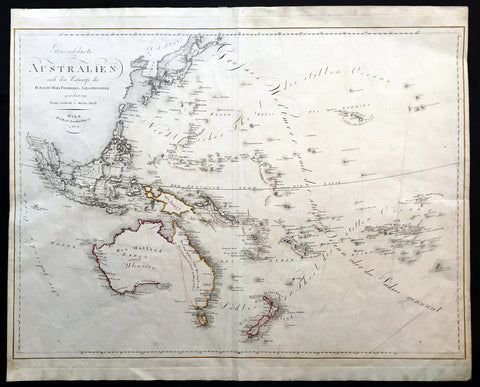
1815 Swoboda & Hartl Large Old, Antique Map of Australia, Ulimaroa New Zealand - Rare
- Title : Generalcharte von Australien nach dem entwurfe des H.Joseph Marx Freiherrn v. Liechtenstern
- Date : 1815
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16258
- Size: 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original & scarce antique map of New Holland also named Ulimaroa, New Zealand and the South Pacific by Franz Swoboda and Martin Hartl was published in Vienna in 1815 - dated.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Paper size: - 27in x 20 3/4in (685mm x 525mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (7mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Vertical crease right image
Verso: - None
This map is typical of the affect of Cooks discoveries on European cartography. Australia regularly became a focus on regional maps. The name "Ulimaroa" was often used, mainly by German & Austrian cartographers, at this time. It was term Cook learned from the New Zealand Maoris before discovering the east coast of Australia during his first voyage of discovery. When this map was printed there was a strong belief that the Australian continent was possibly divided by an internal sea strait, separating the east from the west coasts. It was explorers such as Flinders and Baudin who set out to find this elusive passage and if so the possible point at which a ship could enter.
Only a few years before in 1798 Flinders and Bass had proved that there was a strait dividing Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) from the rest of the continent so now the race was on to find the other passage. On Swoboda’s map a line has been drawn from the bottom of Carpentaria to the eastern part of present day Victoria. This line represented two things, the potential shape of the eastern landmass split by the sea and the extent to English territory in the newly settled colonies, only 17 years old. The Southern Coastline is not shown as even though Flinders had by 1803 mapped the entire region he was in 1805 still under house arrest on the islands of Mauritius by the French, he would not publish his discoveries until 1814. Therefore this map shows Australia at a pivotal point in its history when most of the continent was still open for settlement by other nations and the coastlines and mysteries were still to be confirmed. (Ref: Clancy; M&B; Tooley)
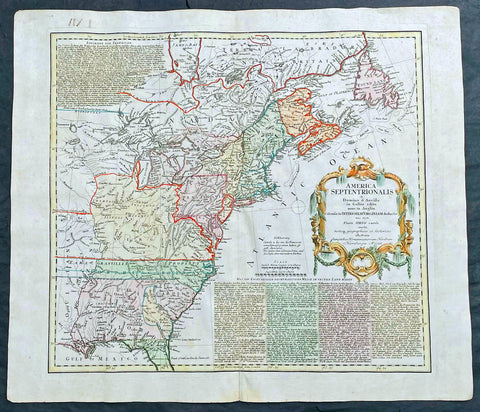
1756 Homann Antique Map Colonial United States North America French Indian War
- Title : America Septentrionalis a domino d Anville in Galiis edita nunc in Anglia coloniis in interiorem Virginiam deductis nec non fluvii Ohio cursu aucta notisq geographicis et historicis illustrata.....1756
- Ref #: 17001
- Size: 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique 1st edition map of the Colonial United States, at the beginning of the French-Indian war, was engraved in 1756 - dated in cartouche - by the Homann firm, Germany.
First edition Homann map of the English Colonies in North America prior to the start of the French and Indian War. The map stretches just west of the Mississippi River to the east and from James Bay through the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Although most of the text is in German, there is also much in English, including numerous place named annotations associated the French and Indian War, such as the locations of Fort Duquesne and Fort Necessity, both taken by the French in 1754. Thus although the cartographer credits D Anville for the basic cartography, it is clear he is drawing from English, not French, sources. Bottom right and upper left are notes offering the history of North America.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - All margins extended from border
Plate area: - Light crease adjacent to centerfold, soiling in top right border
Verso: - Light soiling.
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1756 Homann Antique Map Colonial United States North America French Indian War
- Title : America Septentrionalis a domino d Anville in Galiis edita nunc in Anglia coloniis in interiorem Virginiam deductis nec non fluvii Ohio cursu aucta notisq geographicis et historicis illustrata.....1756
- Ref #: 27018
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique 1st edition map of the Colonial United States, at the beginning of the French-Indian war, was engraved in 1756 - dated in cartouche - by the Homann firm, Germany.
This map has original margins and colour on heavy clean sturdy paper.
First edition Homann map of the English Colonies in North America prior to the start of the French and Indian War. The map stretches just west of the Mississippi River to the east and from James Bay through the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Although most of the text is in German, there is also much in English, including numerous place named annotations associated the French and Indian War, such as the locations of Fort Duquesne and Fort Necessity, both taken by the French in 1754. Thus although the cartographer credits D Anville for the basic cartography, it is clear he is drawing from English, not French, sources. Bottom right and upper left are notes offering the history of North America.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light staining in lower margins, bottom margin centerfold rejoined with transparent archival tape
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
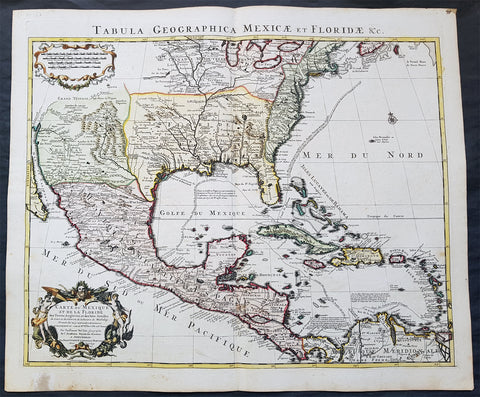
1722 G. Delisle and Covens & Mortier Antique Map of North America - 5th State
- Title : Carte Du Mexique et de la Floride des Terres Angloises et des Isles Antilles du Cours...1722
- Date : 1722
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70814
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Description:
In the world of early 18th century American cartography, no one published as many landmark maps of North America as the French family firm of Delisle. This large original copper-plate engraved scarce map of North America became one of the most copied map of the next 100 years by the likes of Homann, Seutter, Lotter, Sanson and many others.
Re-engraved and published by Covens & Mortier in Amsterdam, this map is the 5th state of seven, published in the Atlas Nouveau.
The 7 states outlined by Tooley are:
- State 1 (1703): De LIsles first address on Rue Des Canettes.
- State 2 (1703): address changed to Quai de lHorloge Couronne de Diamans and the imprint of Renard.
- State 3 (1708): Couronne de Diamans is erased and se trouve a Amsterdam chez L. Renard Libraire prez de la Bourse is added
- State 4 (1708): A Paris Chez L Auteur sur le Quai de l Horloge is added and Couronne de Diamans and Renards imprint are removed and the engravers name (Simoneau) appears below the cartouche.
- State 5 (1722): A Amsterdam Chez Jean Covens & Corneille Mortier avec Privilege 1722 Re-engraved and published by Covens & Mortier in Atlas Nouveau
- State 6 (1745): Philippe Buache imprint added below neatline at right.
- State 7 (1783): Title altered to Carte du Mexique et des Etas Unis d Amerique, Partie Meridionale, issued by Dezauche, showing US States and boundaries.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Very heavy and stable
Paper colour: - Off white
Age of map colour: - Original & later
Colours used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General colour appearance: - Fresh
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in bottom margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of this landmark map by Guillaume Delisle cannot be overstated. It was the first map to accurately depict the course and mouth of the Mississippi River. Much of the map was drawn from reports brought back to France from the survivor's of the La Salle expedition into the interior of North America and from information derived from the explorations of Bienville and d'Iberville. In the year preceding the publication of the map, Delisle utilised his position with the King of France to gain access to the best available information from the new world.
During this time, he compiled the geographical data from the reports of the French Jesuit Missionaries and explorer's in North America, along with Spanish manuscript maps (often copied by the Missionaries while they were acting in the service of the Spanish as spiritual guides and gaining their confidence). The result of this work were a series of 4 landmark maps of America, including his map of North America (L'Amerique Septentrionale, 1700), Canada and the Great Lakes (Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France 1703) and the Mississippi Valley & Gulf Coast (Carte de la Louisiane et du Cours du Mississipi 1708) and of course this map.
Carl Wheat called this map a "towering landmark along the path of Western cartographic development." De L'Isle's map also inlcuded greater accuracy in the Great Lakes region and in its depiction of English settlements along the East Coast. Excellent detail of the Indian villages in East Texas, based upon the reports of Iberville and the Spanish missionaries. The best depiction of the Southwest to date, with early trails & Indian tribes. Cumming described the map as "profoundly influential. This is a beautifully engraved and hand coloured map by one of the finest French cartographers of the 18th century. (Ref: Cummings; M&B; Tooley)
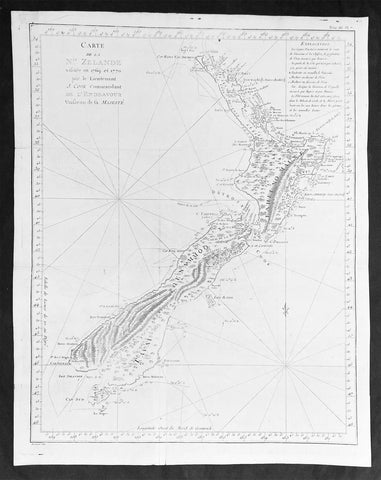
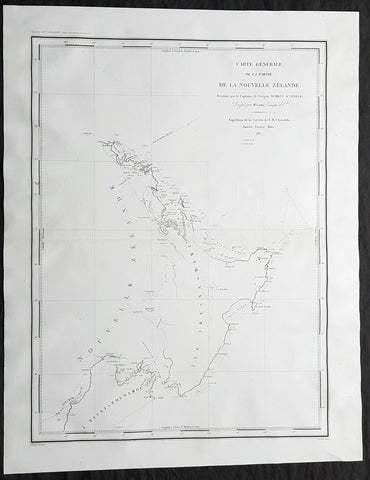
1774 Captain James Cook Antique Map, 1st Printed Chart of New Zealand
- Title : Carte de la Nle. Zelande visitée en 1769 et 1770 par le Lieutenant J. Cook Commandant de l'Endeavour vasseau de sa Majesté.
- Date : 1774
- Size: 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (520mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27004
Description:
This magnificent large original copper plate engraved scarce antique map, the first printed chart of New Zealand by Captain James Cook, during his circumnavigation of New Zealand in 1769-70, was published in the 1st French edition of Hawkeworths Voyages in 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (520mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 394mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, professional restoration of tear to center of map, no loss
Verso: - Folds as issued, professional restoration of tear to center of map, no loss
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasman\\\'s place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including \\\'Cape Maria van Diemen\\\' (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the \\\'Three Kings\\\' islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty\\\'s choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cook\\\'s party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cook\\\'s intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavour\\\'s voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cook\\\'s crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavour\\\'s return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiraltys choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
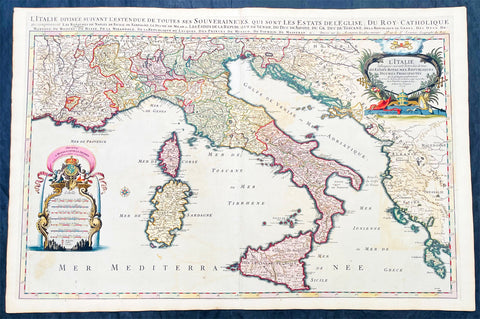
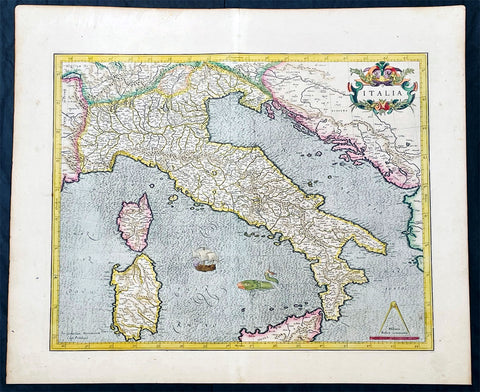
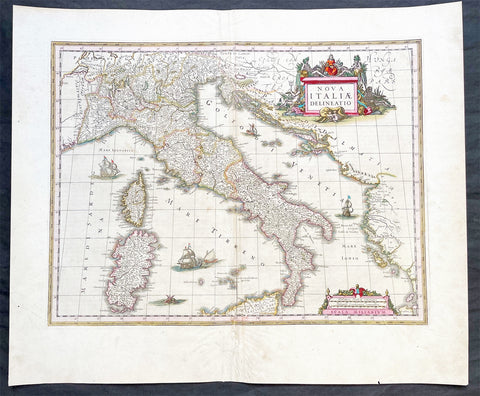
1692 Alex Jaillot Large Antique Map of Italy, Sicily - Gold Imperial Highlights
Antique Map
- Title : L' Italie Divisee Suivant Les l'estendue de tous Les Estats, Royaumes, Republiques, Duches, Principates...1692.
- Ref #: 35631
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 37 1/2in x 24 3/4in (940mm x 630mm)
- Date: 1691
- Price: $1599.00US
Description:
This original, beautifully hand coloured (with gold highlights) antique, very large map of Italy was engraved in 1692 - dated in Cartouche - and was published by Hubert Jaillot in his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
This map is beautifully hand coloured with gold highlights along country borders and the cartouches indicating it was once part of an Imperial Atlas.
The Imperial atlases were hand coloured using gold highlights and other rare colours which at the time was extremely expensive and available at the time only to royalty and the very rich.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, blue, gold
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37 1/2in x 24 3/4in (940mm x 630mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/2in x 23in (900mm x 590mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - Age toning to verso
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by Portolan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
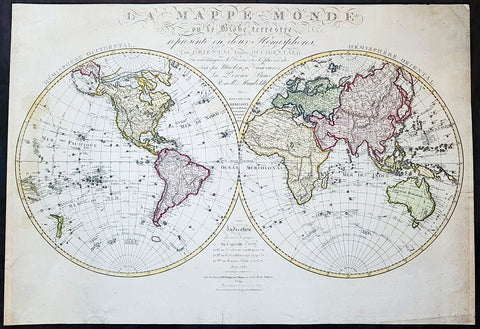
1827 Herisson Large Rare Original Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map, Capt J Cook
- Title : La mappe-monde ou le globe terrestre, représenté en deux hemisphères, l'un oriental l'autre occidental, où sont marquées les découvertes les plus récentes, faites par Mackenzie, Vancouver, La Pérouse, Bruce, Renell, Mungo Park, Joub [sic] Barrow, Franklin et Parry. Dressée par Hérisson, élève de Mr. Bonne / Indication des trois voyages de Cook et de celui de La Pérouse … … À Paris : chez Basset, 1827
- Date : 1827
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Ref #: 70815
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This impressive scarce & large scale double hemisphere original antique map, by the French cartographer Eustache Herisson, was published in 1827, dated in text.
The main feature of the map is the illustration of the tracks taken by most recent explorers of the time. From Captain James Cook, to George Vancouver in Canada, Jean-Francois la Perouse in the Pacific, Alexander Humboldt in America, John Franklin and William Parry in Canada.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Several small repairs to margin not affecting the image, age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning, repairs as noted
Background:
With the exception of the Arctic region of North America, which shows a land bridge connecting Greenland with Alaska and an inland polar sea, the landmasses are drawn with contemporary accuracy. Politically the world was a very different place. North America was still divided by the Old World major powers, Britain, France & Spain. As already noted northern Canada was still to be fully mapped, the interior of Africa was still largely unexplored by Europeans. The European settlement of Australia & New Zealand was still in its infancy Australia and the Antarctic region was still only known by the voyage of Cook some 40 years earlier. The explorers noted below were some of the 18th century adventurers responsible for filling in the cartographically unknown
Captain James Cook FRS 1728 – 1779 was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the Royal Navy. Cook made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific Ocean, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand.
Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years\' War, and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the Saint Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec. This helped bring Cook to the attention of the Admiralty and Royal Society. This notice came at a crucial moment in both Cook\'s career and the direction of British overseas exploration, and led to his commission in 1766 as commander of HM Bark Endeavour for the first of three Pacific voyages.
In three voyages Cook sailed thousands of miles across largely uncharted areas of the globe. He mapped lands from New Zealand to Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean in greater detail and on a scale not previously achieved. As he progressed on his voyages of discovery he surveyed and named features, and recorded islands and coastlines on European maps for the first time. He displayed a combination of seamanship, superior surveying and cartographic skills, physical courage and an ability to lead men in adverse conditions.
Cook was attacked and killed while attempting to kidnap Kalaniʻōpuʻu, a Hawaiian chief, during his third exploratory voyage in the Pacific in 1779. He left a legacy of scientific and geographical knowledge which was to influence his successors well into the 20th century, and numerous memorials worldwide have been dedicated to him.
Captain George Vancouver 1757 – 1798 was a British officer of the Royal Navy, best known for his 1791–95 expedition, which explored and charted North America\'s north-western Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of contemporary Alaska, British Columbia, Washington, and Oregon. He also explored the Hawaiian Islands and the southwest coast of Australia.
In Canada, Vancouver Island and the city of Vancouver are named after him, as are Vancouver, Washington, in the United States, Mount Vancouver on the Yukon/Alaska border, and New Zealand\'s sixth highest mountain
Jean François de Galaup, comte de La Perouse 1741 – 1788 was a French Naval officer and explorer whose expedition vanished in Oceania after the French government decided to complete the work of Captain james Cook.
Alexander Humboldt 1769 – 1859 was a Prussian geographer, naturalist, explorer, and influential proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher, and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt (1767–1835). Humboldt\'s quantitative work on botanical geography laid the foundation for the field of biogeography. Humboldt\'s advocacy of long-term systematic geophysical measurement laid the foundation for modern geomagnetic and meteorological monitoring.
Between 1799 and 1804, Humboldt travelled extensively in Latin America, exploring and describing it for the first time from a modern scientific point of view. His description of the journey was written up and published in an enormous set of volumes over 21 years. Humboldt was one of the first people to propose that the lands bordering the Atlantic Ocean were once joined (South America and Africa in particular). Humboldt resurrected the use of the word cosmos from the ancient Greek and assigned it to his multi-volume treatise, Kosmos, in which he sought to unify diverse branches of scientific knowledge and culture. This important work also motivated a holistic perception of the universe as one interacting entity. He was the first person to describe the phenomenon and cause of human-induced climate change, in 1800 and again in 1831, based on observations generated during his travels.
Rear-Admiral Sir John Franklin 1786 –1847 was an English Royal Navy officer and explorer of the Arctic. Franklin also served as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen\'s Land (now Tasmania) from 1837 to 1843. He disappeared on his last expedition, attempting to chart and navigate a section of the Northwest Passage in the Canadian Arctic. The icebound ships were abandoned and the entire crew perished from starvation, hypothermia, tuberculosis, lead poisoning and scurvy.
Rear Admiral Sir William Edward Parry, RN, FRS 1790 - 1855 was an English rear-admiral and Arctic explorer. His 1819 voyage through the Parry Channel was probably the most successful in the long quest for the Northwest Passage. In 1827 he attempted one of the earliest expeditions to the North Pole. He reached 82°45′ North latitude, setting the record for human exploration farthest North that stood for nearly five decades before being surpassed at 83°20′26″ by Albert Hastings Markham in 1875–1876.
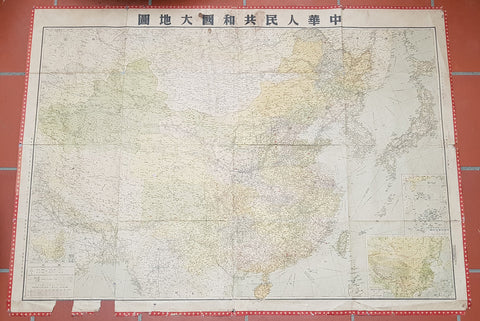
1950 Large Antique Map of the PR China - Ist Map by PRC after Revolution 1949 Rare
- Title : The Great Land and The People of China (Translated)
- Date : 1950
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Ref: 93112
- Size: 58 1/2in x 42 1/2in (1.485m x 1.080m)
Description:
This original extremely large very rare folding antique lithograph wall map of the Peoples Republic of China and surrounding countries was published by the Peoples Republic of China in 1950.
Considering the Chinese Communist State was established after the revolution of 1949, this map is one of the earliest, if not the earliest, available map of China released by the communist state and given the secretive nature of the PRC in the 1950s the rarity of this map cannot be overstated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 58 1/2in x 42 1/2in (1.485m x 1.080m)
Plate size: - 58 1/2in x 42 1/2in (1.485m x 1.080m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Loss to bottom sections of margins
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced on verso with archival tape
Background:
Following the Chinese Civil War and victory of Mao Zedongs Communist forces over the Kuomintang forces of Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek, who fled to Taiwan, Mao declared the founding of the Peoples Republic of China on October 1, 1949. Maos first goal was a total overhaul of the land ownership system, and extensive land reforms. Chinas old system of gentry landlord ownership of farmland and tenant peasants was replaced with a distribution system in favor of poor/landless peasants which significantly reduced economic inequality. Over a million landlords were executed. In Zhangzhuangcun, in the more thoroughly reformed north of the country, most landlords and rich peasants had lost all their land and often their lives or had fled. All formerly landless workers had received land, which eliminated this category altogether. As a result, middling peasants, who now accounted for 90 percent of the village population, owned 90.8 percent of the land. Mao laid heavy theoretical emphasis on class struggle, and in 1953 began various campaigns to persecute former landlords and merchants, including the execution of more powerful landlords. Drug trafficking in the country as well as foreign investment were largely wiped out.
Mao believed that socialism would eventually triumph over all other ideologies, and following the First Five-Year Plan based on a Soviet-style centrally controlled economy, Mao took on the ambitious project of the Great Leap Forward in 1958, beginning an unprecedented process of collectivization in rural areas. Mao urged the use of communally organized iron smelters to increase steel production, pulling workers off of agricultural labor to the point that large amounts of crops rotted unharvested. Mao decided to continue to advocate these smelters despite a visit to a factory steel mill which proved to him that high quality steel could only be produced in a factory. He thought that ending the program would dampen peasant enthusiasm for his political mobilization, the Great Leap Forward.
The implementation of Maoist thought in China may have been responsible for 40–70 million deaths including famine during peacetime, with the Great Leap Forward, Anti-Rightist Campaign of 1957–1958, and the Cultural Revolution. Millions died from both executions and forced labour. Because of Maos land reforms during the Great Leap Forward, which resulted in massive famines, thirty million perished between 1958 and 1961. By the end of 1961 the birth rate was nearly cut in half because of malnutrition. Active campaigns, including party purges and reeducation resulted in the imprisonment or execution of those deemed to hold views contrary to Maoist ideals. Maos failure with the Leap reduced his power in government, whose administrative duties fell to Liu Shaoqi and Deng Xiaoping.
To impose socialist orthodoxy and rid China of old elements, and at the same time serving certain political goals, Mao began the Cultural Revolution in May 1966. The campaign was far reaching into all aspects of Chinese life. Red Guards terrorized the streets as many ordinary citizens were deemed counter-revolutionaries. Education and public transportation came to a nearly complete halt. Daily life involved shouting slogans and reciting Mao quotations. Many prominent political leaders, including Liu and Deng, were purged and deemed capitalist-roaders. The campaign would not come to a complete end until the death of Mao in 1976.
Publishing in the Peoples Republic of China
Publishing in China dates from the invention of woodblock printing around the eighth century A.D. and was greatly expanded with the invention of movable clay type in the eleventh century. From the tenth to the twelfth century, Kaifeng, Meishan, Hangzhou, and Jianyang were major printing centers. In the nineteenth century, China acquired movable lead type and photogravure printing plates and entered the age of modern book and magazine printing. The largest of the early publishing houses were the Commercial Press (Shangwu Yinshuguan), established in 1897, and the China Publishing House (Zhonghua Shuju), established in 1912, both of which were still operating in 1987. Following the May Fourth Movement of 1919, publishers, especially those associated with various groups of intellectuals, proliferated. During the Chinese civil war, New China Booksellers (Xinhua Shudian) published a large amount of Marxist literature and educational materials in the communist-controlled areas. On the eve of the establishment of the People\\\'s Republic in 1949, there were over 700 New China Booksellers offices.
Between 1949 and 1952, the New China Booksellers offices scattered throughout the country were nationalized and given responsibility publishing, printing, and distribution. Also, several small private publishers were brought under joint stateprivate ownership, and by 1956 all private publishers had been nationalized. After a brief flourishing during the Hundred Flowers Campaign of 1956-57, the publishing industry came under strong political pressure in the Anti-Rightist Campaign of 1957. The industry had not fully recovered from this campaign when it was plunged into the Cultural Revolution, a period in which publishing was severely curtailed and limited mainly to political tracts supporting various campaigns. Following the Cultural Revolution, publishing again flourished in unprecedented ways. In 1982 the China National Publishing Administration, the umbrella organization of Chinese publishers, was placed under the Ministry of Culture, but actual management of the industry was directed through four systems of administration: direct state administration; administration by committees or organizations of the State Council or the party Central Committee; armed forces administration; and administration by provinces, autonomous regions, or special municipalities.
1744 Bellin & de Maurepas Large Antique Map North America Colonial United States
- Title : Carte De La Louisiane Cours Du Mississipi et Pais Voisins...N Bellin 1744
- Date : 1744
- Size: 23in x 16 1/4in (585mm x 415mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27094
Description:
This important, original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of North America and the colonial states by Nicolas Bellin in conjunction with Jean-Frédéric Phélypeaux, the Comte de Maurepas, was engraved and published in 1744, dated.
This detailed map depicts the region of Louisiana and the Mississippi River, as well as neighboring territories such as Florida, the Great Lakes, and the Gulf of Mexico. The map is richly decorated with a detailed cartouche featuring a Native American figure, various animals, and a scale bar.
The map is highly detailed and accurate, with the major waterways, coastlines, and settlements clearly marked. The topographical features such as mountains, forests, and swamps are also depicted in great detail. The map includes annotations in French, indicating the locations of various Native American tribes and European settlements.
One interesting feature of the map is the depiction of the river system, with numerous tributaries branching out from the Mississippi River. The map also includes illustrations of the mouth of the Mississippi River and various settlements along its banks.
Overall, Carte De La Louisiane Cours Du Mississipi et Pais Voisins is a beautiful and informative example of 18th-century cartography. Bellin's map reflects the geopolitical tensions of the era, as France and England were competing for control over the region, and it remains a valuable resource for historians and collectors alike.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 16 1/4in (585mm x 415mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 16 1/4in (585mm x 415mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Right margin extended from border
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The Comte de Maurepas and Nicolas Bellin were both influential figures in the French Navy during the 18th century, and they worked closely together on several important projects.
Jean-Frédéric Phélypeaux, the Comte de Maurepas, was a French statesman who served as Secretary of State for the Navy under Louis XV. He was a strong supporter of naval exploration and cartography, and he played a key role in promoting the work of cartographers such as Nicolas Bellin.
Nicolas Bellin, as mentioned earlier, was a French cartographer, hydrographer, and engineer who produced numerous maps and atlases that were highly regarded for their accuracy and detail. Bellin worked closely with the Comte de Maurepas on several projects, including the creation of the Neptune François, a collection of maps and nautical charts of the world's oceans.
The Neptune François was a major undertaking that involved the collaboration of numerous cartographers and hydrographers, including Bellin. The project was overseen by the Comte de Maurepas and was intended to provide French sailors with the most up-to-date and accurate information about the world's oceans.
Bellin's contributions to the Neptune François were extensive, and he was responsible for creating numerous maps and charts that covered a wide range of regions, including the Mediterranean, the Caribbean, and North America. His work on the project helped establish him as one of the leading cartographers of his time.
Overall, the Comte de Maurepas and Nicolas Bellin were both instrumental in advancing the field of cartography during the 18th century. Through their collaboration on projects such as the Neptune François, they helped to establish the French Navy as a leading authority on maritime exploration and mapping.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1753 Bellin Antique Map of Australia & New Zealand - Carte Reduite.....Australes
- Title : Carte Reduite des Terres Australes pour Servir a l'Histoire des Voyages...1753
- Ref #: 17027
- Size: 13 1/2in x 10in (340mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of Australia - one of the earliest, near complete maps, dedicated to the Island Continent - was engraved in 1753 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin - date engraved in the title -and was published in Antoine Prevosts Histoire Generale Des Voyages.
Background: This is one of the few 18th century maps to focus on the Australian continent prior to Cook's famous first voyage from 1768-1771. Mainland Australia is connected to both Tasmania (Terre de Van Diemen) and Papua New Guinea (Nouv. Guinee). Along the imaginary eastern coastline is a note that reads: "I suppose that the land of Diemen can join with the land of the Holy Ghost, but this is without proof." A partial coastline of New Zealand is shown peeking out of the corner of the map, with a note that it was discovered by Abel Tasman in 1642 and speculation that it might be part of a great southern continent. This is an important map of Australia depicting the interesting theories made prior to exploration of the region later in the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 10in (340mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (295mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1753 Bellin Antique Map of Australia & New Zealand - Carte Reduite.....Australes
- Title : Carte Reduite des Terres Australes pour Servir a l'Histoire des Voyages...1753
- Ref #: 17040
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Australia - one of the earliest, near complete maps, dedicated to the Island Continent - was engraved in 1753 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin - date engraved in the title -and was published in the 1753 edition of Prevosts Histoire Generale Des Voyages.
Background: This is one of the few 18th century maps to focus on the Australian continent prior to Cook's famous first voyage from 1768-1771. Mainland Australia is connected to both Tasmania (Terre de Van Diemen) and Papua New Guinea (Nouv. Guinee). Along the imaginary eastern coastline is a note that reads: "I suppose that the land of Diemen can join with the land of the Holy Ghost, but this is without proof." A partial coastline of New Zealand is shown peeking out of the corner of the map, with a note that it was discovered by Abel Tasman in 1642 and speculation that it might be part of a great southern continent. This is an important map of Australia depicting the interesting theories made prior to exploration of the region later in the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (295mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1695 Gerard Valk Antique Map of North & South America, California as an Island
- Title : L'Amerique Septentrionale & Meridionale divisee en ses principales parties
- Ref #: 35624
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Size: 24 1/4in x 20 3/4in (615mm x 530mm)
- Date: 1695
Description:
This original, copper plate engraved scarce antique map of the Americas, showing California as an Island, was published in the last decade of the 18th century in ca 1695.
This map is relatively rare as it was not included in any standard atlas but was optional, allowing the buyer to choose this along with other engraved map, to include in a bespoke atlas.
This map has undergone some professional restoration, it is complete and has been re-enforced in places on the verso along existing creases to the left and right side center of the map (please see images) as well as re-enforcement along centerfold and corners. Please see images and description below. Priced with condition in mind.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - White
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/4in x 20 3/4in (615mm x 530mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 3/4in (590mm x 505mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top right & bottom left corners of margins restored, age toning, several small repairs to margins not affecting the images
Plate area: - Creasing to image, centerfold re-joined
Verso: - Old creasing re-enforced with archival tape to verso, creasing, age toning
Background:
Scarce map of America, published in Amsterdam by Gerard Valk. Valk's map of California shows many of the most fascinating myths of the 17th Century. California is shown as an island on the so-called "second Sanson Model." A massive land bridge extends from just west of Capo Blanco on the northern California coastline to Niphon, a curious adaptation of the legend of Compagnie Land (shown here as a place name -- Terre de la Compagne) and the continuous land bridge from America to Asia, although adding the Detroit de Tzungaar (Strait of Tzungaar), a very rarely mentioned mythical Strait between two islands of Japan.
The Great Lakes are oddly configured, with Lake Superior and Lake Michigan open ended to the West. The Mississippi River is very ill conceived, pre-dating the radical improvements which would come with Guilluame De L'Isle's map of North America of 1700 and Carte du Mexique of 1703.
The fine allegorical cartouches depict the booming trade then being conducted by Europeans in the New World.
Valk, Gerard 1651 - 1726
Gerard Valk was a prominent Dutch engraver, publisher, and art dealer during the late 17th and early 18th centuries. He is best known for his contributions to the field of cartography and his collaborations with renowned artists and mapmakers of his time.
Valk was born on April 6, 1651, in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Little is known about his early life and education, but it is believed that he received training as an engraver, possibly under the tutelage of his father, Balthasar Valk, who was also an engraver and publisher.
In the late 1670s, Gerard Valk established his own publishing firm in Amsterdam, specializing in the production of maps, atlases, and prints. He quickly gained recognition for his skill as an engraver and his ability to produce high-quality, detailed maps. Valk's maps were often based on the work of renowned cartographers of the time, such as Frederik de Wit and Nicolaes Visscher, whose plates he acquired and reprinted.
Valk's maps covered a wide range of geographical regions, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. His maps were meticulously crafted, featuring elaborate cartouches, decorative elements, and accurate geographic information. He also collaborated with notable artists and engravers, such as Jan Luyken and Romeyn de Hooghe, who provided illustrations and embellishments for his publications.
Apart from cartography, Valk also published and sold prints of various subjects, including portraits, landscapes, historical scenes, and genre paintings. He catered to a diverse clientele, ranging from collectors and scholars to wealthy individuals and institutions.
Valk's publishing business flourished, and he enjoyed considerable success and acclaim during his lifetime. His maps and prints were highly sought after for their quality and accuracy. He maintained a strong network of contacts throughout Europe, including fellow publishers, mapmakers, and merchants, which allowed him to expand his business and reach a wider market.
Gerard Valk passed away on August 26, 1726, in Amsterdam, leaving behind a legacy as a skilled engraver, publisher, and contributor to the development of cartography. His work played a significant role in disseminating geographical knowledge and capturing the aesthetic beauty of maps during the late 17th and early 18th centuries. Today, Valk's maps and prints are considered valuable collectors' items, cherished for their historical and artistic value.
1691 Alex Jaillot Large Antique Map of South America, Gold Imperial Highlights
Antique Map
- Title : Amerique Meridionale Divisee en ses Principales Parties...1691
- Ref #: 35630
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 37 1/2in x 24 3/4in (940mm x 630mm)
- Date: 1691
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured (with gold highlights) antique very large map of South America was engraved in 1691 - dated in Cartouche - and was published by Hubert Jaillot in his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
This map is beautifully hand coloured with gold highlights along country borders and the cartouches indicating it was once part of an Imperial Atlas.
The Imperial atlases were hand coloured using gold highlights and other rare colours which at the time was extremely expensive and available at the time only to royalty and the very rich.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, blue, gold
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37 1/2in x 24 3/4in (940mm x 630mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/2in x 23in (900mm x 590mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning along margins
Plate area: - Crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The map include lines of latitude and longitude, some topographical details, location of settlements, rivers, and lakes (including the lakes Parime, thought to be where the fabulous El Dorado was located) as well as the boundaries of the possessions of the European claimants to South America.
Extremely decorative cartouche with dedication to Le Dauphin, and his coat of arms in top.
After Nicolas Sanson, Hubert Jaillot and Pierre Duval were the most important French cartographers of the seventeenth & eighteenth centuries. Jaillot, originally a sculptor, became interested in geography after his marriage to the daughter of Nicolas Berey (1606-65), a famous map colourist, and went into partnership in Paris with Sanson's sons. There, from about 1669, he undertook the re-engraving, enlarging and re-publishing of the Sanson maps in sheet form and in atlases, sparing no effort to fill the gap in the map trade left by the destruction of Blaeu's printing establishment in Amsterdam in 1672. Many of his maps were printed in Amsterdam (by Pierre Mortier) as well as in Paris. One of his most important works was a magnificent sea atlas, Le Neptune François, published in 1693 and compiled in co-operation with J D Cassini. This was re-published shortly afterwards by Pierre Mortier in Amsterdam with French, Dutch and English texts, the charts having been re-engraved. Eventually, after half a century, most of the plates were used again as the basis for a revised issue published by J N Bellin in 1753.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1750 J N Bellin Large Antique World Map on Mercators Projection - 27091
- Title : An Essay of a New and Complet Map Containing the Known Part of the Terrestial Globe by N Bellin....MDDCL
- Date : 1750
- Size: 30 1/2in x 22 1/2in (825mm x 570mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27091
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on Mercators Projection by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved by Jacobus van der Schley in 1750 - dated in the title - and was published in Dutch/English by Pierre d Hondt, publisher, operated out of the Hague.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30 1/2in x 22 1/2in (825mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin extended from plate -mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
First edition of Bellins large mid-18th century world map, published in Paris. This map pre-dates the major world discoveries of the late 18th century including the North West coast of America, the Sandwich Islands, and the Voyages of Capt Cook soon to map the East Coast of Australia & NZ.
This edition is most noteworthy for its marvelous early projection of Australia and New Zealand, each with largely speculative coastlines. Australia is still attached to New Guinea and has several notes of early exploration shown. New Zealand is barely known and with only a portion of its western coastline.
No sign of Antarctica and the NW Coast of America includes the first notes of Russian exploration.
In North America Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de l’Ouest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the “Archipel de Nord”.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labelled “Nouvelle Holland”, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1775 Thomas Jefferys Antique Map North America & Colonial States, Pre Revolution
- Title : North America from the French of Mr. D Anville Improved with the English Surveys made Since the Peace NB. The Boundaries of the Provinces since the conquest of Canada are laid down as settled by the King in Council..London Printed for Robt. Sayer & J Bennett Map & Printseller, No 53 Fleet Street as the act directs 10 June 1775
- Size: 20 1/2in x 18 1/2in (510mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1775
- Ref #: 93045
Description:
This very important scarce original copper-plate engraved antique map of North America & the colonial States, is sectioned and laid down on linen as issued. The map by Thomas Jefferys - after JB D Anville, was engraved in 1775 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published by Robert Sayer and John Bennett, London.
Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d Anville was the successor to Guillaume De l Isle and maintained the rigorous standard for accuracy that De l Isle had established. D Anville was the last French mapmaker to establish an international reputation, superior to all his contemporaries, with respect shown by the English and other cartographers and publishers during an era when England & France were often at conflict with one another.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 18 1/2in (510mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 18 1/2in (510mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom right margin cropped to border
Plate area: - Spotting
Verso: - Linen strong and robust, spotting
Background:
This third state is the second edition of the map issued after the conclusion of the French and Indian War. The map shows the Colonies on the eve of the American Revolutionary War. A note in the title cartouche states that the Boundaries of the Provinces since the conquest of Canada are laid down as settled by the King in Council. This note appears in the second state as well. The map shows the various colonial claims running to the Mississippi, but the colourist has conservatively limited the borders to the Appalachian Mountains. The boundary between New England and Virginia as established by Charter in 1609 is shown, although the date is omitted.
The map is rich with details west of the Appalachians, including Indian Tribes, early French and English forts and other contemporary information on the eve of the revolution. Main is named, but [New] Hampshire takes up all of Vermont. Massachusetts Bay and Delaware Bay are named, as are East and West Florida. The region west of the Mississippi is dominated by Spanish Louisiana Territory, with the lands between the Mississippi and the Appalachians controlled by Indian Tribes. A nice wide margin example of this map of the Colonies, which was included in Jefferys American Atlas prior to and during the American Revolutionary War.
1785 De Vaugondy & Jefferson Antique Early Map of The United States of America
- Title : Etats-Unis de l'Amerique Septentrionale avec les Isles Royale, de Terre Neuve de St. Jean, l'Acadie &c. 1785 M. Robert de Vaugondy....Boudet....
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93513
- Size: 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved very important, early & scarce antique early map of the United States (Etats-Unis De L Amerique), during what is know as the Confederation Period, by Robert De Vaugondy was published by the French printer Antoine Boudet (1715 - 1787) for the supplement of de Vaugondys Atlas Universal
This scarce first state map is very important to the formation of the United States of America. The map is the first to describe what is know as the Jeffersonian Ordinance, showing the new international borders of the fledgling United States, the inclusion of the original 13 states in the bottom right text box (the first map to do so) along with the inclusion of Michigan, ratified under the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
The successor to De Vaugondy, Charles Francois Delamarche (1740 - 1817) was a known correspondent to Thomas Jefferson and along with the printer Boudet would have played an important part in the publication of this map. The Ordinance of 1784 was a plan to outline the new territories and states, that would eventually make up the foundation of the United States, ratified by the Treaty of Paris. Given that this map was engraved in 1785 or possibly earlier and that Delamarche was a friend of Jefferson, it is not a stretch to believe that he was one of the first, if not the first, to map the new country of the United States (Etats-Unis De L Amerique)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (670mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25 1/2in x 19 1/2in (650mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Confederation Period was the era of United States history in the 1780s after the American Revolution and prior to the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1781, the United States ratified the Articles of Confederation and prevailed in the Battle of Yorktown, the last major land battle between British and American forces in the American Revolutionary War. American independence was confirmed with the 1783 signing of the Treaty of Paris. The fledgling United States faced several challenges, many of which stemmed from the lack of a strong national government and unified political culture. The period ended in 1789 following the ratification of the United States Constitution, which established a new, more powerful, national government.
The Articles of Confederation established a loose confederation of states with a weak federal government. An assembly of delegates acted on behalf of the states they represented. This unicameral body, officially referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, had little authority, and could not accomplish anything independent of the states. It had no chief executive, and no court system. Congress lacked the power to levy taxes, regulate foreign or interstate commerce, or effectively negotiate with foreign powers. The weakness of Congress proved self-reinforcing, as the leading political figures of the day served in state governments or foreign posts. The failure of the national government to handle the challenges facing the United States led to calls for reform and frequent talk of secession.
The Treaty of Paris left the United States with a vast territory spanning from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mississippi River. Settlement of the trans-Appalachian territories proved difficult, in part due to the resistance of Native Americans and the neighboring foreign powers of Great Britain and Spain. The British refused to evacuate US territory, while the Spanish used their control of the Mississippi River to stymie Western settlement. In 1787, Congress passed the Northwest Ordinance, which set an important precedent by establishing the first organized territory under the control of the national government.
After Congressional efforts to amend the Articles failed, numerous national leaders met in Philadelphia in 1787 to establish a new constitution. The new constitution was ratified in 1788, and the new federal government began meeting in 1789, marking the end of the Confederation Period. Some historians believe that the 1780s were a bleak, terrible time for the US, while others have argued that the period was actually stable and relatively prosperous.
1930 Evan Gill Antique Map of Missions in PNG - Brother to Eric & MacDonald Gill - Unique
- Title : The Territory of Papua Eastern Portion shoqing the Stations of The Anglican Missions...Evan R Gill 1930.
- Size: 34in x 19in (865mm x 485mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1930
- Ref #: 92580
Description:
This unique manuscript original antique map of Papua New Guinea ,and the Stations of the Anglican Missions in the eastern portion of the country, was drawn by Evan Robertson Gill, brother of the Arts and Crafts artist Eric Gill and map-maker Macdonald - Max - Gill in 1930 - dated.
The maps is also signed and addressed on the verso of the map by Evan.
This map was purchased a number of years ago but its significance only became apparent later with the direct connection to Evans (in)famous brother Eric and his equally well known brother MacDonald Gill, known as Max, and his famous map of the London Underground map known as the Wonderground Map.
Our research has been unable to find any other maps by Evan but we were understandably excited once the connection was made to his three brothers from the artistic and PNG missionary connection.
The map must have been commissioned by Evans brother Archdeacon Stephen Romney Gill, missionary in PNG during the first half of the 20th century, who famously survived in the Lae area of New Guinea, near the Kokoda trail, during the occupation of PNG by the Japanese in 1942/3.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 34in x 19in (865mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 34in x 19in (865mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repairs to tears in left margin, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Repairs to tears in left margin, no loss
Background:
Gill, Evan Robertson 1892 - 1968. Gill was born in Brighton England one of thirteen children. His father Arthur Gill was a clergyman with a family background of missionary work in the South Seas. Evan had three well known brothers Eric Gill the (in)famous Arts and Crafts artist, Macdonald Gill (Max) the decorative map maker - famous for designing the 1914 Wonderground Map of the London Underground - and Stephen Romney Gill 1886 - 1954, Anglican Archdeacon in Papua New Guinea in the early 20th century and during the occupation of PNG by the Japanese in 1942/3.
His brothers Stephen & Dr Cecil Gill, were missionaries in Papua New Guinea from 1905 until the 1950s after their Grandfather George Gill & Great Uncle William Gill, both missionaries in the Cook Islands.
Leslie MacDonald Gill 1884 – 1947 commonly known as MacDonald Gill or Max Gill, was a noted early-twentieth century graphic designer, cartographer, artist and architect.
Born in Brighton, Gill was the younger brother of Eric Gill, one of the leading figures of the Arts and Crafts movement.
In 1914 his Wonderground Map, commissioned by Frank Pick, and hung at every station, helped to save the London Underground by presenting an accurate map which also had a humorous side in cartoon style. Produced in poster form, it was also made available for sale to members of the public and proved to be very popular. Elder brother Eric, who at that time was engaged in a commission for Westminster Cathedral, was included at the bottom of the map. Gill showed three works at the first annual exhibition of the newly-formed Society of Graphic Art in 1921.
He was the designer of the standard upper case lettering used on headstones and war memorials by the Imperial War Graves Commission. But it is perhaps his illustrated maps for which he is most well known. These maps have featured in a series of exhibitions including Magnificent Maps exhibition in 2010 at the British Library, an exhibition MacDonald Gill, Out of the Shadows in 2011 at the University of Brighton and at the Mind the Map exhibition in 2012 at the London Transport Museum.
Arthur Eric Rowton Gill 1882 – 1940 was an English sculptor, typeface designer, and print-maker, who was associated with the Arts and Crafts movement. He is a controversial figure, with his well-known religious views and subject matter generally viewed as being at odds with his sexual behaviour.
Gill was born in 1882 in Hamilton Road, Brighton and grew up in the Brighton suburb of Preston Park. One of twelve children, he was the elder brother of MacDonald Max Gill (1884–1947), the graphic artist. In 1897 the family moved to Chichester. He studied at Chichester Technical and Art School, and in 1900 moved to London to train as an architect with the practice of W.D. Caroe, specialists in ecclesiastical architecture.
Frustrated with his training, he took evening classes in stone-masonry at the Westminster Technical Institute and in calligraphy at the Central School of Arts and Crafts, where Edward Johnston, creator of the London Underground typeface, became a strong influence. In 1903 he gave up his architectural training to become a calligrapher, letter-cutter and monumental mason.
Working from Ditchling in Sussex, where he lived with his wife, in 1910 Gill began direct carving of stone figures. These included Madonna and Child (1910), which English painter and art critic Roger Fry described in 1911 as a depiction of pathetic animalism, and Ecstasy (1911). Such semi-abstract sculptures showed Gill\'s appreciation of medieval ecclesiastical statuary, Egyptian, Greek and Indian sculpture, as well as the Post-Impressionism of Cézanne, van Gogh and Gauguin.
His first public success was Mother and Child (1912). A self-described disciple of the Ceylonese philosopher and art historian Ananda Coomaraswamy, Gill was fascinated during this period by Indian temple sculpture. Along with his friend and collaborator Jacob Epstein, Gill planned the construction in the Sussex countryside of a colossal, hand-carved monument in imitation of the large-scale Jain structures at Gwalior Fort in Madhya Pradesh, to which he had been introduced by William Rothenstein.
In 1914 Gill produced sculptures for the stations of the cross in Westminster Cathedral. In the same year he met the typographer Stanley Morison. After the war, together with Hilary Pepler and Desmond Chute, Gill founded The Guild of St Joseph and St Dominic at Ditchling. There his pupils included David Jones, who soon began a relationship with Gills daughter, Petra.
Gill designed several war memorials after the First World War, including the Grade II* listed Trumpington War Memorial. Commissioned to produce a war memorial for the University of Leeds, Gill produced a frieze depicting Jesus driving the money-changers from the temple, showing contemporary Leeds merchants as the money-changers. Gill contended that the money men were a key cause of the war. This is at the Michael Sadler Building at the University.
In 1924, Gill moved to Capel-y-ffin in Powys, Wales, where he established a new workshop, to be followed by Jones and other disciples. In 1928, he set up a printing press and lettering workshop in Speen, Buckinghamshire. He took on a number of apprentices, including David Kindersley, who in turn became a successful sculptor and engraver, and his nephew, John Skelton, noted as an important letterer and sculptor. Other apprentices included Laurie Cribb, Donald Potter and Walter Ritchie. Others in the household included Gills two sons-in-law, Petra\'s husband Denis Tegetmeier and Joanna\'s husband Rene Hague.
In 1928–9, Gill carved three of eight relief sculptures on the theme of winds for Charles Holdens headquarters for the London Electric Railway (now Transport for London) at 55 Broadway, St James. He carved a statue of the Virgin and Child for the west door of the chapel at Marlborough College.
In 1932, Gill produced a group of sculptures, Prospero and Ariel and others for the BBCs Broadcasting House in London. In 1934, Gill visited Jerusalem where he worked at the Palestine Archaeological Museum (now the Rockefeller Museum). He carved a stone bas-relief of the meeting of Asia and Africa above the front entrance together with ten stone reliefs illustrating different cultures and a gargoyle fountain in the inner courtyard. He also carved stone signage throughout the museum in English, Hebrew and Arabic.
Gill was commissioned to produce a sequence of seven bas-relief panels for the façade of The People\'s Palace, now the Great Hall of Queen Mary University of London, which opened in 1936. In 1937, he designed the background of the first George VI definitive stamp series for the post office. In 1938 Gill produced The Creation of Adam, three bas-reliefs in stone for the Palace of Nations, the League of Nations building in Geneva, Switzerland. During this period he was made a Royal Designer for Industry, the highest British award for designers, by the Royal Society of Arts and became a founder-member of the Faculty of Royal Designers for Industry when it was established in 1938. In April 1937, Gill was elected an Associate member of the Royal Academy.
Gills only complete work of architecture was St Peter the Apostle Roman Catholic Church in Gorleston, built in 1938–39.
1650 Jan Jansson Large Rare Antique Map of India and The Bay of Bengal
- Title : Sinus Gangeticus Vulgo Golfo De Bengala
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 60604
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Description:
This exceedingly impressive hand coloured original antique map of the Bay of Bengal, India - stretching from Sri Lanka to the west coast of Thailand - was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris. There were far fewer editions of this atlas published than Janssons more prevalent Atlas Novus.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Very light spotting
Verso: - Very light spotting
Background:
Maps of India, much distorted in shape, appear in most world atlases from the time of Ptolemy, the earliest usually showing India as a relatively small extension of Southern Asia, dominated by the very large island of Taprobana (Ceylon). In later sixteenth-century maps de Jode, Ortelius and Mercator gave a much improved outline of both lands but India was still shown too small in relation to the whole continent. Most publishers in the seventeenth century continued to issue maps but with little improvement in detail until about 1719 when a French Jesuit priest, Father Jean Bouchet, compiled an accurate map of South India, subsequently used by G. Delisle (1723), Homann Heirs (1735) and by J. B. B. d'Anville, then the French East India Company's cartographer, as the basis for his greatly improved maps in 1737 and 1752.
In the next decade Alexander Dalrymple published a collection of newly surveyed coastal charts and plans of ports and, about the same time, in 1764, James Rennell, a young British Army officer who showed a remarkable aptitude for surveying, was appointed - at the age of 21- Surveyor General of Bengal; he immediately set in motion a comprehensive survey of the Company's lands, subsequently publishing maps of Bengal and other provinces which eventually formed The &ngal Atlas (1779). His other works included a Map of Hindoustan (1782-85) and The Provinces of Delhi, Agra etc and the Indian Peninsula (1788-94). These maps by Reunell provided the basis for a Trigonometrical Survey of India which was initiated in 1802 and for splendid maps published in London by Cary, the Arrowsmiths (1804-22) and the Wylds. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1748 J N Bellin Large Antique World Map on Mercators Projection - 27007
- Title : Essay d une Carte Reduite Contenant les parties connuees Du Globe Terrestre...1748
- Date : 1748
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27007
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on Mercators Projection was engraved in 1748 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin - dated in the title.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (710mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin extended from plate -mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
First edition of Bellins large mid-18th century world map, published in Paris. This map pre-dates the major world discoveries of the late 18th century including the North West coast of America, the Sandwich Islands, and the Voyages of Capt Cook soon to map the East Coast of Australia & NZ.
This edition is most noteworthy for its marvelous early projection of Australia and New Zealand, each with largely speculative coastlines. Australia is still attached to New Guinea and has several notes of early exploration shown. New Zealand is barely known and with only a portion of its western coastline.
No sign of Antarctica and the NW Coast of America includes the first notes of Russian exploration.
In North America Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de l’Ouest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the “Archipel de Nord”.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labelled “Nouvelle Holland”, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1720 Herman Moll Large Antique Map of The Netherlands - 7 x Town Plans Amsterdam
- Title : A New and Exact Map of the United Provinces, or Netherlands &c. According to the Newest and Most Exact Observations by Herman Moll Geographer
- Size: 41in x 25in (1.04m x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1720
- Ref #: 93007
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Netherlands by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 41in x 25in (1.02m x 635mm)
Plate size: - 39 1/4in x 24 1/2in (1.00m x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issyed
Verso: - Backed onto contemporary paper
Background:
An attractive, large scale map of The Netherlands or the United Provinces by the highly regarded cartographer and engraver Herman Moll. on the right-hand side views of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Middelburg, Utrecht, Groningen, Het Loo Palace and a plan of the ancient Roman Castle at the mouth of the Rhine river Arx Britannica (Huis Britten, Brittenberg). The upper left corner of the map has an inset map of the coasts, sands and banks of the North Sea, the stretch of water that lies between England and The Netherlands. Moll dedicates his map to ‘The Right Hon Charles Lord Viscount of Townsend &c one of his Majesty’s Principal Secretaries of State’
This magnificent map was printed by John Bowles of Cornhill, London and published in Moll’s 1719 New and Complete Atlas, but it may also have been separately issued earlier. Moll came to London probably from Bremen around 1678 and by 1688 he had his own shop in Vanley\'s Court in London\'s Blackfriars, between 1691 and 1710 at the corner of Spring Gardens and Charing Cross, when he moved to Beech Street where he remained until his death. In 1701 he published his first work A System of Geography. He was publishing atlases and separately issued maps, and from 1710 was also known as a maker of pocket globes. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, M&B)
1650 Jan Jansson Antique Map Island of Java, Indonesia - Dutch East India Co
- Title: Insulae Java Cum Parte insularum Borneo Sumatrae
- Date: 1650
- Ref: 60603
- Size: 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large elegant & very impressive hand coloured original antique map, a sea chart of the Indonesian Island of Java including Sumatra, Borneo and Bali was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 3/4in (520mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair & ink notations
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Java & the port of Batavia was at the time of publication of the utmost importance to the Dutch East India Company and its domination of the Spice Trade.
This elegant chart focuses on the islands coast with the lack of detail on the interior correctly reflecting the lack of knowledge (or possible lack of importance) to the Dutch, who's primary concern was the sea and sea charts used in the trade of the ever lucrative Spice Trade.
The Dutch capital in the East Indies is Batavia (Jakarta) located on the NW coast. The beautiful chart is richly embellished with two fine cartouche featuring local Javanese warrior and Chinese merchants flanking the title and Neptune and mermaids surrounding the scale of miles... The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia. It was the second multinational corporation in the world (the British East India Company was founded two years earlier) and the first company to issue stock. It was also arguably the first mega-corporation, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, coin money, and establish colonies.
Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asian trade on 4,785 ships, and netted for their efforts more than 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. By contrast, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882,412 people from 1500 to 1795, and the fleet of the English (later British) East India Company, the VOC’s nearest competitor, was a distant second to its total traffic with 2,690 ships and a mere one-fifth the tonnage of goods carried by the VOC. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century.
Having been set up in 1602, to profit from the Malukan spice trade, in 1619 the VOC established a capital in the port city of Batavia (now Jakarta) on the Indonesian Island of Java. Over the next two centuries the Company acquired additional ports as trading bases and safeguarded their interests by taking over surrounding territory. It remained an important trading concern and paid an 18% annual dividend for almost 200 years.
Weighed down by corruption in the late 18th century, the Company went bankrupt and was formally dissolved in 1800, its possessions and the debt being taken over by the government of the Dutch Batavian Republic. The VOC's territories became the Dutch East Indies and were expanded over the course of the 19th century to include the whole of the Indonesian archipelago, and in the 20th century would form Indonesia. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1696 Alexis Hubert Jaillot Large Antique Map of Asia - Saudi Arabia to Australia
- Title : L' Asie divisee en ses Principales Regions....Hubert Jaillot....1696
- Ref #: 17022
- Size: 35 1/2in x 23in (900mm x 585mm)
- Date : 1696
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This very large original hand coloured antique map of Asia, from Arabia to the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia, was engraved in 1696 - dated in title - and was published by Alexis Hubert Jaillot in his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 35 1/2in x 23in (900mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 22 1/2in (875mm x 570mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margin
Plate area: - Re-enforced along centerfold, light age toning, old ink text to bottom of map
Verso: - Soiling
Background:
The map include lines of latitude and longitude, some topographical details, location of settlements, rivers, and lakes (including the lakes Parime, thought to be where the fabulous El Dorado was located) as well as the boundaries of the possessions of the European claimants to South America.
Extremely decorative cartouche with dedication to Le Dauphin, and his coat of arms in top.
After Nicolas Sanson, Hubert Jaillot and Pierre Duval were the most important French cartographers of the seventeenth & eighteenth centuries. Jaillot, originally a sculptor, became interested in geography after his marriage to the daughter of Nicolas Berey (1606-65), a famous map colourist, and went into partnership in Paris with Sanson's sons. There, from about 1669, he undertook the re-engraving, enlarging and re-publishing of the Sanson maps in sheet form and in atlases, sparing no effort to fill the gap in the map trade left by the destruction of Blaeu's printing establishment in Amsterdam in 1672. Many of his maps were printed in Amsterdam (by Pierre Mortier) as well as in Paris. One of his most important works was a magnificent sea atlas, Le Neptune François, published in 1693 and compiled in co-operation with J D Cassini. This was re-published shortly afterwards by Pierre Mortier in Amsterdam with French, Dutch and English texts, the charts having been re-engraved. Eventually, after half a century, most of the plates were used again as the basis for a revised issue published by J N Bellin in 1753.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1674 Alex Jaillot Large Antique 1st edition Map of Africa - L Afrique Divisee
- Title : L Afrique Divisee Suivant l'Estendue de ses Principales Parties...Alexis Hubert Jaillot...1674
- Ref #: 50667
- Size: 36in x 24 1/2in (915mm x 620mm)
- Date : 1674
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large, exquisitely hand coloured, original antique 1st edition map of Africa by Alexis Hubert Jaillot - after Nicolas Sanson - was engraved in 1674 - the date is engraved in the scale cartouche.
This is a beautifully presented map, fantastic colour on sturdy & heavy paper with a deep clear impression, signifying a very early pressing.
This 1st edition map is not to be confused with the later smaller more common version of the map published by A.H. Jaillot. There are 5 editions of this map published in 1674, 1685, 1690, 1692 & 1695.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, orange.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 36in x 24 1/2in (915mm x 620mm)
Plate size: - 35in x 23in (890mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins, bottom margin corners cropped
Plate area: - Light age toning & creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning & creasing along centerfold
Background: Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
After Nicolas Sanson, Hubert Jaillot and Pierre Duval were the most important French cartographers of the seventeenth centuries. Jaillot, originally a sculptor, became interested in geography after his marriage to the daughter of Nicolas Berey (1606-65), a famous map colourist, and went into partnership in Paris with Sanson's sons. There, from about 1669, he undertook the re-engraving, enlarging and re-publishing of the Sanson maps in sheet form and in atlases, sparing no effort to fill the gap in the map trade left by the destruction of Blaeu's printing establishment in Amsterdam in 1672. Many of his maps were printed in Amsterdam (by Pierre Mortier) as well as in Paris. One of his most important works was a magnificent sea atlas, Le Neptune François, published in 1693 and compiled in co-operation with J D Cassini. This was re-published shortly afterwards by Pierre Mortier in Amsterdam with French, Dutch and English texts, the charts having been re-engraved. Eventually, after half a century, most of the plates were used again as the basis for a revised issue published by J N Bellin in 1753.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1880s Alphonse & Jules Lebegue 21in x 12in Diameter Antique Desk Globe
- Title : Globe Terrestre J Lebegue & Cie Editeurs 36 Rue Nenve, 36 Bruxelles
- Size: 12in (305mm) Diameter Globe/Standing 21in (530mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1880s
- Ref #: 30072
Description:
This fantastic original antique 12in (305mm) Diameter Desk Globe, standing 21in (530mm), was made by the French Publishing Company of Alphonse & Jules Lebegue, Belgium & Paris in the 1880s.
Globes that have survived are rare, as most globes constructed in history have either been damaged or literally thrown away. The globe itself has sustained some damage but is overall stable and sturdy. The wooden stand along with the globe brass ring are in excellent condition. The specific damage to the globe is:
- Dent and damage between Indonesia and Japan
- Dent and damage off the coast of western South America
- Small dent in mid Pacific
- Light abrasion at north Pole
- Overall browning.
But even with the above this is a wonderful piece of cartographic history.
Total Dimensions;
Globe Diameter: 12in (305mm
Standing Complete: 21in (530mm)
Width of Stand: 19in (480mm)
Weight: 5.5kg
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in (305mm) Diameter Globe/Standing 21in (530mm)
Plate size: - 12in (305mm) Diameter Globe/Standing 21in (530mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see description above
Plate area: - Please see description above
Verso: - Please see description above
Background:
A globe is a spherical model of Earth, of some other celestial body, or of the celestial sphere. Globes serve similar purposes to maps, but unlike maps, do not distort the surface that they portray except to scale it down. A globe of Earth is called a terrestrial globe. A globe of the celestial sphere is called a celestial globe.
A globe shows details of its subject. A terrestrial globe shows land masses and water bodies. It might show nations and prominent cities and the network of latitude and longitude lines. Some have raised relief to show mountains. A celestial globe shows stars, and may also show positions of other prominent astronomical objects. Typically it will also divide the celestial sphere up into constellations.
The word globe comes from the Latin word globus, meaning sphere. Globes have a long history. The first known mention of a globe is from Strabo, describing the Globe of Crates from about 150 BC. The oldest surviving terrestrial globe is the Erdapfel, wrought by Martin Behaim in 1492. The oldest surviving celestial globe sits atop the Farnese Atlas, carved in the 2nd century Roman Empire.
The sphericity of the Earth was established by Greek astronomy in the 3rd century BC, and the earliest terrestrial globe appeared from that period. The earliest known example is the one constructed by Crates of Mallus in Cilicia (now Çukurova in modern-day Turkey), in the mid-2nd century BC.
No terrestrial globes from Antiquity or the Middle Ages have survived. An example of a surviving celestial globe is part of a Hellenistic sculpture, called the Farnese Atlas, surviving in a 2nd-century AD Roman copy in the Naples Archaeological Museum, Italy.
Early terrestrial globes depicting the entirety of the Old World were constructed in the Islamic world. According to David Woodward, one such example was the terrestrial globe introduced to Beijing by the Persian astronomer, Jamal ad-Din, in 1267.
The earliest extant terrestrial globe was made in 1492 by Martin Behaim (1459–1537) with help from the painter Georg Glockendon. Behaim was a German mapmaker, navigator, and merchant. Working in Nuremberg, Germany, he called his globe the Nürnberg Terrestrial Globe. It is now known as the Erdapfel. Before constructing the globe, Behaim had traveled extensively. He sojourned in Lisbon from 1480, developing commercial interests and mingling with explorers and scientists. In 1485–1486, he sailed with Portuguese explorer Diogo Cão to the coast of West Africa. He began to construct his globe after his return to Nürnberg in 1490.
Another early globe, the Hunt–Lenox Globe, ca. 1510, is thought to be the source of the phrase Hic Sunt Dracones, or Here be dragons. A similar grapefruit-sized globe made from two halves of an ostrich egg was found in 2012 and is believed to date from 1504. It may be the oldest globe to show the New World. Stefaan Missine, who analyzed the globe for the Washington Map Society journal Portolan, said it was part of an important European collection for decades. After a year of research in which he consulted many experts, Missine concluded the Hunt–Lenox Globe was a copper cast of the egg globe.
A facsimile globe showing America was made by Martin Waldseemueller in 1507. Another remarkably modern-looking terrestrial globe of the Earth was constructed by Taqi al-Din at the Constantinople Observatory of Taqi ad-Din during the 1570s.
The worlds first seamless celestial globe was built by Mughal scientists under the patronage of Jahangir.
In the 1800s small pocket globes (less than 3 inches) were status symbols for gentlemen and educational toys for rich children.
Traditionally, globes were manufactured by gluing a printed paper map onto a sphere, often made from wood.
The most common type has long, thin gores (strips) of paper that narrow to a point at the poles, small disks cover over the inevitable irregularities at these points. The more gores there are, the less stretching and crumpling is required to make the paper map fit the sphere. This method of globe making was illustrated in 1802 in an engraving in The English Encyclopedia by George Kearsley .
Modern globes are often made from thermoplastic. Flat, plastic disks are printed with a distorted map of one of the Earths Hemispheres. This is placed in a machine which molds the disk into a hemispherical shape. The hemisphere is united with its opposite counterpart to form a complete globe.
Usually a globe is mounted so that its spin axis is 23.5° from vertical, which is the angle the Earths spin axis deviates from perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. This mounting makes it easy to visualize how seasons change.
Lebegue, Alphonse Nicolas 1814 - 1885
Jules Lebegue (son)
Lebègue was a publisher of maps, plans as well as terrestrial and celestial globes, in Paris & Brussels. He was born in Paris in 1814 & died on December 12th 1885 in Brussels. He was the son of the Parisian printer and bookseller Jean Lebègue, with business on the Rue des Noyers, Paris.
In 1854 he established a printing press and publishing house in Brussels, Belgium and becoming A. N. Lebegue and C (ie), becoming one of the best-known publishing houses in the Belgian capital. His business launched a weekly newspaper in 1858, with an Advertising Office that became one of the most popular organs of the local Liberal Partywhile specialising in the works of Pierre Joseph Proudhon . At this time, Lebègue expanded his publishing business into maps, plans and globes. Beside his publishing business, Lebègue wrote several books, often novels of a historical nature and during the second empire, became close to the French publisher Hetzel
Alphonse was the uncle to both Alphonse-Nicolas Lebègue (1856-1938) the French paleographer and Ernest Lebègue (1862-1943) the French historian. He died on December 12, 1885 in Brussels, leaving his business to his son Jules Lebègue.
1676 John Speed Antique Map of County of Midlesex Views London & Westminster
- Title : Midle-sex Described with the most Famous Cities of London and Westminster
- Date : 1676
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 405mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35602
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map & views of London and the English county of Middlesex by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine.
The map is embellished with the famous birds-eye views of London, Westminster and the churches of St Peters (Westminster Abbey) and old St Pauls before the great fire of London in 1666. English descriptive text of London on the verso.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/2in (520mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Re-enforced along centerfold, light uplift
Verso: - Re-enforced along centerfold, two small repair to top of map, no affect to image
Background:
This county map of Middlesex, now greater London, illustrates the market towns of Enfield, Pancras, Osterley and Staines. The map is dominated by four large vignettes with the environs of London and the county situated in the central portion of the map. The actual cartography is based on the surveys performed by John Norden, the earlier English antiquary and map maker, who unsuccessfully attempted to publish an updated county atlas of the United Kingdom before Speed. Norden also lived most of his life in Middlesex, thus becoming an obvious source for the map.
The City of London is clearly shown on the lower right of the map with villages such as Hamsted, Pancras, Kensington and Paddington marked around the city. To the lower centre of the map is an acknowledgement to the original survey by Norden, augmented by Speed himself.
Although the cartography is of some note, it is the vignettes for which this map is justly famous. To the two bottom corners are the famous Churchs of St. Peter (Westminster Abbey) Westminster on the left and St. Pauls to the right. This is the medieval Cathedral of St. Pauls, just after it had lost its spire in 1561 and before the Great Fire of 1666, in which it was destroyed then rebuilt in its present form by Sir Christopher Wren. Above these two church vignettes are two text panels in the form of books, the one on the left describing the two churches and the other on the right with a description of London itself.
Finally, two large vignettes on the upper left and right corners depict the two cities of Westminster and London respectively. It is believed that Speed was not responsible for either of these images, more likely drawing from Norden, although there are no surviving evidence of this, to date yet to be found. There are also theories that these two views may have come from either a German sources or other lost birds-eye views of London by unknown persons.
Due to modern growth of London and border changes, the county of Middlesex no longer exists, but there is little doubt this is the most the best map of London and Middlesex published in the 17th century. English text on verso
1644 Willem Blaeu Antique Map of Iceland - Beautiful Original Hand Colouring
- Title :Tabula Islandia Auctore Georgio Carolo Flandro
- Ref #: 35625
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (590mm x 510mm)
- Date: 1644
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map, with beautiful original hand colouring by Willem Blaeu, was engraved by Jodocus Hondius after Joris Carolus, and was published by Guillaume Blaeus in the 1644 Latin edition of Atlas Nouvs.
This is beautiful example of this early map of Iceland with fresh original hand colouring, on uniform aged paper with original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (590mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform aged toning
Plate area: - Uniform aged toning
Verso: - Uniform aged toning
Background:
This map of Iceland is perhaps the most familiar of all the outlines of the island ever published. The author is stated to be one Joris Carolus, a Dutch navigator from Enkhuizen, whose map was first engraved and prepared by Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1628, whose plates were bought by Willem Blaeu in 1629. Iceland bears the imprint of Willem Blaeu who issued it in his Appendix of 1630.
The Carolus map was copied by virtually all mapmakers throughout the rest of the 17th century and well into the 18th. Some of the information is derived from a map made famous by the Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius, the Islandia of Gudhbrandur Thorlaksson (1541 - 1627) Bishop of Holar, who had studied mathematics and astronomy as well as theology, while other information, such as place names, is derived from Gerard Mercator's map of 1595.
Willem Blaeu reprinted the map without change in his subsequent atlas editions, as did Joan after him, including the great atlas of 1662. In the southern southern part is shown the lively impression of Hekla in full eruption, described as mons perpetuo ardens while immediately to the west, the Bishopric of Skalholt is marked. To the south a note by Eiapialla hokel (Eyjafjallajokull) states that here may be found falcones albi or white falcons, presumably referring to the gyr falcon.
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America, Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean
- Title : Insulae Americanae in Oceano Septentrionali cum terris adiacentibus
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 43142
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Gulf of Mexico, The Caribbean, Virginia to Florida to Texas and Central America, Venezuela was published in the 1639 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Nouvs.
This map has been re-joined along the centerold and has some uplift along the centerfold and has been priced accordingly.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595.
After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 andcontinued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/4in (525mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light uniform age toning, centerfold re-joined with light uplift
Verso: - Light age toning
Background: Cartographically this map draws on the extremely rare chart by Hessel Gerritsz, c.1631. The area of coverage is exactly the same with the exception of the addition of the west coast of Central America. The nomenclature of the North American part is virtually identical, the only notable addition being the naming of Virginia. It reflects the firsthand knowledge of Gerritsz during his voyage to South America and the West Indies undertaken in 1628. The distance between Chesapeake Bay and Albemarle Sound is accurately portrayed at 1°; even in Gerritsz's acclaimed NOVA ANGLIA ..., for de Laet, 1630, this distance is over 2°. It seems likely that a Spanish chart was used as the nomenclature along the south-east coast lacks any of the French influences often seen at the time.(Ref: Burden; Tooley, Koeman)
1827 Dumont D Urville Large Antique Early Map of New Zealand
- Title : Carte Generale de la Partie De La Nouvelle Zelande Reconnue par le Capitaine de Fregate Dumont D Urville Dressee par Mr Loottin Enseigue de v au Expedition de la Corvette de S M L Astrolobe Janvier, Fevrier, Mars, 1827
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1827
- Ref #: 42011
Description:
This magnificent large original & scarce copper-plate engraved antique map of the North Island & part of the South Island of New Zealand by Dumont D Urville and Lieutenant Victor Lottin, aboard the ship The Astrolabe during the first D Urville voyage to the South Seas 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Alphonse Chassant, 1808-1907 and published in the 1836 edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Fantastic & rare map by D Urville & Lottin with surveys made of the north, south east coasts of New Zealands North Island & the north west part of the South Island, between January and March 1827.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
On 25 April 1826, Dumont d Urville, with the rank of commander, sailed from Toulon as chief of the ship formerly named the Coquille, renamed Astrolabe, on a voyage of exploration and scientific inquiry which lasted till 24 March 1829. On 10 January 1827 the Astrolabe came in sight of the north-west coast of the South Island of New Zealand. On 14 January the ship passed the entrance to the modern Golden Bay, which had been visited by Abel Tasman. The ship anchored off the west side of Tasman Bay. This bay had not been investigated at close quarters previously. In the following days d Urville established that it was a great deal bigger than Cooks mapping indicated, and his officers surveyed and charted it. Adele Island, Pepin Island, and Croisilles Harbour are modern names derived from those given by d Urville. On 23 January d Urville made for a channel which he had noticed at a distance some time before, and which seemed to him to communicate between Tasman Bay and Cooks Admiralty Bay. This was the channel culminating in French Pass and dividing D Urville Island from the mainland. Victor Lottin and Gressien, two of d Urville\'s officers, on the same day saw the pass at close quarters from two of the ships boats. On 25 January d Urville went through the pass into Admiralty Bay in a ship\'s boat. On 28 January the Astrolabe made the hazardous passage into Admiralty Bay. The investigation of Tasman Bay and the discovery of French Pass and the insularity of D Urville Island were significant contributions by d Urville to the discovery of New Zealands coastline.
From Cook Strait d Urville went north along the coast to Whangarei Harbour, which was surveyed and charted on 21–23 February 1827. The Astrolabe then doubled back to Hauraki Gulf, passing between the main coastal islands on the west side of the gulf on 25–27 February. The Astrolabe had been preceded in this passage by the Prince Regent in 1820, but the surveys and charts made under d Urville\'s command were notable contributions to the cartography of New Zealands coast. Lottin crossed the isthmus on 26 February and made a survey of Manukau Harbour, discovered in 1820 by Samuel Marsden. From Hauraki Gulf d Urville proceeded to North Cape and then to the Bay of Islands, leaving New Zealand in March 1827.
Lottin, Victor Charles 1795 - 1858. Lottin was a French frigate captain and geographer who took part in the voyage made around the world by the Astrolabe, under the command of Dumont-d Urville. He served as a lieutenant on the research expedition to Iceland and Greenland. During these two excursions, Lottin drew several maps and gathered a large quantity of objects of natural history, and made mention of the aurora borealis, inserted in the Annales Maritimes (1839). He was a member of the Academy of Sciences, Section of Geography and Navigation (elected in 1852) and a Knight of the Legion of Honour.
He died at Versailles on 18 February 1858.
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map of Italy, Italia - Beautiful 1st Ed.
Antique Map
- Title : Italia
- Ref #: 35627
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18 1/2in (615mm x 470mm)
- Date: 1628
- Price: $1050.00US
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Italy by Gerard Mercator, his first map of Italy for Atlas, was published in the 1628 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes De Fabrica Mundi
This is a beautiful map with original hand colouring, heavy age toned paper with a deep impression. Beautiful map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18 1/2in (615mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
1690 Nicolas Visscher Large Original Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africae Accurata Tabula ex officina...Nic Visscher
- Date : 1690
- Size: 24 1/2in x 21in (620mm x 535mm)
- Ref #: 61158
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Africa was published by Nicholas Visscher in 1690.
This is a fine map with beautiful hand colouring on strong sturdy paper with original margins & a fresh deep impression denoting an early pressing.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 21in (620mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/4in (540mm x 435mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin repair, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Old tape top & bottom margin not affecting the image
Background: The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (M&B; Tooley)
1759 J.B. D' Anville Large Original Antique Map of Africa - Beautiful
- Title : Afrique Publiee sous les Auspices de Monseigneur le Duc D\'Orleans Premier Prince du Sang Par le Sr D Anville MDCCXLIX
- Date : 1759
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 92322
- Size: 40in x 40in (1.02m x 1.02m)
Description:
This large finely engraved and highly detailed original antique map of Africa by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D'Anville was engraved in 1759 - dated in the tile cartouche - by Guillaume Delahaye and was published D'Anville's large elephant folio Atlas Generale.
This is one of the largest and most influential maps of Africa to appear in the mid-18th century. Anville\'s map covers the entire continent of Africa from the Mediterranean to the Cape of Good Hope and from the Cape Verde Islands to Madagascar. Anville was a careful cartographer known for his scientific approach to mapmaking, and nowhere is this more evident than in this, his greatest and most innovative map of Africa. Following the trajectory set by Guillaume de L\'Isle half a century earlier, D\'Anville takes a number of significant steps forward in addressing the confusions inherent in mapping this vast though mostly, in the mid-17th century, unexplored continent. These include unreliable cartographic suppositions regarding the African interior dating practically to antiquity. Many of these, including such speculative ideas as the \'Mountains of Kong,\' have been diminished if not removed entirely from this map, leaving vast unexplored areas throughout.
What was known of Africa, however, Anville incorporates here in an impressive compilation of the most up to date reports from colonial, missionary, and exploratory entradas into the interior of the continent. Thus well mapped parts of the continent are limited to the Mediterranean Coast, Morocco, the Senegambia, the Congo, South Africa, the Kingdom of Monomatapa, Abyssinia, and egypt. Morocco, egypt, and the southern Mediterranean Coast (Barbary) were well known to europeans since antiquity and Anville\'s accurate mapping of these regions reflects continual contact. Further south the colonial enclaves along the Niger River (Senegal and Gambia), the Congo River, and South Africa reflect considerable detail associated with european penetration by trader and missionaries. The land of Monomopota around the Zambezi River was explored early in the 16th century by the Portuguese in hopes that the legendary gold mines supposedly found there would counterbalance the wealth flowing into Spain from the New Word. Unfortunately these mines, often associated with the Biblical kingdom of Ophir, were mostly tapped out by the 15th century. Abyssinia (modern day ethiopia) was mapped in detail by early Italian missionaries and of considerable interest to europeans first, because it was (and is) predominantly Christian; second, because it was a powerful well-organized and unified kingdom; and third because the sources of the Blue Nile were to be found here.
The remainder of the continent remained largely speculative though Anville rarely lets his imagination get the upper hand. He does however follow the well-established Ptolemaic model laid down in the Geographica regarding the sources of the White Nile – here seen as two lakes at the base of the semi-apocryphal Mountains of the Moon. However, he also presents a curious network of interconnected rivers extending westward from the confused course of the White Nile following the popular 18th century speculation that the Nile may be connected to the Niger. To his credit Anville does not advocate this and offers no true commerce between the two river systems.
Lake Malawi, here identified as Maravi, appears in a long thin embryonic state that, though it had not yet been \'discovered,\' is remarkably accurate to form. Lake Malawi was not officially discovered until Portuguese trader Candido Jose da Costa Cardoso stumbled upon it in 1849 – one hundred years following Anville\'s presentation of the lake here. Anville\'s inclusion of Lake Malawi is most likely a prescient interpretation of indigenous reports brought to europe by 17th century Portuguese traders. Its form would be followed by subsequent cartographers well into the mid-19th century when the explorations of John Hanning Speke, David Livingstone, Richard Francis Burton and others would at last yield a detailed study of Africa\'s interior.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 40in x 40in (1.02m x 1.02m)
Plate size: - 39in x 39in (1.0m x 1.0m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light spotting bottom of image, folds as issued, light toning along folds
Verso: - Light spotting bottom of image, folds as issued, light toning along folds
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1750 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of Colonial North America, 1st Edition
- Title : Amérique Septentrionale, dressée, sur les Relations les plus modernes des Voyageurs et Navigateurs, et divisée suivant les differentes possessions des Européens...Par Le Sr Robert De Vaugondy 1750 [North America, drawn from the most recent accounts of the Voyagers and Navigators, and divided according to the different possessions of the Europeans...Robert De Vaugondy 1750
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93358
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21in (700mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original 1st edition antique map of North America by Robert De Vaugondy in 1750 - dated in cartouche - was published in the 1757 edition of Atlas Universel, one of the most important atlases of the 18th century.
A beautifully executed & iconic mid 18th century antique map of the entire continent of North America, from Arctic Canada to Central America.
This map is a must for any American map collection. Beautiful original hand colour, a heavy impression (denoting an early pressing) on heavy sturdy paper with original margins, an exciting map .
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21in (700mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling in top margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
This attractive map depicts a fascinating period time in the history of North America, immediately before the French and Indian War. The British Thirteen Colonies hug the Atlantic seaboard, while the immense Gallic empire, embracing both New France (Canada) and Louisiana (the Mississippi Basin) occupy the majority of the interior of the continent. This highly detailed map labels numerous native villages and European forts in the interior of the continent. Spanish Mexico reaches all the way north to modern-day Colorado, and Baja California is shown accurately to be a peninsula, and not an island as previously thought. The Pacific Northwest remains entirely enigmatic, labelled as the Terres Inconnues. The map also depicts the islands of the Caribbean, which are shown to be in the possession of the various European powers. Vaugondy consulted several sources in devising his map including Bellins excellent rendering of the Great Lakes, and Guillame De L Isles and Jean-Baptiste D\'Anvilles maps of the Mississippi Basin. The composition is graced by an elegant title cartouche featuring a waterfall inhabited by a cayman, and framed by coulisses of palm trees accompanied by native Americans.
1719 H. Chatelain Large Antique Map of North America Canada Great Lakes, Detroit
- Title : Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France, & des Decouvertes qui y ont ete Faites, Dressee sur les observations les plus Nouvelles, & sur divers Memoires tant Manuscrits qu' imprimez
- Ref #: 17044
- Size: 23 1/4in x 19in (590mm x 480mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique & important early map of The Great Lakes, Canada & the Upper Mid-West - with descriptive French text to the right of the map - was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/4in x 19in (590mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (525mm x 415mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nice example of Chatelain's edition of De L'Isle's seminal map of Canada, the Great Lakes and Upper Midwest, first issued in 1703.
Chatelain's map of Canada & the Great Lakes was the first printed map to locate Detroit, first issued only 2 years after the founding of the Village by Cadillac. De L'Isle studied at the French Maritime Ministry from 1700 to 1703, during which time he took extensive notes on the work of the Jesuit Missionaries, including Franquelin, Jolliet and others. Karpinksi note that the fruits of De L'Isle's substantial efforts are born out by the great improvements in the mapping of the 5 Great Lakes and other parts of the map.
The map is one of the most important maps of Canada printed during its time, and was included in Chatelain's Atlas Historique. Numerous trading posts and missions in New France and the major towns of the adjacent British colonies are shown. The area around Hudson's Bay is inhabited by native tribes referred to as the "Christinaux or Kilistinons," while Labrador is home to the "Eskimaux."
The map features a number of notes specifically referring to the names of explorers and the dates in which they discovered certain places, such as the reference to 'Nouveau Danemarc', discovered by the Danish explorer Jan Munk in 1619. The depiction of the upper Mississippi and Ohio basins is also quite detailed, noting the French fort of 'St. Louis' or 'Crevecouer' near the present-day site of Peoria, Illinois. Perhaps the most fascinating aspect of the map is its portrayal of the "Riviere Longue," one of the most sensational and enduring cartographic misconceptions ever devised. This mythical river was reported to flow from the 'Pays des Gnacsitares' in the far west, promising the best route through the interior of the continent, supposedly placing one within close reach of the Pacific Ocean. It is a product of the imagination of the Baron Lahontan, a French adventurer, whose best-selling travel narrative Nouveaux voyages dans l'Amérique septentrionale (1703) convinced many of the world's greatest intellects of the existence of this mythical waterway. The text, 'Remarque Historique' that fills the northwestern part of the map describes the history of New France from the days of Jacques Cartier to contemporary times.
1748 (1770) Nicolas Bellin Large Antique World Map updated by Capt. Cook
- Title : Essay d une Carte Reduite Contenant les parties connuees Du Globe Terrestre...Par N Bellin...1748
- Size: 30 1/2in x 22in (785mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1748 (1770)
- Ref #: 93353
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique World Map, on Mercators Projection, is dated 1748 by Nicolas Bellin, updated showing the discoveries of Captain James Cook in his first voyage of Discovery from 1769-1772.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30 1/2in x 22in (785mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2in x 20 1/2in (725mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The map presents the entire world on Mercator Projection based on a Paris (LIsle de Fer) meridian, exhibiting post-Cook geography throughout, but most specifically in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America.
North America to the west of the Mississippi is vaguely rendered according to 16th century expeditions into the region by Coronado, La Salle, De Soto, and others.
Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de lOuest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the Archipel de Nord.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labeled Nouvelle Holland, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemens Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state.
It is of interest that there is a common misconception regarding this map that suggests the first edition was dated 1748. There are editions with a printed date of 1748, but these are actually later editions. The 1748 date is a printing error in which 8 and 4 are transposed, the actual date of publication being 1784. The first edition of this map is the 1778 example shown here. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1629 Willem Blaeu Antique Map of the Holy Land Palestine Jerusalem Twleve Tribes
- Title : Terra Sancta quae in Sacris Terra Promissionis olim Palestina....Guiljesmi Blaeuw 1629
- Date : 1629
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93509
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (590mm x 495mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper plate engraved antique map of the Holy Land, Terra Sancta, Palestine was one of the very few dated maps printed by Willem Blaeu. The map was engraved by Jodocus Hondius the younger and published by Willem Blaeu in the 1643 French edition of Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (590mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 384mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This is one of the very few maps published in Blaeus Atlas that bears a date. It was actually made by Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1629, but was not printed until after the plate was purchased by Willem Blaeu (who added his imprint in the lower part of the cartouche)
At this time, many of the maps of Palestine were oriented to show the east at the top to focus on Jerusalem. Here, the orientation is inverted so that Blaeus map shows Palestine as it might have been viewed by Moses from the top of Mt Pisgah. The decorative features are Old Testament in inspiration: Moses holding the Tablets of the Law, stands to the left of the cartouche, Aaron to the right, while in the Mediterranean Jonah is about to be swallowed by the whale and in the Sinai is shown the route of the Exodus. In the Red Sea at Yam Suf, Pharaohs armies are shown drowning. The lands of the Twelve Tribes are shown straddling both banks of the Jordan and the city of Jerusalem can be seen occupying a place of honour in the upper centre of the map.
The geographical detail of the map is taken from an large inset on a large map of Palestine by the traveller Pieter Laicksteen and the mapmaker to Phillip II of Spain, Christian s Grooten, published at Antwerp in 1570. This inset map, its importance recognised by Hondius and by Blaeu, was unorthodox in its treatment of the outline of the Red Sea and its triangular outline for the Sinai peninsula - lone before either was finally admitted by mapmakers as more accurate than traditionally accepted versions.
The Blaeus retained this map for all editions of the firms atlas for more than thirty years from 1630, even though the rival publisher Johannes Jansson issued a more detailed seven sheet map of the region in his own atlas.
1680 Frederick de Wit Large Antiue Map of Tartary, China, Japan, Mogul, Formosa
- Title : Magnae Tartariae Magni Mogolis Imperii, Japoniae et Chinae...F de Wit
- Ref #: 17030
- Size: 25in x 22 1/2in (635mm x 570mm)
- Date : 1680
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, handsome original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Tartary including China, Japan, Central Asia, parts of the Mogul Empire, Persia and Siberia - was published by Fredrick De Wit in 1680.
The map is finely engraved with detail, with fine original colour on sturdy, strong paper.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 22 1/2in (635mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Although Arabia, Persia, the Silk road to China and those parts of Northern India conquered by Alexander the Great were known to the classical world, it was not until the year AD 1375 that a map giving some idea of the real shape and size of Asia was compiled. This was the famous Catalan Map, based on reports of Franciscan missionaries and the writings of Marco Polo. A century or so later in the first Ptolemaic Atlases, there were altogether twelve maps of Asia which, of course, revealed no more or less than Ptolemy's view of the Ancient world, but in the expanded Waldseemuller editions of 1513 and 1532 there were modern regional maps including much information from Marco Polo's travels.
Later 16th century maps continue to show many of the distorted outlines copied from Ptolemy although by this time India, Ceylon and the Indies were gaining more recognizable shape. Munster was again the first publisher to print a separate map of Asia and later Ortelius issued the first separately printed map of China in 1584 and Japan in 1595. In the next century highly decorative maps were published by Van Den Keere in 1614, Speed 1627, Blaeu 1630, De Wit 1660, Visscher 1680 and others too numerous to list. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1794 Laurie & Whittle Large Very Rare Blueback Map, Sea Chart of The Baltic Sea
- Title : A New Chart of the Baltic or East Sea Drawn Principally from the Maritime Surveys Collected in the Russian Neptune compared with the Observations of the most experienceed Pilots, and Chiefly with the Charts and Draughts of Professor Christian Charles Lous, Nils Mareluis and James Schmid Published by Authority at Copenhagen, Stockholm and St Petersburg...London Published by Laurie & Whittle No 53 Fleet Street as the Act, 12th May, 1794
- Size: 48in x 39in (1.225m x 1.015mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1794
- Ref #: 93046
Description:
This is a very large, extremely rare, copper-plate engraved and highly detailed working Blueback Nautical Chart or Maritime map of the Baltic or East Sea was engraved in 1794 and published by the Laurie & Whittle firm, London 1794. The details for this map have been collected from expeditions by the ship the Russian Neptune and Professor Christian Charles Lous, Nils Mareluis and James Schmid.
This rare Blueback map, a method of mounting working sea charts that was begun by Robert Sayer in the late 18th century. These working maps were extremely expensive to buy and labour intensive to put together so only a limited number were published and sold and even fewer have survived. I have found no other examples of this map either commercially or in other map collections.
The map depicts the Baltic Sea from Scandia Sweden & Pomeranian, Germany in the west to the Baltic States of Estonia and Latvia (Eastland, Livonia, Courland) & southern Finland in the east. The map is highly detailed with numerous cities are labelled, including Copenhagen, Stockholm (Christiana), Gdansk (Dazing), Tallinn (Revel), and Riga. Myriad depth soundings are indicated in the Baltic Sea and along the coastlines. Numerous inset maps are included, the first of Copenhagen and the Straits, the second of Stockholm and directions through the various channels and islands, the third inset is Rogerwick Bay, the fourth is the Island of Gottland and the fifth of Riga and Bay. Copious notes about sailing directions, channels, entrance to the Duna River.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 48in x 39in (1.225m x 1.015mm)
Plate size: - 48in x 39in (1.225m x 1.015mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, chipping to edges not affecting the image
Plate area: - Soiling, light brown spots top of map, light creasing
Verso: - Original Blueback
Background:
Blueback Charts
Blueback nautical charts began appearing in London in the late 18th century. Bluebacks, as they came to be called, were privately published large format nautical charts known for their distinctive blue paper backing. The backing, a commonly available blue manila paper traditionally used by publishers to warp unbound pamphlets, was adopted as a practical way to reinforce the low-quality paper used by private chart publishers in an effort to cut costs. The earliest known Blueback charts include a 1760 chart issued by Mount and Page, and a 1787 chart issued by Robert Sayer. The tradition took off in the early 19th century, when British publishers like John Hamilton Moore, Robert Blachford, James Imray, William Heather, John William Norie, Charles Wilson, David Steel, R. H. Laurie, and John Hobbs, among others, rose to dominate the chart trade. Bluebacks became so popular that the convention was embraced by chartmakerJacques Nicholas Bellins outside of England, including Americans Edmund March Blunt and George Eldridge, as well as Scandinavian, French, German, Russian, and Spanish chartmakers. Blueback charts remained popular until the late 19th century, when government subsidized organizations like the British Admiralty Hydrographic Office and the United States Coast Survey, began issuing their own superior charts on high quality paper that did not require reinforcement.
1692 Vincenzo Coronelli Large Original Antique Globe Gore Map of South America
-
Title : South America
- Ref #: 17007
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19 1/2in x 12 1/4in (495mm x 310mm)
- Date : 1692
Description:
This large original antique copper plate engraved Globe Gore, a map of South America - from Vincenzo Coronellis original 42in Globe - was published by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli in the 1696 Venice edition of Isolario dell Atlante Veneto.
To my mind Coronellis maps are some of the most beautifully engraved maps of the 17th century and the epitome of these are his Globe Gores.
In 1696 Coronelli published all his globe gores - from the 2in to the 42 in Globes - in an atlas, Libero dei Globi, part of the great series of atlases, Isolario dell Atlante Veneto that was published by Coronelli to ensure his work was available to a wider audience, as very few could afford travel to Venice, Rome or Paris to view his completed globes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 12 1/4in (495mm x 310mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 11in (455mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The original globe gores for the 42in Terrestrial & Celestial Globe were printed on 12 full length sheets - with two polar calottes - in 1688.
To help fit into Coronellis future publications of Atlante Veneto, Libro dei Globi and Isolario dell Atlante Veneto the gore sheets were re-issued as the same size but cut into smaller sections. This effectively allowed the gores to be published in their original size but instead of one sheet per gore there were 2, 4 or 6 sheets making up the one gore.
The first edition of Coronellis 3 ½-foot celestial globe was engraved by Nolin in Paris after drawings provided by the Italian geographer and was printed in 1688. At the same time, its terrestrial counterpart was engraved and printed in Venice under Coronellis direction. These globes were produced in part as replicas of the gigantic and unique 15 foot-diameter pair of globes that Coronelli constructed and presented to Louis XIV, the King of France, in 1683, and which secured his fame as Europes premier globe maker. In 1693, soon after Coronelli engraved and printed the first Venetian edition of the 3 ½-foot celestial globe, Nolin engraved at Paris an entirely new edition on new plates. This globe was based on Coronellis work, but with the main legends in Latin, not Italian, as befitted a French market. The 3 ½ foot celestial globe was one of the crowning glories of Coronellis output and was also the grandest celestial globe of the 17th century.
(Ref: Shirley; Armao, Ermanno. Vincenzo Coronelli Cenni sulluomo e la sua Vita Catalogo... Bibliopolis, Florence pp.130-134)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1640 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Italy
- Title : Nova Italiae Delineatio
- Ref #: 17021
-
Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (595m x 495mm)
- Date : 1640
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of Italy by Joan Blaeu was published in his 1640 edition of Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (595m x 495mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (595m x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small restoration to bottom margin centerfold, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light creasing & uplift along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1676 John Speed Antique Atlas Title Pages x 2 Empire of Great Britaine & World
- Title : The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine, A Prospect of the most famous Parts of the World by John Speed...London Thomas Bassett and Richard Chiswell 1676; The Achievement of our Soveraigne King Charles the 11D.
- Date : 1676
- Size: 22 1/2in x 17 1/2in (570mm x 445mm)
- Ref #: 42005/42006
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Price: $1250.00US
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured, copper plate engraved antique Title and Dedication Pages was published for the 1676 edition of John Speeds double atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine & Atlas A Prospect of the most Famous Parts of the World printed by Thomas Bassett and Richard Chiswell, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 17 1/2in (570mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/4in x 9 3/4in (385mm x 250mm) each
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
John Speeds The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published in 1610/11 by John Sudbury and George Humble, and contained the first set of individual county maps of England and Wales besides maps of Ireland and a general map of Scotland. Most, but not all, of the county maps have town plans on them; those showing a Scale of Passes being the places he had mapped himself. The county maps were the first consistent attempt to show territorial divisions, such as boundaries of hundreds, but it was Speed’s town plans that were a major innovation and probably his greatest contribution to British cartography. The Theatre was an immediate success: the first print run of around 500 copies must have sold quickly because many editions followed. Sudbury and Humble realized, given the increasing popularity of both county and world atlases and in the light of the success of Abraham Ortelius’s Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the potential demand for an English world atlas.
In 1627, two years before his death, Speed published Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World with 21 finely engraved maps, which was the first world atlas produced by an Englishman. There is a fascinating text describing the areas shown on the back of the maps in English, although a rare edition of 1616 of the British maps has a Latin text – this is believed to have been produced for the Continental market. Its maps are famous for their bordering panels of national characters in local costume and panoramic views depicting the areas of major towns and cities. Much of the engraving was done in Amsterdam at the workshop of Jodocus Hondius. The maps of the world and America show California as an island and are amongst the earliest ever printed to depict this seventeenth-century cartographic myth.
1698 Alexis Jaillot Large Antique Map European Russia, Poland, Baltics, Crimea
- Title : La Estats Du Czaar De La Russie Blanche Grand Duche Moscovie...
- Size: 37in x 24in (940mm x 610mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1698
- Ref #: 61034
Description:
This very large, beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of European Russia was published by Alexis Hubert Jaillot in the 1698 edition of his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37 1/2in x 24in (960mm x 620mm)
Plate size: - 35in x 23in (890mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, several small repairs in margins, no loss
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning, several repairs, no loss
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.